MI 2893 / MI 2892 / MI 2885 Measurement methods
191
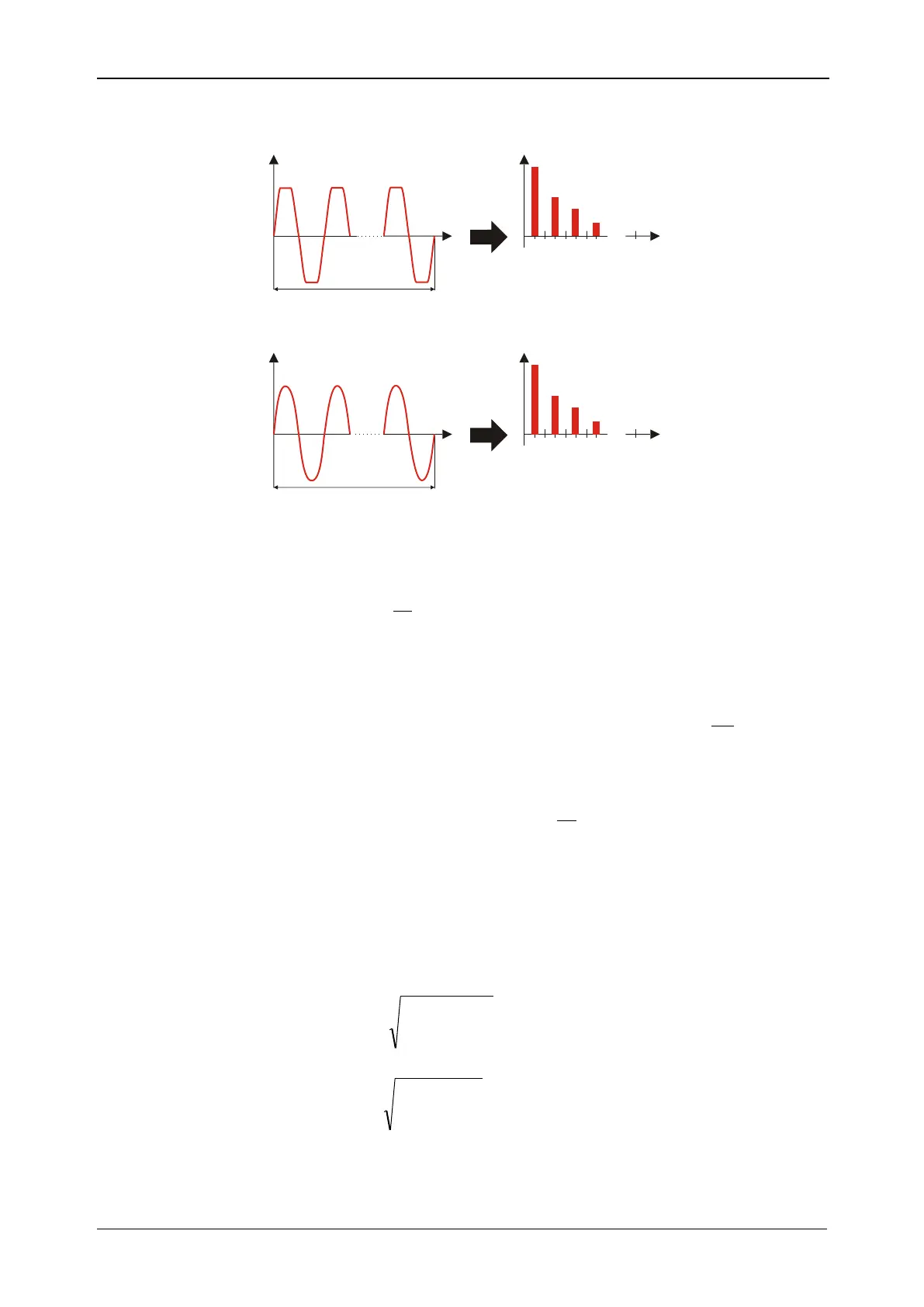
FFT
Voltage harmonics and THD
10 periods
t
n
1
2
3 4
5 6
50
U
FFT
10 periods
t
n
1
2
3 4
5 6
50
I
Uhn
Ihn
Current harmonics and THD
Figure 156: Current and voltage harmonics
k
k
k
tf
k
cctu
1
1024
1
0
2
10
sin)(
f
1
– frequency of signal fundamental (in example: 50 Hz)
c
0
– DC component
k – ordinal number (order of the spectral line) related to the frequency basis
T
N
– is the width (or duration) of the time window (T
N
= N*T
1
; T
1
=1/f
1
). Time window is that time
span of a time function over which the Fourier transformation is performed.
c
k
– is the amplitude of the component with frequency
k
– is the phase of the component c
k
U
c,k
– is the RMS voltage value of component c
k
I
c,k
– is the RMS current value of component c
k
Phase voltage and current harmonics are calculated as RMS value of harmonic subgroup (sg): square
root of the sum of the squares of the RMS value of a harmonic and the two spectral components
immediately adjacent to it.
Total harmonic distortion is calculated as ratio of the RMS value of the harmonic subgroups to the RMS
value of the subgroup associated with the fundamental:

 Loading...
Loading...











