MI 2893 / MI 2892 / MI 2885 Measurement methods
192
Total voltage harmonic distortion:
2
40
2
1
n
p
np
p
U
hU
hU
THD
Total current harmonic distortion:
2
40
2
1
n
p
np
Ip
hI
hI
THD
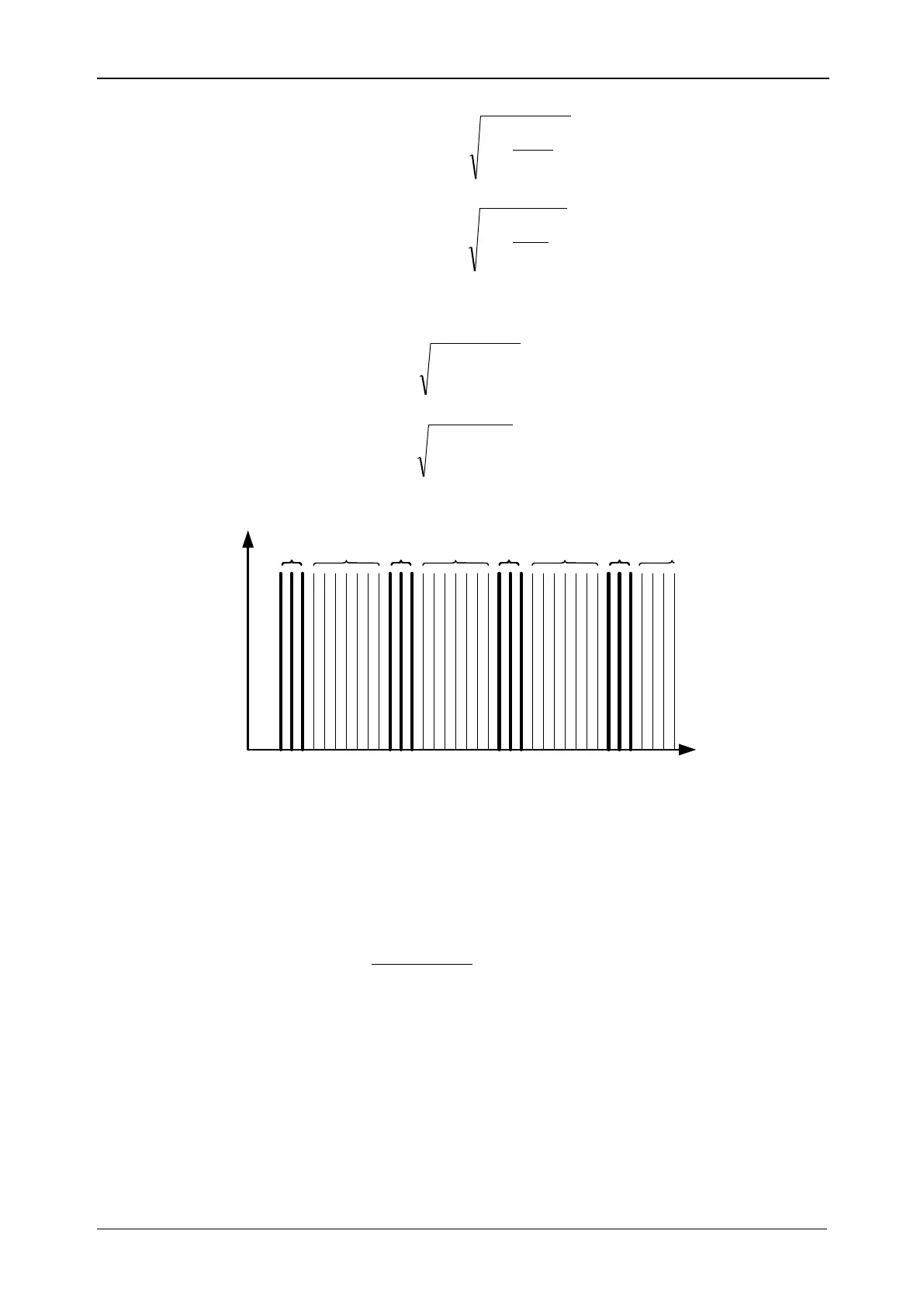
Spectral component between two harmonic subgroups are used for interharmonics assessment. Voltage
and current interharmonic subgroup of n-th order is calculated using RSS (root sum square) principle:
n
th
voltage interharmonic:
n
th
current interharmonic:
50
100 150 200
Uc,k
Uh1 Uh2 Uh3 Uh4
Freqency
Uih1 Uih2 Uih3
Figure 157: Illustration of harmonics / interharmonics subgroup for 50 Hz supply
The K factor is a factor that is developed to indicate the amount of harmonics that the load
generates. The K rating is extremely useful when designing electric systems and sizing components. It is
calculated as:
50
1
2
50
1
2
)(
n
np
n
np
p
hI
nhI
K
5.1.9 Signalling
Standard compliance: IEC 61000-4-30 Class A (Section 5.10)
Signalling voltage is calculated on a FFT spectrum of a 10/12-cycle interval. Value of mains signalling
voltage is measured as:
RMS value of a single frequency bin if signalling frequency is equal to spectral bin frequency, or

 Loading...
Loading...











