Copyright© Orphée SA. All Rights Reserved.
8.3 ERYTHROCYTE ANALYSIS
The erythrocyte analysis is done by impedance in the RBC counting chamber and by analysis of the
hemoglobin inside WBC chamber as previously described. Seven parameters are obtained:
Pathologies (adjustment section 3.4.4.1)
Erythrocytosis : RBC>RBC h
Microcytosis : VMC<VMC b
Macrocytosis : VMC>VMC h
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
Hypochromia : MCHC<MCHC b
Cold Agglutinin : MCHC>MCHC h
Red blood cells Distribution Width (CV)
Anisocytosis : RDWC>RDWC h
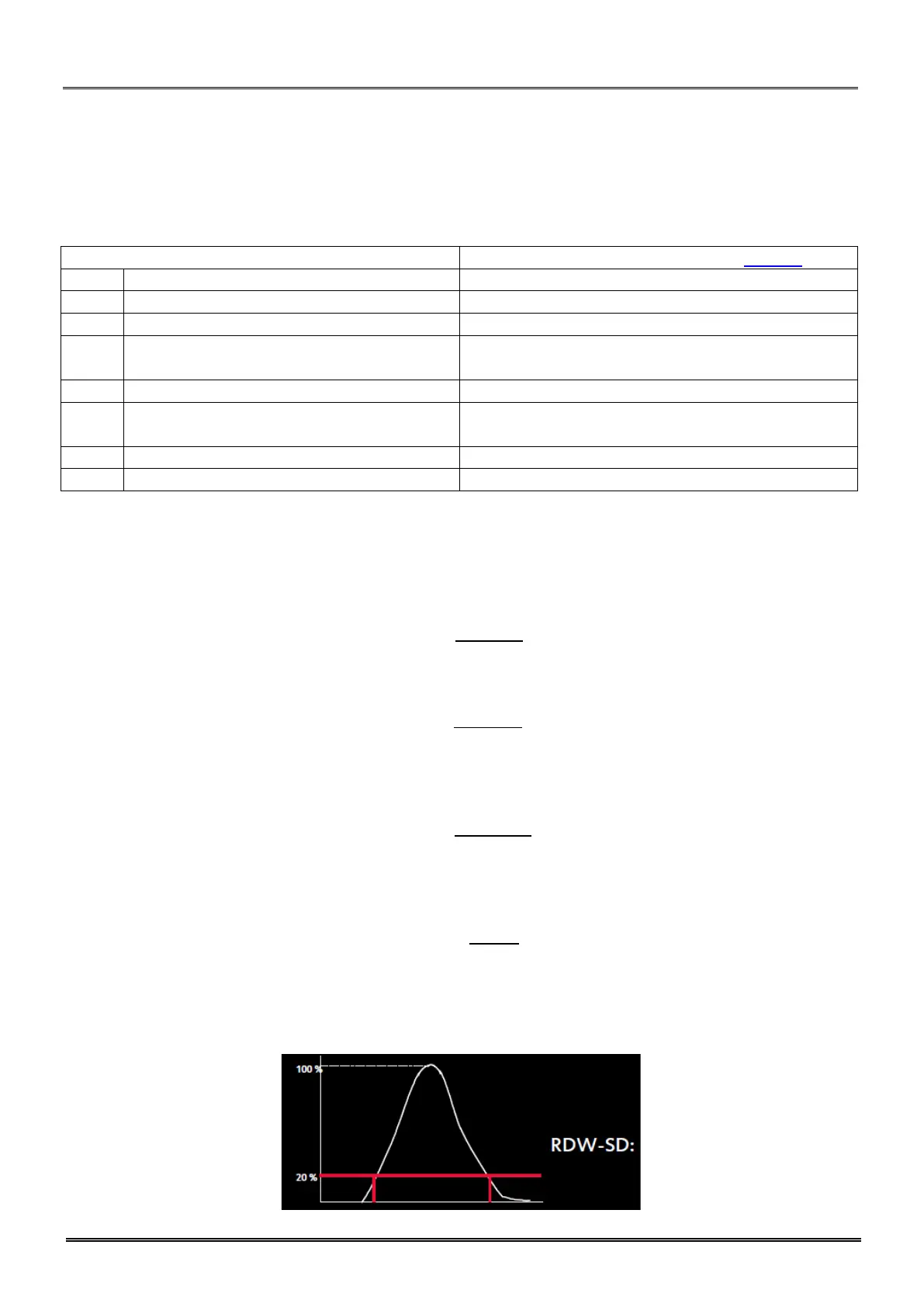
Red blood cells Distribution Width (SD)
HCT is measured by integration volume of all red blood cells which flow in the RBC counting chamber
aperture.
MCV is obtained by calculation, following the formula:
MCV = HCT ● 10
RBC
The Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) calculation is made from HGB and RBC by the formula below :
MCH = HGB ● 10
RBC
The Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) is made from HGB and HCT by the formula below :
MCHC = HGB ● 100
HCT
RDWC is an expression of the standard deviation divided by MCV. This parameter evaluates the RBC
anisocytosis.
RDWC = k ● SD
MCV
RDWS determination is an actual measurement of the width of the RBC distribution curve. This
measurement is performed at a relative height of 20% above the baseline see picture below).
 Loading...
Loading...