Programming Your Application 1-65
690+ Series Frequency Inverter
Functional Description
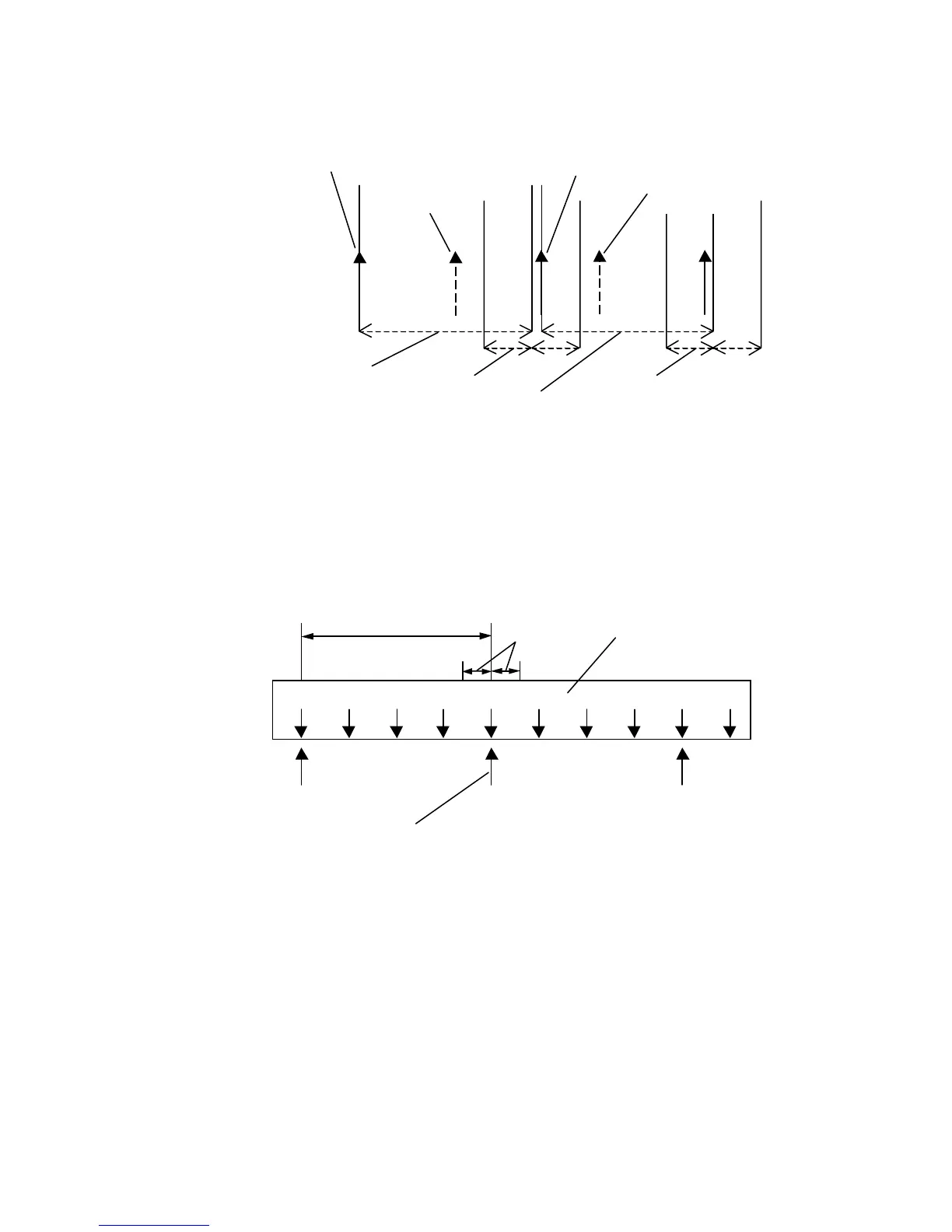
Nominal Length
Tolerance
Nominal Length
Tolerance
Bad Mark
Too early
Good Mark
Good Mark
Bad Mark
Too late
Setting a window using the nominal repeat length and tolerance eliminates rogue marks. The
window opens before the expected arrival point and remains open until a mark arrives. If the
new mark is inside the window it is accepted and a new mark is looked for, otherwise it is
rejected.
This form of windowing allows for the rejection of repetitive marks that fall regularly between
repeats on the other channel. An example of this would be a knife that cut every N marks on the
web. In this case it would not matter which mark the knife synchronised to.
Web
Knife
Nominal Length
Tolerance
This form of windowing will not work as a means of discriminating against noise between
marks. If used in a system like this, a missing mark may result in the system synchronising to
the noise. For more complex forms of mark discrimination, an intelligent eye must be used.
A large number of false marks will indicate that the system may not work reliably. Check the
quality of the sensors and increase measures to reduce EMC interference.

 Loading...
Loading...











