CIRAS-3 Operation Manual V. 1.09 40 support@ppsystems.com
Section 3. Summary of System Design
Overview and Theory
CIRAS-3 is designed to function as a self-contained open-system gas analyzer, manufactured and
calibrated for high-precision detection of CO
2
and H
2
O gasses. CIRAS stands for Combined Infra-Red
Analysis System. Its open-path design allows for continuous, unattended air sampling, as the pumps
introduce fresh sample gas to the essential components, the IRGAs. CIRAS-3, like previous generations
of CIRAS, has four non-dispersive IRGAs (Infra-red Gas Analyzers) – CO
2
Reference, CO
2
Analysis, H
2
O
Reference, H
2
O Analysis, a true differential analyzer.
The IRGAs form the core of gas analysis systems that measure CO
2
and water vapor (i.e. portable
photosynthesis system, eddy covariance, soil CO
2
efflux, etc.). Non-dispersive infra-red (NDIR) refers to
the transmission of broad-band infra-red wavelengths from the IRGAs source lamps. A single IRGA
consists of four basic components:
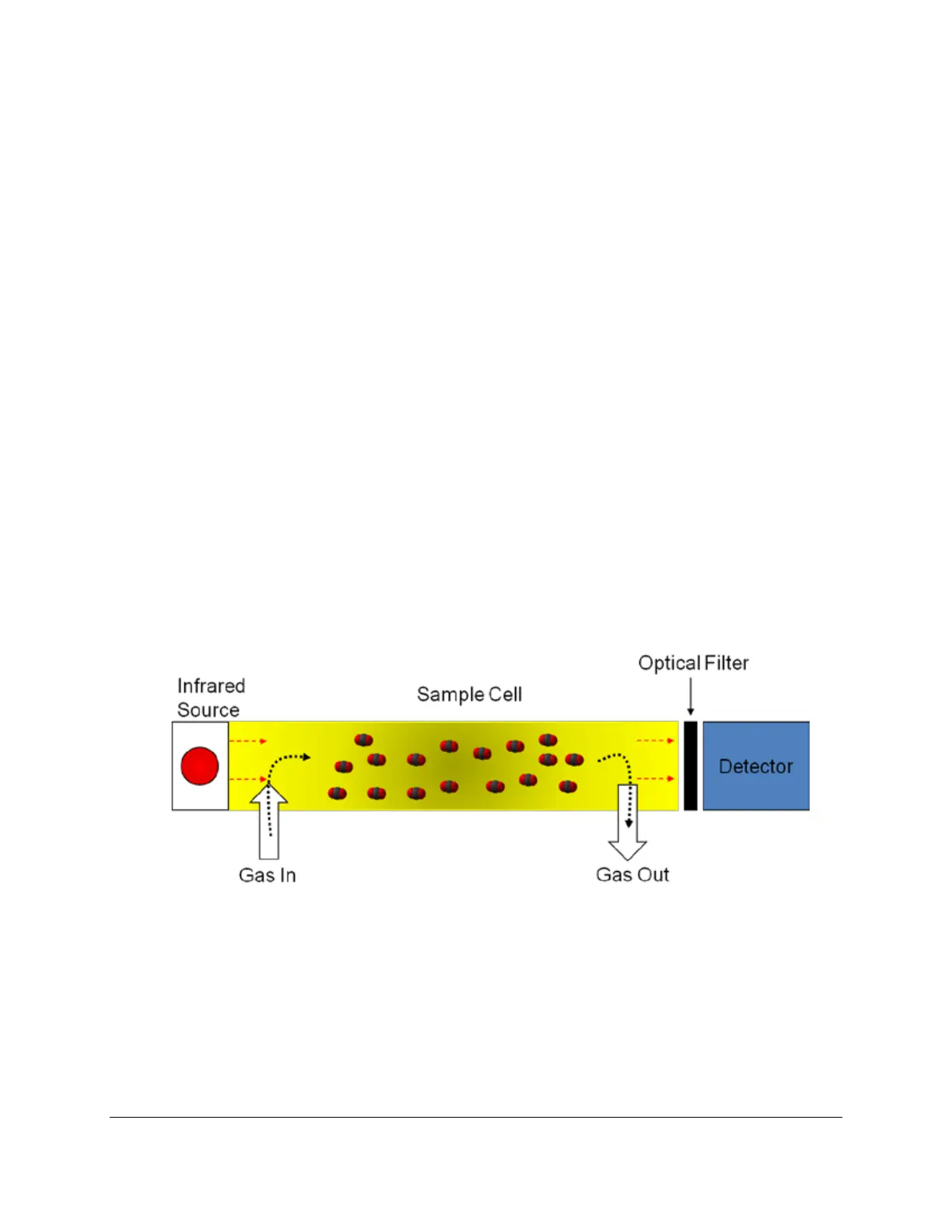
• Infra-red source
• Sample cell of known path length and volume
• Optical interference filter
• Infra-red detector
The theory itself is quite simple – light from mid-infra-red wavelengths is produced by the source and
pulsed through a gold plated cell. The interference filter narrows the bandwidth of the IR source received
by the detector to the signature wavelength absorbed by the target gas molecule, e.g. CO
2
. The CO
2
and
H
2
O cells each employ a unique optical filter. As the sample gas fills the cell, it absorbs IR, and the
reduction in IR source strength is measured instantaneously by the detector. The higher the target gas
concentration, the lower the infra-red signal received at the detector, as defined by the Lambert-Beer Law
of Attenuation.

 Loading...
Loading...