Configuration Guide Configuring Wireless Location
5.3.1 WL
Working Principle
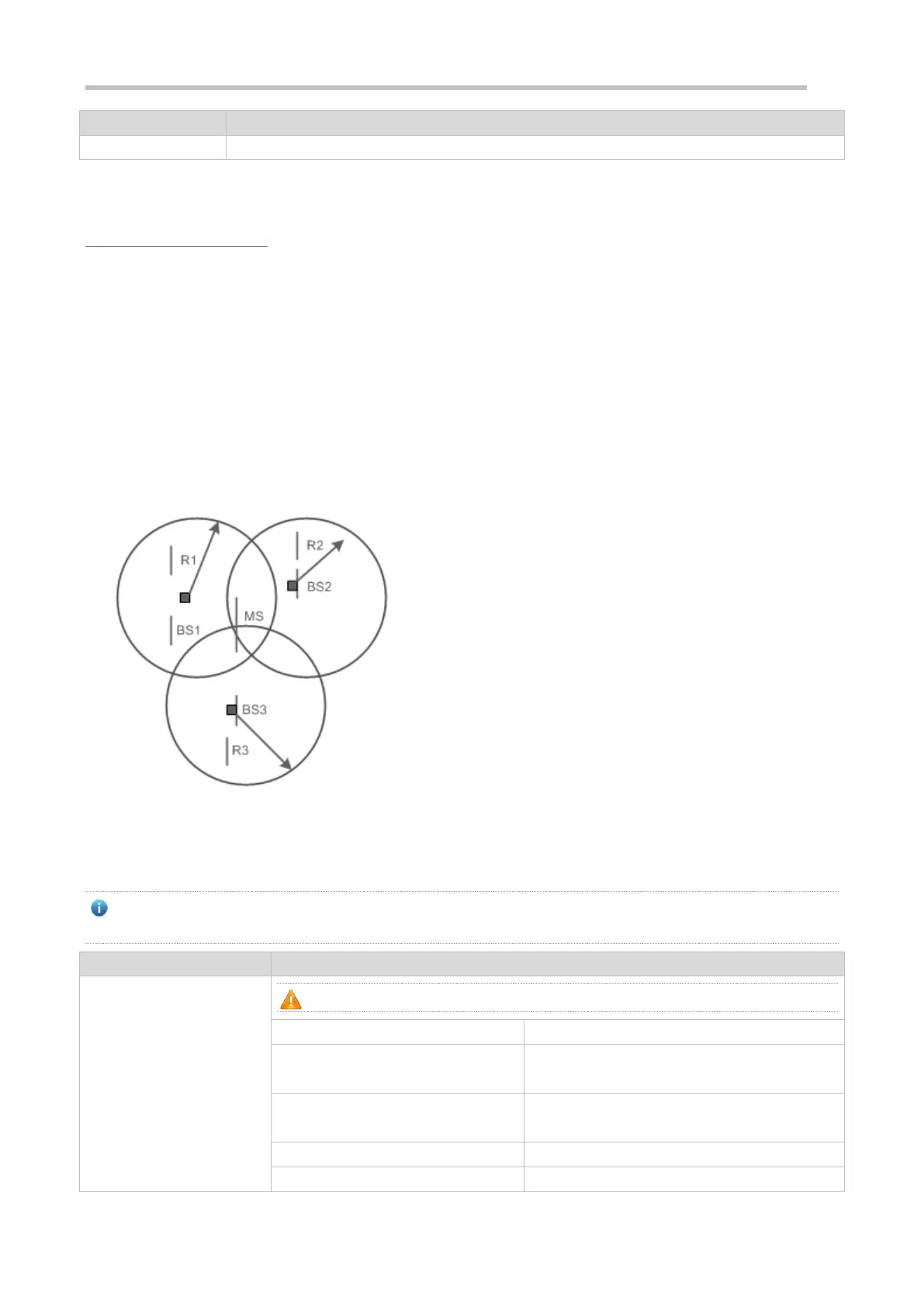
Based on the measurement of RSSI from an MU received by a base station (BS) and the channel transmission model, the
distance between them can be estimated to be d. In this way, for a BS (i), the MU must be on the circle centered at BS (i)
with a radius of d. When three or more BSs are used for distance measurement of the same MU, the location of this MU
can be determined. In this method, the main causes for location error are the multipath effect generated during signal
transmission and the shadow effect generated during obstacle crossing. More accurate location can be achieved in open
space without obstacles. However, in many circumstances, the location accuracy is significantly affected because of
uncertainties, such as the multipath effect, attenuation, and scattering, due to various obstacles.
Figure 5-1
5.4 Configuration
The WLAN location function is not supported on AP110-W or AP120-W because of memory and is not supported on
AP5280 at present.
Configuring WL Basic
Features
(Mandatory) It is used to enable WL.
Enables WL on a specified AP.
Configures the IP address of the Locator
connected to a specified AP.
Configures the port ID (PID) of the Locator
connected to a specified AP.
Enables MU location on a specified AP.
Enables TAG location on a specified AP.

 Loading...
Loading...











