PVA-3000 Reference Manual
December 2, 2019 Sifos Technologies
The DC Unbalance Test is accessed either with PVA Interactive (see Section 3.12.3) or PowerShell PSA (see Section
4.16). In order to run, the test must know the PowerSync Analyzer network (IP) address and test slot (slot, port). It
also may need to know the PSE type, that is, Type-1 (15.4 watt), Type-2 (30 watt) with 2-event classification, or Type-
2 (30 watt with LLDP classification). Finally, it requires the maximum DC Unbalance to be applied during testing.
All PSE’s may be treated as IEEE 802.3at Type-1 if maximum DC Unbalance (I
unb
) target is below 50mA. If DC
Unbalance target is above 50mA and the PSE is a 802.3at Type-2 LLDP capable PSE, then it is also required that the
PowerSync Analyzer utilized be enabled for the LLDP emulation feature.
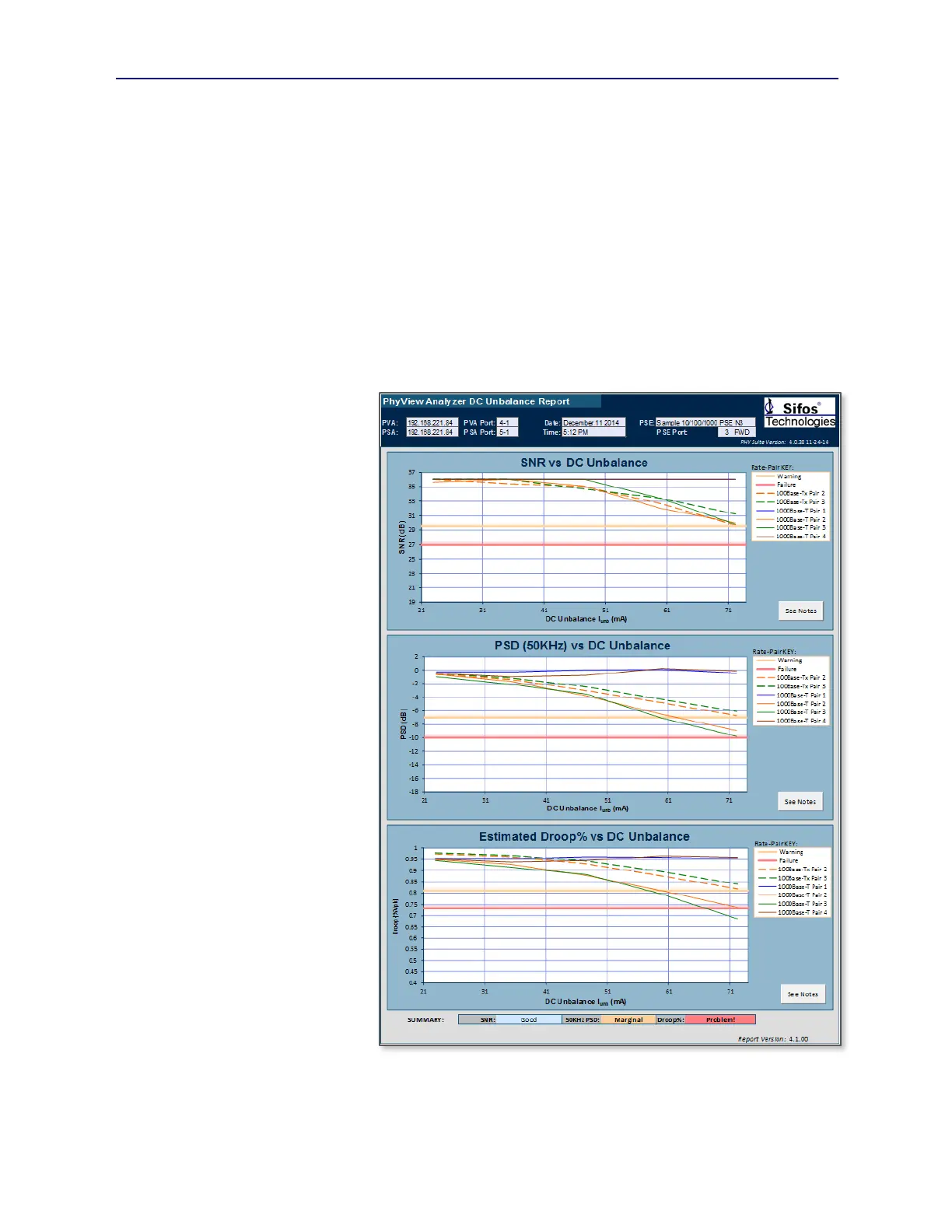
5.7. PSE DC Magnetic Unbalance Reporting
The results of the PSE DC Magnetic Unbalance Analyzer are reported graphically using a pop-up Excel spreadsheet
(see Figure 5.21). The effects of DC Unbalance on SNR , Low Frequency (50KHz) PSD, and estimated Pulse Droop
are shown in graphical form. (Note: Droop% is waveform percentage of peak value at 500nsec.)
The upper graph shows SNR
degradation by pair designator to
DC Unbalance levels ranging up
to that maximum level requested.
Dotted lines show 100BaseTx
SNR and solid lines 1000BaseT
SNR.
From Figure 5.20, it is clear that
the PSE is utilizing ALT-A
meaning that it is applying power
on pairs 2 and 3 (orange and
green). The ALT-B pairs, 1 and
4, are completely undisturbed by
the presence of DC load
unbalance because they are not
conducting any DC load.
The second graph shows the
impact to 50KHz PSD and the
third graphs shows the impact to
estimated Droop%. Again, there
is degradation as the level of DC
Unbalance increases and the low
frequencies begin to cut out.
The goal for SNR would be to
remain above ≈27 dB at all DC
Unbalance levels, preferably > 29
dB. Low Frequency PSD should
ideally remain above –7 dB.
Figure 5.21 PSE DC Unbalance Standard Report
 Loading...
Loading...