UG-1828 Preliminary Technical Data
Rev. PrB | Page 70 of 277
In this case, in all power saving modes, the PLL tuning is performed during enableSetupDelay instead of enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay.
Therefore, enableSetupDelay is much longer as it must allow time to tune the PLL. This means that the additional power up durations
t
PowerUpPSM
are much shorter and thus higher power savings can be achieved while setting the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay to a much
smaller value.
Impact of Power Savings on Timing Parameter Selection
As explained in the previous section, certain power savings modes cannot be entered if the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay for that channel
is not greater than the duration of the additional power up procedures needed in that mode.
For transmit channels, if the propagation delay is quite large, the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay chosen may already be larger than the
longest power up procedure duration, that is, t
PowerUpPSM2
. In this case, there is no impact to the selection of the timing parameters.
For receive channels, or transmit channels with short propagation delays, the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay must be chosen larger than
t
PowerUpPSM1
to enter Power Savings Mode 1 and larger than t
PowerUpPSM2
to enter Power Savings Mode 2 and higher. The
enableRiseToOnDelay, if it is being used, must also increase as it must always be larger than enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay. However,
none of the other timing parameters are affected by the power savings mode.
At the end of the frame, the power-down procedures take some small but finite time. For receiver channels with large propagation delay,
this may have no impact because the digital datapath might be on for a long time after the analog has powered down.
For transmit channels or receive channels with short propagation delays, the minimum period between the channel enable falling edge
and the next rising edge must be enableHoldDelay plus the additional time needed for the extra power down procedures (t
PowerUpPSM1
,
t
PowerUpPSM2
). This prevents PLL or LDO from beginning power up in the new frame even before it has finished powering down in the old
one.
Hardware and Software Restrictions for Timing Parameters
As previously mentioned, the bounds provided for each of these timing parameters and the guard times between rising and falling edges
of the receiver and transmitter enable signals are only guidelines. There are almost no hardware or software restrictions preventing users
from setting these parameters anyway they like including harmful or useless ways. There are in place a few restrictions, however, which
are outlined as follows:
• All timing parameters that must be provided by user have to be within the range of 0 ms to 91 ms. These bounds are specified,
assuming the delay generation blocks run at 184.32 MHz (system clock). If operating at a different frequency, the maximum bound
scales accordingly. For example, if using a 160 MHz clock, the max delay is 91 ms/184.32 × 160 = 79 ms).
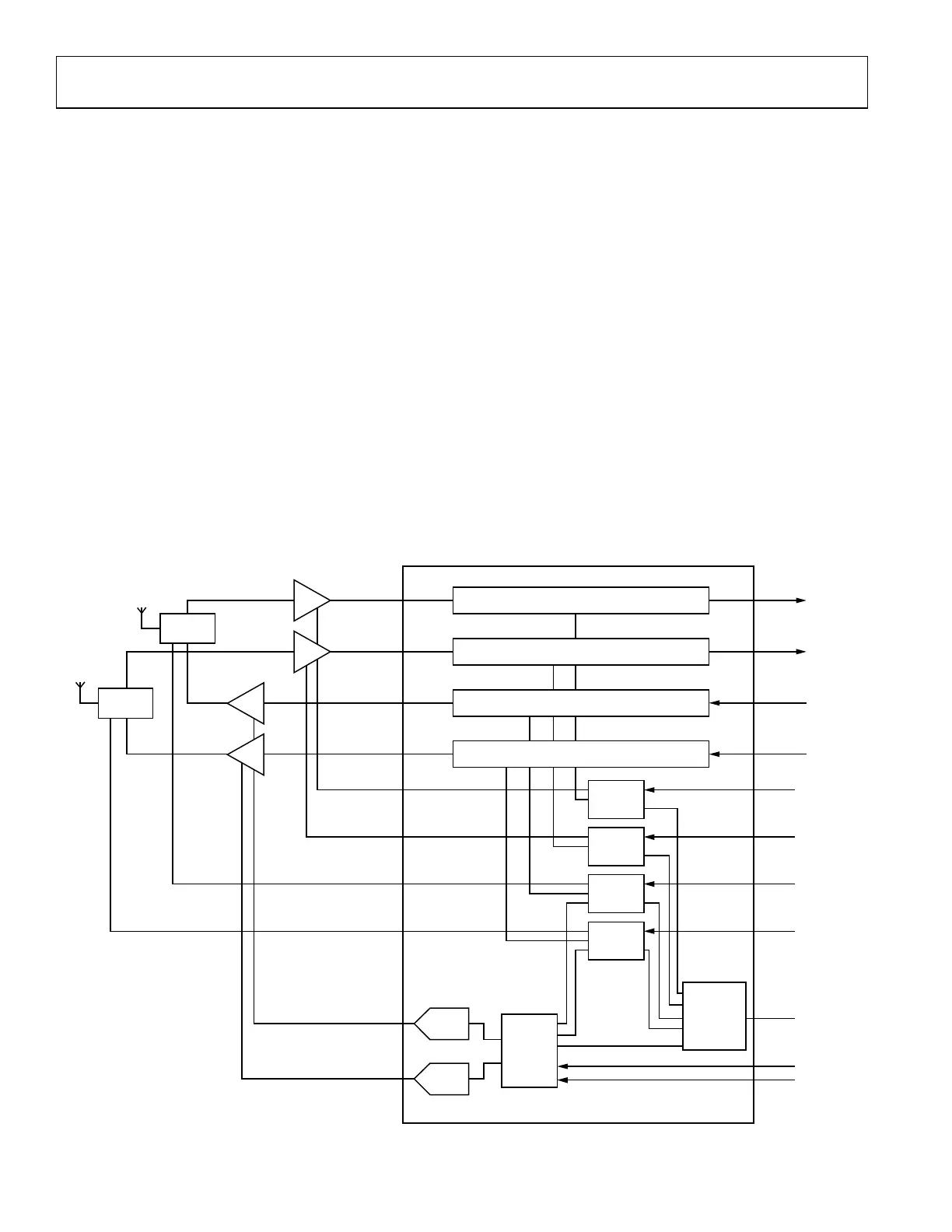
• For all channels the enableRiseToOnDelay must be greater than or equal to the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay, provided the
enableRiseToOnDelay parameter is being used, that is, ADRV9001 is controlling antenna switch and/or LNA power.
• For transmitter channels, the enableHoldDelay must be less than or equal to the enableFallToOffDelay.
• For receiver channels, the enableFallToOffDelay must be less than or equal to the enableHoldDelay.
• For a specific channel, Power Savings Mode 2 or higher is disallowed when the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay is less than t
PowerUpPSM2
.
• For a specific channel, Power Savings Mode 1 or higher is disallowed when the enableRiseToAnalogOnDelay is less than t
PowerUpPSM1
.
API Programming and Default Values for Timing Parameters
A set of API commands are provided to the user to configure timing parameters. Because the timing parameters are related to the
channel power saving mode, users should set the channel power saving mode first before configuring the timing parameters. API
Command adi_adrv9001_arm_ChannelPowerSaving_Configure( ) is provided to the user to set the channel power saving mode for a
specified channel when the channel is in the calibrated, primed, or RF_ENABLED state. After that, users could use API Command
adi_adrv9001_Radio_ChannelEnablementDelays_Configure( ) to configure the timing parameters for the selected channel. The
following data structure holds all the ADRV9001 required timing parameters:
typedef struct adi_adrv9001_ChannelEnablementDelays
{
uint32_t riseToOnDelay; /* Delay from rising edge until antenna switch (Tx) or LNA
(Rx) is powered up */
uint32_t riseToAnalogOnDelay; /* Delay from rising edge until Tx/Rx analog power up
procedure commences */
uint32_t fallToOffDelay; /* Delay from falling edge until antenna switch (Tx) or LNA
(Rx) is powered down */
uint32_t guardDelay; /* Reserved for future use*/

 Loading...
Loading...