54733-10BA2L
3 – 420 02.2017
7 Explanations Volume 3
7.5 Radiation Interference Detection
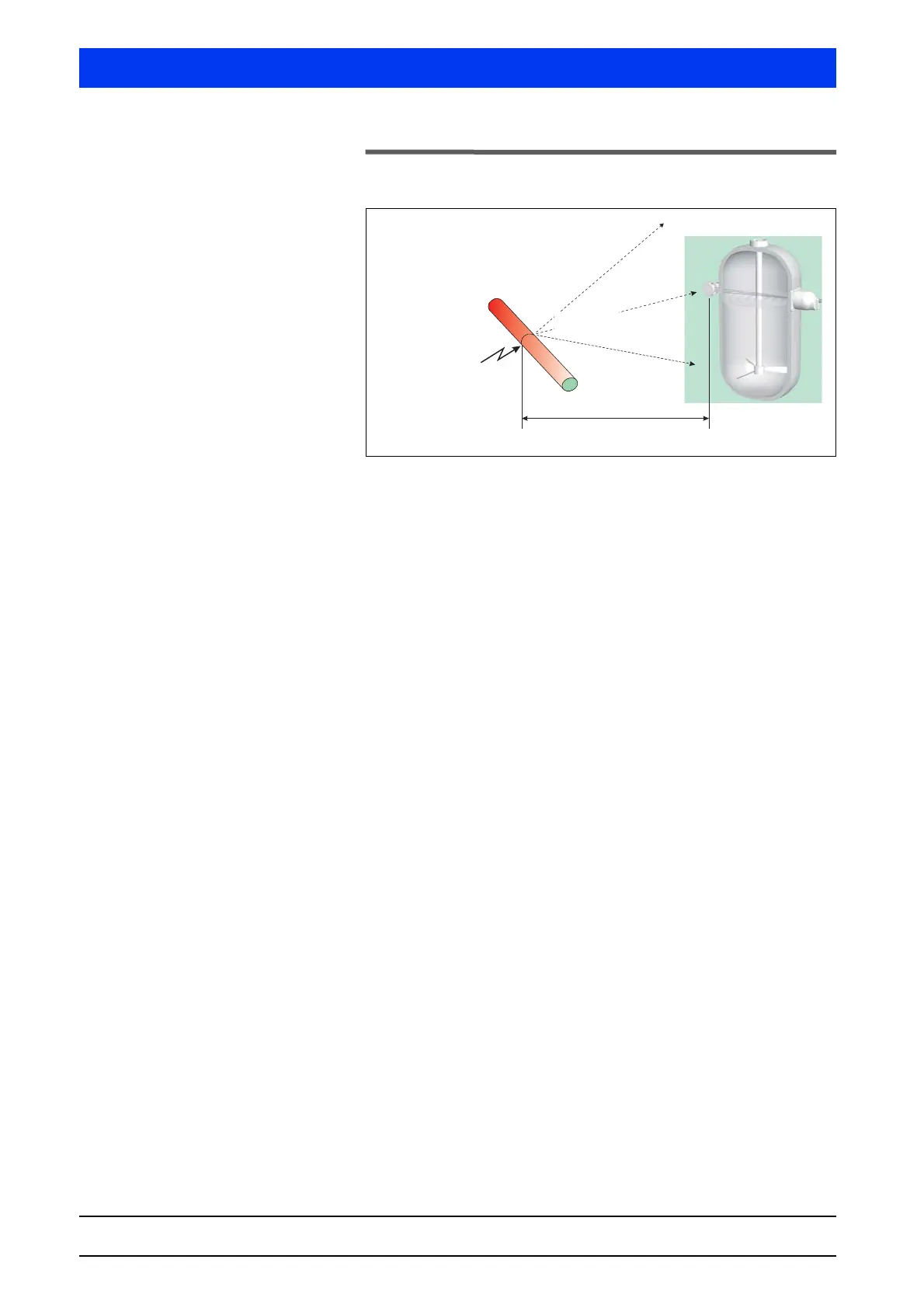
Fig. 7-11 Radiation interference
7.5.1 Detecting Interference Radiation
The high Gamma sensitivity of scintillation detectors may cause a
false reading. To detect interfering radiation, a double plausibility
check can be enabled.
The alarm is triggered by:
Scenario A: Maximum possible count rate (empty calibration)
Is > Io * 1.5
Is = current count rate in cps integrated over one second
Io = maximum count rate at empty calibration
Scenario B: Mean value of current count rate monitored.
The system sensitivity, i.e. the distance of the alarm thresholds is
defined as the multiple of the mean statistical variations and can be
entered as Sigma value as needed. The time constant is one sec-
ond.
When reaching the alarm threshold, a message is output via the
error relay and on the device display.
Is > Im + n * Sigma
Im = current count rate integrated over one second
n = multiple value of Sigma
Further information on scenario A: A relative limit value is monitored, i.e. the alarm threshold is
reached when exceeding a maximum dose rate (calibration value at
empty vessel) at the detector.
False alarms due to operative factors are not possible. However,
only stronger interfering radiation is detected.
Welding seam tests
with X-rays
Pipe
up to 200 m
Radiation interference
 Loading...
Loading...