Unicast and multicast addresses support scoping as follows:
• Unicast addresses support two types of scope: global scope and local scope. In turn, local scope supports site-local addresses
and link-local addresses. IPv6 address types describes global, site-local, and link-local addresses and the topologies in which
they are used.
• Multicast addresses support a scope eld, which IPv6 address types describes.
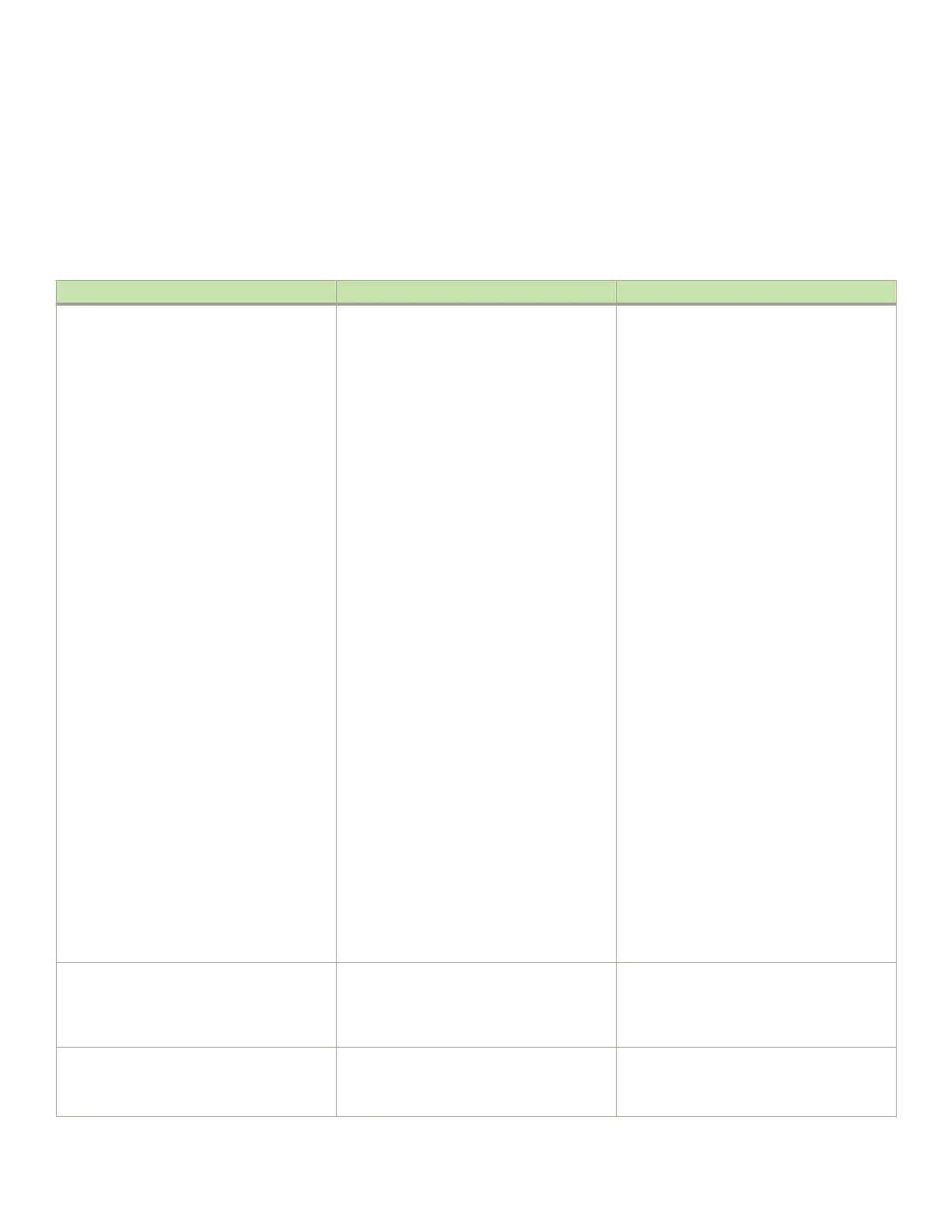
TABLE 29 IPv6 address types
Address type Description Address structure
Unicast An address for a single interface. A packet sent
to a unicast address is delivered to the interface
identied by the address.
Depends on the type of the unicast address:
• Aggregatable global address--An
address equivalent to a global or
public IPv4 address. The address
structure is as follows: a xed prex of
2000::/3 (001), a 45-bit global
routing prex, a 16-bit subnet ID, and
a 64-bit interface ID.
• Site-local address--An address used
within a site or intranet. (This address
is similar to a private IPv4 address.) A
site consists of multiple network links.
The address structure is as follows: a
xed prex of FEC0::/10 (1111
1110 11), a 16-bit subnet ID, and a
64-bit interface ID.
• Link-local address--An address used
between directly connected nodes on
a single network link. The address
structure is as follows: a xed prex of
FE80::/10 (1111 1110 10) and a
64-bit interface ID.
• IPv4-compatible address--An
address used in IPv6 transition
mechanisms that tunnel IPv6 packets
dynamically over IPv4 infrastructures.
The address embeds an IPv4 address
in the low-order 32 bits and the high-
order 96 bits are zeros. The address
structure is as follows:
0:0:0:0:0:0:A.B.C.D.
• Loopback address--An address
(0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 or ::1) that a switch
can use to send an IPv6 packet to
itself. You cannot assign a loopback
address to a physical interface.
• Unspecied address--An address
(0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 or ::) that a node can
use until you congure an IPv6
address for it.
Multicast An address for a set of interfaces belonging to
dierent nodes. Sending a packet to a multicast
address results in the delivery of the packet to all
interfaces in the set.
A multicast address has a xed prex of
FF00::/8 (1111 1111). The next 4 bits dene
the address as a permanent or temporary
address. The next 4 bits dene the scope of the
address (node, link, site, organization, global).
Anycast An address for a set of interfaces belonging to
dierent nodes. Sending a packet to an anycast
address results in the delivery of the packet to
the closest interface identied by the address.
An anycast address looks similar to a unicast
address, because it is allocated from the unicast
address space. If you assign a unicast address to
multiple interfaces, it is an anycast address. An
IPv6 addressing overview
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
53-1003627-04 153

 Loading...
Loading...











