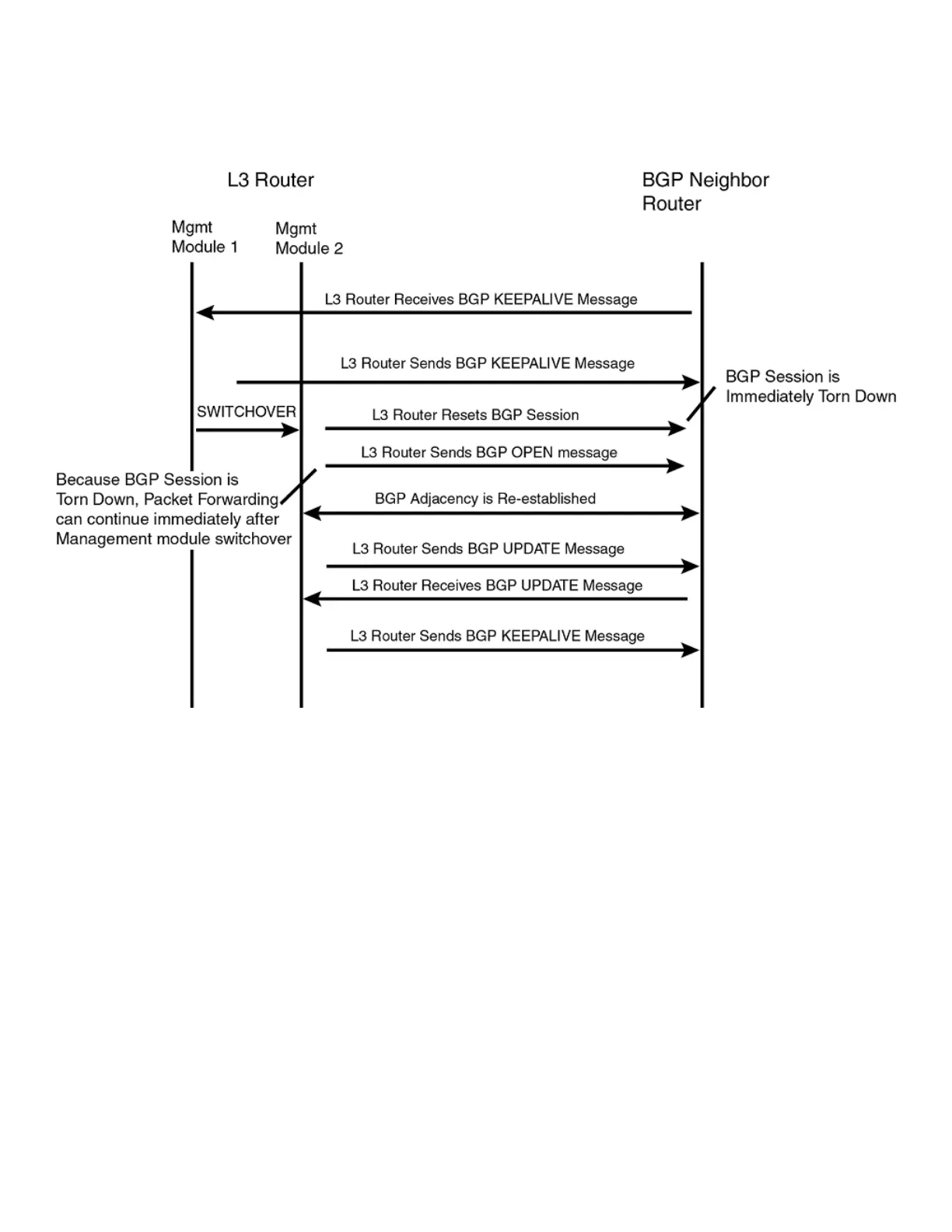
FIGURE 28 Management module switchover behavior for BGP4 peer notication
If the active management module fails due to a fault, the management module does not have the opportunity to reset BGP4 sessions
with neighbors as described for intentional failovers. In this situation the management module will reboot, or the standby management
module becomes the new active management module. Since the new active management module does not have the TCP/BGP4
information needed to reset the previous sessions, a remote BGP4 peer session is only reset when it sends a BGP4/TCP keep-alive
packet to this device, or when the BGP4 hold-time expires.
To help reduce the reconnection time after a management module failover or system reload, if an incoming TCP packet contains an
MD5 digest, and no matching TCP session is found, the device attempts to nd a matching BGP4 peer based on the IP address. If a
BGP4 peer conguration can be found, the device looks up the MD5 password congured for the peer, and uses it to send a RESET
packet.
BGP4 neighbor local AS
This feature allows you to congure a device so that it adds a peer to an AS that is dierent from the AS to which it actually belongs. This
feature is useful when an ISP is acquired by another ISP. In this situation, customers of the acquired ISP might not want to (or might not
be able to) adjust their conguration to connect to the AS of the acquiring provider.
In this example, Customer C is connected to ISP-A which is in AS 100 and ISP-B which is in AS 200.
BGP4 restart
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
358 53-1003627-04

 Loading...
Loading...











