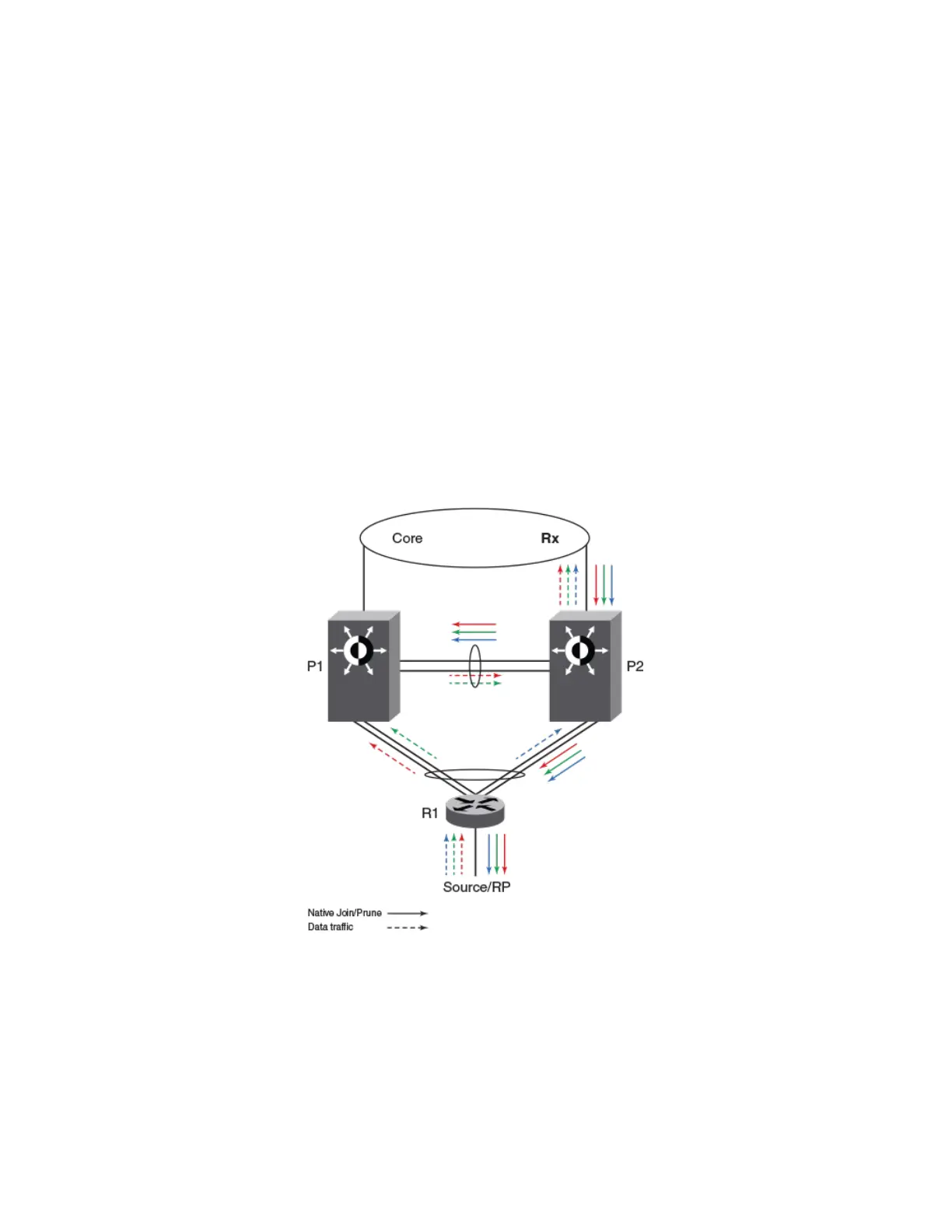
Join or prune exchange and mcache state:
• As receivers are connected to R1, R1 creates *,G state and sends a join state towards RP and sends it on the MCT LAG. This
join, like any other packet, is received by only one of the MCT peers.
• Suppose P2 receives the *,G join natively. This join is processed or consumed and is also ooded to P1 over ICL.
• P1 processes the join received over ICL as if it is received on CCEP.
• Both P1 and P2 create *,G state with CCEP as OIF.
• Both the peers send the *,G join towards RP and both the peers pull the trac.
• When the trac arrives, the S,G state is created on both the peers but only one of them forwards based on the software hashing
algorithm.
MCT peer as intermediate Downstream router
P1 and P2 are the MCT peers and are acting as downstream routers for R1. R1 is the intermediate router.
P1, P2 and R1 are
congured with PIM on the MCT VE interface. RP and source are beyond R1.
FIGURE 46 MCT peer as immediate downstream router
Hello exchange and neighbor state:
It acts and works as the upstream router.
Join or prune exchange and mcache state:
• The *,G joins come from the core to P2.
• P2 creates *,G state with uplink as OIF by consuming the join state.
Layer 3 behavior with MCT
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
53-1003627-04 583

 Loading...
Loading...











