12-2
Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-9639-07
Chapter 12 Configuring Private VLANs
Understanding Private VLANs
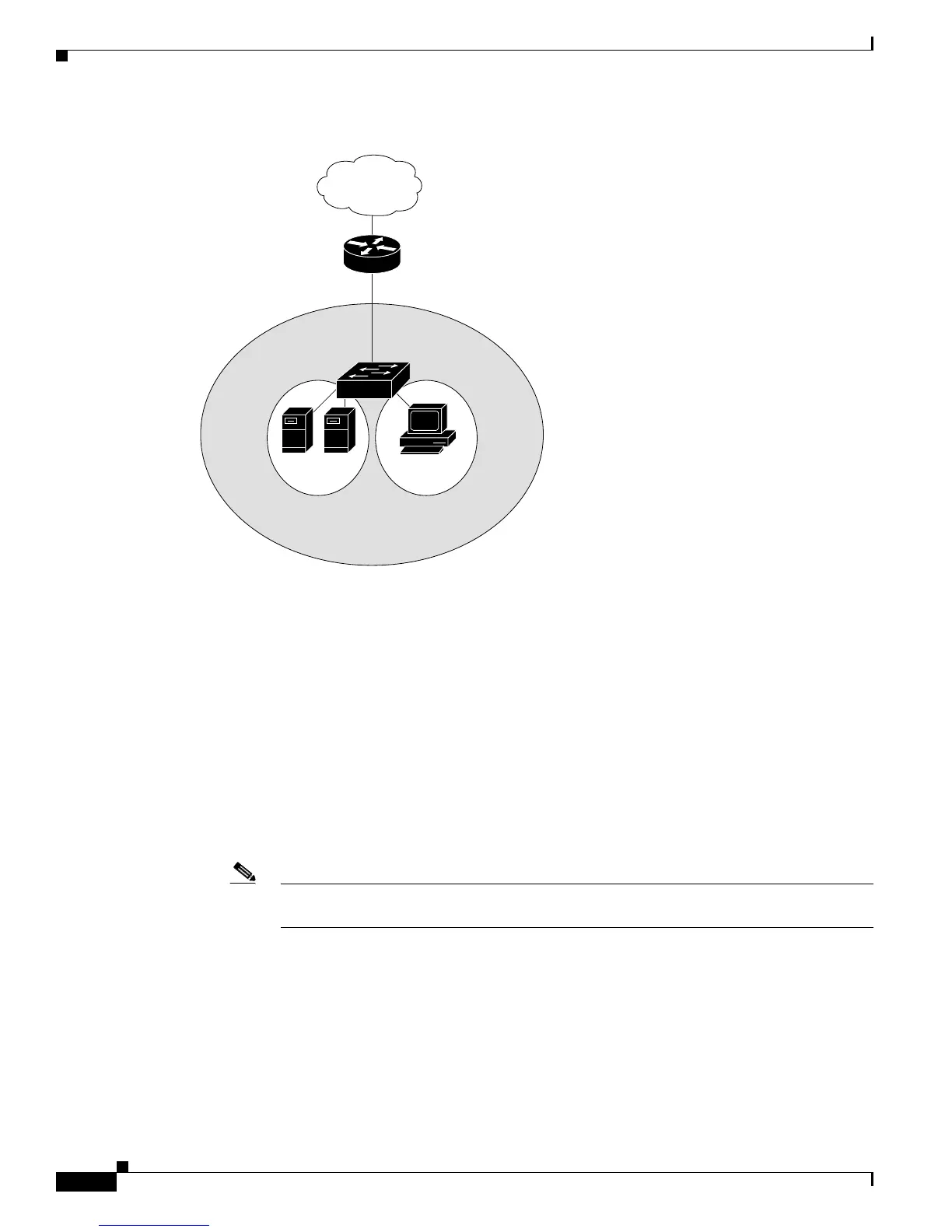
Figure 12-1 Private-VLAN Domain
There are two types of secondary VLANs:
• Isolated VLANs—Ports within an isolated VLAN cannot communicate with each other at the
Layer
2 level.
• Community VLANs—Ports within a community VLAN can communicate with each other but
cannot communicate with ports in other communities at the Layer 2 level. A community VLAN can
include a combination of no more than eight user network interfaces (UNIs) and enhanced network
interfaces (ENIs).
Private VLANs provide Layer 2 isolation between ports within the same private VLAN. Private-VLAN
ports are access ports that are one of these types:
• Promiscuous—A promiscuous port belongs to the primary VLAN and can communicate with all
interfaces, including the community and isolated host ports that belong to the secondary VLANs
associated with the primary VLAN.
Note Promiscuous ports must be network node interfaces (NNIs). UNIs or ENIs cannot be
configured as promiscuous ports.
• Isolated—An isolated port is a host port that belongs to an isolated secondary VLAN. It has
complete Layer 2 separation from other ports within the same private VLAN, except for the
promiscuous ports. Private VLANs block all traffic to isolated ports except traffic from promiscuous
ports. Traffic received from an isolated port is forwarded only to promiscuous ports.
116083
Private
VLAN
domain
Private
VLAN
domain
Primary
VLAN
SubdomainSubdomain
Secondary
community VLAN
Secondary
isolated VLAN
SubdomainSubdomain
Secondary
community VLAN
Secondary
isolated VLAN

 Loading...
Loading...















