12-4
Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-9639-07
Chapter 12 Configuring Private VLANs
Understanding Private VLANs
IP Addressing Scheme with Private VLANs
Assigning a separate VLAN to each customer creates an inefficient IP addressing scheme:
• Assigning a block of addresses to a customer VLAN can result in unused IP addresses.
• If the number of devices in the VLAN increases, the number of assigned address might not be large
enough to accommodate them.
These problems are reduced by using private VLANs, where all members in the private VLAN share a
common address space, which is allocated to the primary VLAN. Hosts are connected to secondary
VLANs, and the DHCP server assigns them IP addresses from the block of addresses allocated to the
primary VLAN. Subsequent IP addresses can be assigned to customer devices in different secondary
VLANs, but in the same primary VLAN. When new devices are added, the DHCP server assigns them
the next available address from a large pool of subnet addresses.
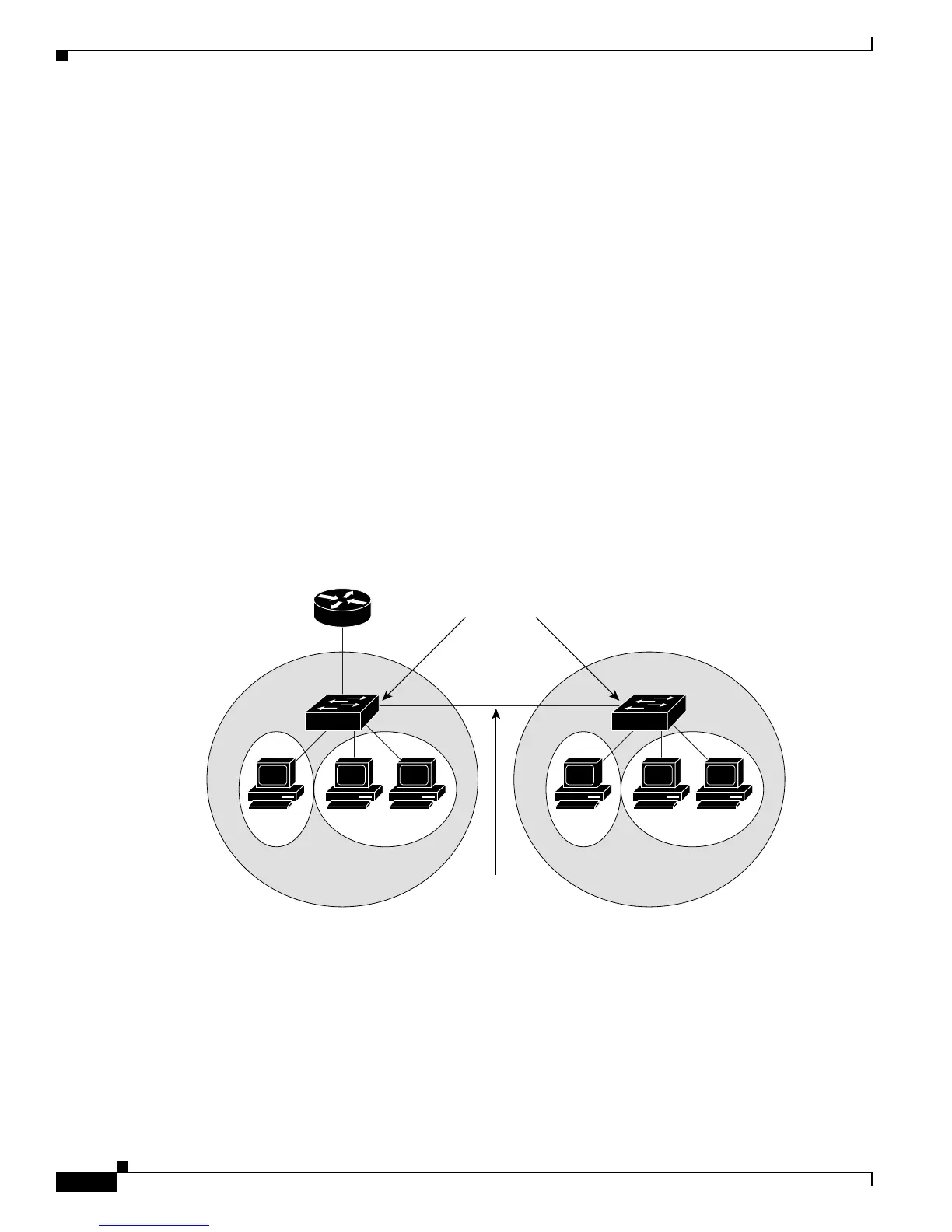
Private VLANs across Multiple Switches
As with regular VLANs, private VLANs can span multiple switches. A trunk port carries the primary
VLAN and secondary VLANs to a neighboring switch. The trunk port treats the private VLAN as any
other VLAN. A feature of private VLANs across multiple switches is that traffic from an isolated port
in switch A does not reach an isolated port on Switch B. See
Figure 12-2.
Figure 12-2 Private VLANs across Switches
You must manually configure private VLANs on all switches in the Layer 2 network. If you do not
configure the primary and secondary VLAN associations in some switches in the network, the Layer 2
databases in these switches are not merged. This can result in unnecessary flooding of private-VLAN
traffic on those switches.
116084
VLAN 100
VLAN 201 VLAN 202
Switch B
VLAN 100
VLAN 100 = Primary VLAN
VLAN 201 = Secondary isolated VLAN
VLAN 202 = Secondary community VLAN
VLAN 201
Carries VLAN 100,
201, and 202 traffic
Trunk ports
VLAN 202
Switch A

 Loading...
Loading...















