33-2
Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-9639-07
Chapter 33 Configuring QoS
Understanding QoS
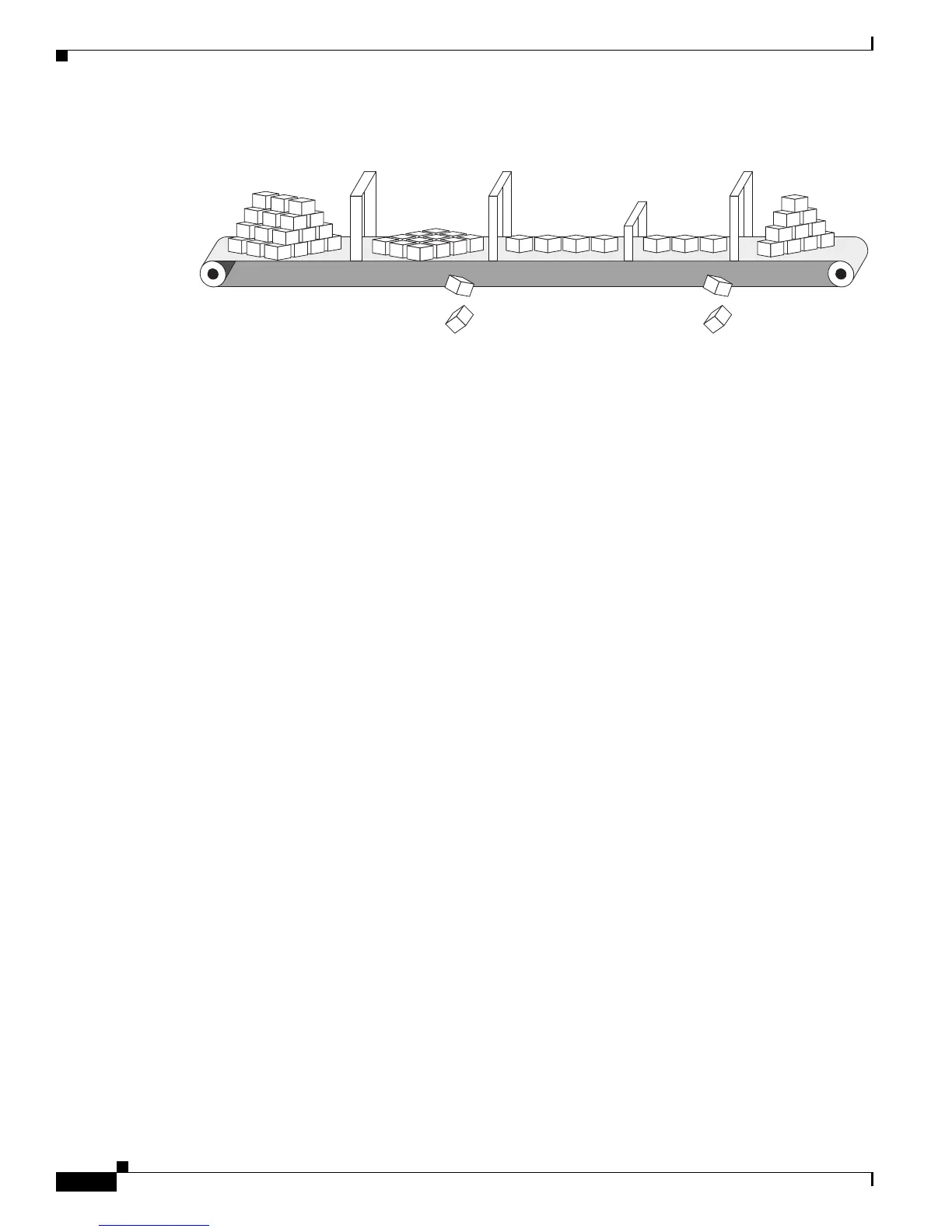
Figure 33-1 Modular QoS CLI Model
Basic QoS includes these actions.
• Packet classification organizes traffic on the basis of whether or not the traffic matches a specific
criteria. When a packet is received, the switch identifies all key packet fields: class of service (CoS),
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP), or IP precedence. The switch classifies the packet based
on this content or based on an access-control list lookup. For more information, see the
“Classification” section on page 33-5.
• Packet policing determines whether a packet is in or out of profile by comparing the rate of the
incoming traffic to the configured policer. You can control the traffic flow for packets that conform
to or exceed the configured policer. For more information, see the
“Policing” section on page 33-14.
• Packet prioritization or marking evaluates the classification and policer information to determine the
action to take. All packets that belong to a classification can be remarked. When you configure a
policer, packets that meet or exceed the permitted bandwidth requirements (bits per second) can be
conditionally passed through, dropped, or reclassified. For more information, see the
“Marking”
section on page 33-19.
• Congestion management uses queuing and scheduling algorithms to queue and sort traffic that is
leaving a port. The switch supports these scheduling and traffic-limiting features: class-based
weighted fair queuing (CBWFQ), class-based traffic shaping, port shaping, and class-based priority
queuing. You can provide guaranteed bandwidth to a particular class of traffic while still servicing
other traffic queues. For more information, see the
“Congestion Management and Scheduling”
section on page 33-20.
• Queuing on the switch is enhanced with the weighted tail-drop (WTD) algorithm, a
congestion-avoidance mechanism. WTD differentiates traffic classes and regulates the queue size
(in number of packets) based on the classification. For more information, see the
“Congestion
Avoidance and Queuing” section on page 33-26.
This section includes information about these topics:
• Modular QoS CLI, page 33-3
• Input and Output Policies, page 33-4
• Classification, page 33-5
• Table Maps, page 33-13
• Policing, page 33-14
• Marking, page 33-19
• Congestion Management and Scheduling, page 33-20
• Congestion Avoidance and Queuing, page 33-26
Classification Policing Marking Congestion
Avoidance
Queuing
Scheduling
Congestion
Drops
Policer
Drops
141149
 Loading...
Loading...















