238
Step Command Remarks
5. Enable route reflection
between clients.
reflect between-clients
By default, route reflection
between clients is enabled.
6. (Optional.) Configure the
cluster ID of the route reflector.
reflector cluster-id { cluster-id |
ip-address }
By default, a route reflector uses its
own router ID as the cluster ID.
Ignoring the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute
This section describes a specific scenario where BGP routers must ignore the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute.
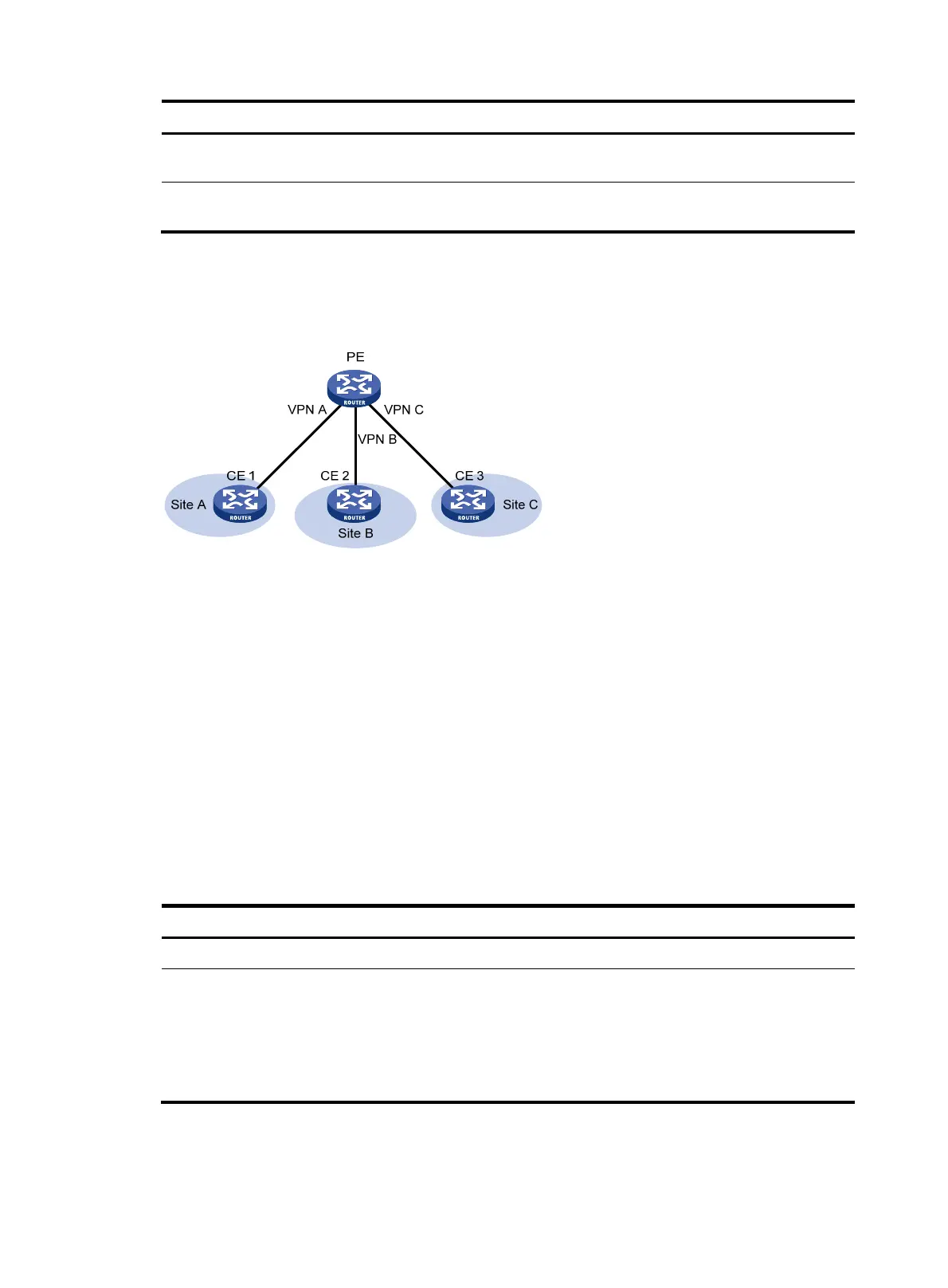
Figure 60 A VPN network where BGP routers must ignore the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute
As shown in Figure 60, in this scenario a PE connects to three sites that belong to different VPNs. Some
of the subnets in the VPNs need to communicate with each other. To meet the requirement, perform the
following configurations on the PE:
• Configure different BGP router IDs for different VPNs so the PE acts as multiple virtual BGP routers
in different VPNs. Each VPN has a virtual BGP router identified by the router ID configured for that
VPN.
• Establish IBGP peer relationships among the virtual BGP routers and configure one router as the
route reflector.
• Configure routing policies to control route distribution among VPNs.
If the virtual routers compare the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute, a VPN will discard another VPN's routes
received from the route reflector. As a result, the VPNs cannot access each other. In this scenario, you
must configure the routers to ignore the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute.
To ignore the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute (IPv4):
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view N/A
2. Enter BGP view or BGP-VPN
instance view.
• Enter BGP view:
bgp as-number
• Enter BGP-VPN instance view:
a. bgp as-number
b. ip vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name
N/A

 Loading...
Loading...











