11: BINARY ARITHMETIC INSTRUCTIONS
11-2 OPENNET CONTROLLER USER’S MANUAL
Valid Operands
For the valid operand number range, see page 6-2.
▲ Internal relays M0 through M2557 can be designated as D1. Special internal relays cannot be designated as D1.
When T (timer) or C (counter) is used as S1 or S2, the timer/counter current value is read out. When T (timer) or C
(counter) is used as D1, the data is written in as a preset value which can be 0 through 65535.
Since the binary arithmetic instructions are executed in each scan while input is on, a pulse input from a SOTU or SOTD
instruction should be used as required.
Valid Data Types
When a bit operand such as I (input), Q (output), M (internal relay), or R (shift register) is designated as the source or des-
tination, 16 points (word or integer data type) or 32 points (double-word or long data type) are used. When repeat is desig-
nated for a bit operand, the quantity of operand bits increases in 16- or 32-point increments.
When a word operand such as T (timer), C (counter), D (data register), or L (link register) is designated as the source or
destination, 1 point (word or integer data type) or 2 points (double-word or long data type) are used. When repeat is desig-
nated for a word operand, the quantity of operand words increases in 1- or 2-point increments.
Using Carry or Borrow Signals
When the D1 (destination) data is out of the valid data range as a result of addition, a carry occurs, and special internal
relay M8003 is turned on. When the D1 (destination) data is out of the valid data range as a result of subtraction, a borrow
occurs, and special internal relay M8003 is turned on.
There are three ways to program the carrying process (see examples below). If a carry never goes on, the program does not
have to include internal relay M8003 to process carrying. If a carry goes on unexpectedly, an output can be programmed to
be set as a warning indicator. If a carry goes on, the number of times a carry occurs can be added to be used as one word
data in a specified register.
Examples: ADD
• Data Type: Word
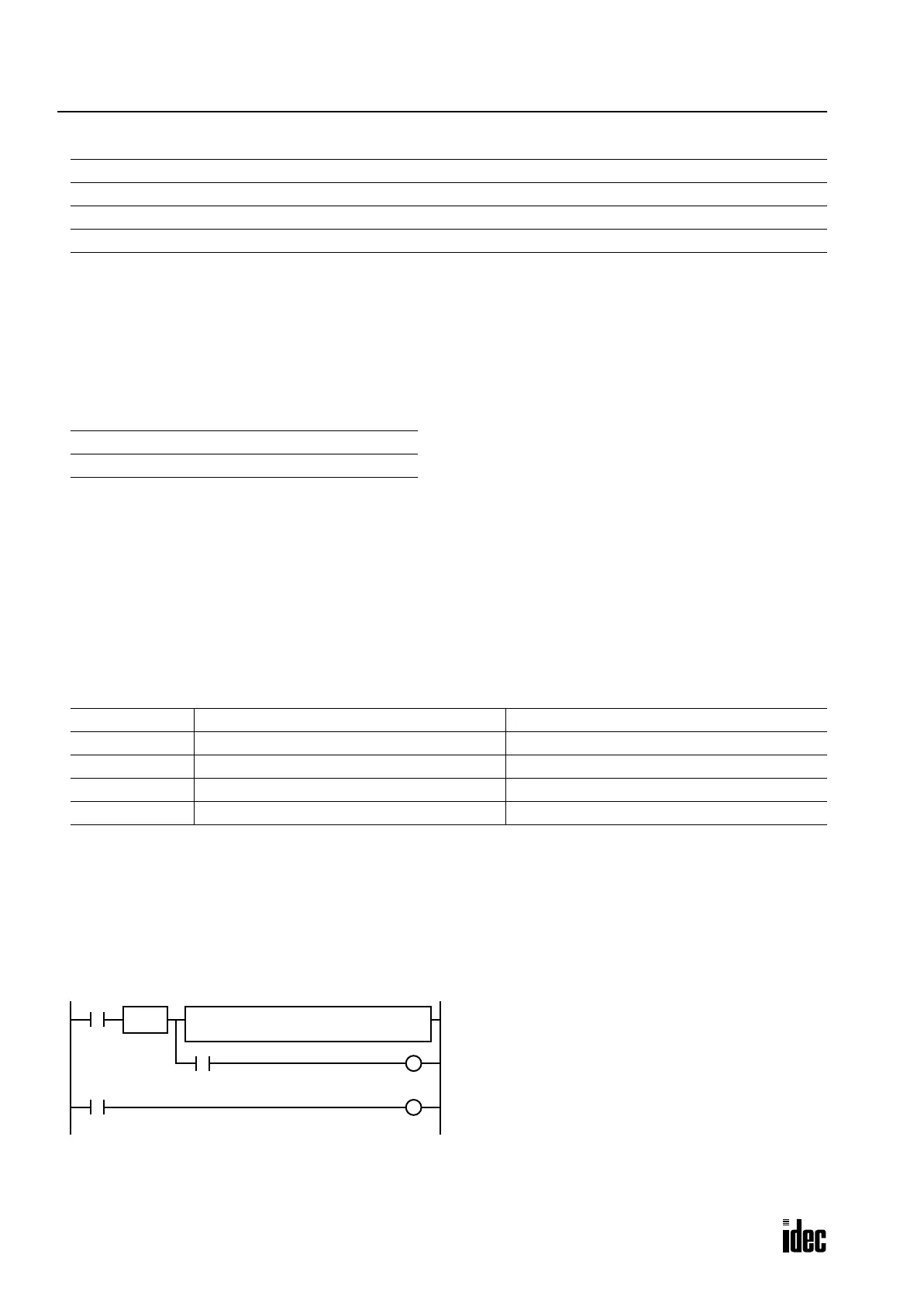
This example demonstrates the use of a carry signal from special internal relay M8003 to set an alarm signal.
Operand Function I Q M R T C D L Constant Repeat
S1 (Source 1) Data for calculation XXXXXXXX X 1-99
S2 (Source 2) Data for calculation XXXXXXXX X 1-99
D1 (Destination 1) Destination to store results — X ▲ XXXXX — 1-99
W (word) I (integer) D (double word) L (long)
XX X X
Data Type Carry occurs when D1 is Borrow occurs when D1 is
W (word) over 65,535 below 0
I (integer) below –32,768 or over 32,767 below –32,768 or over 32,767
D (double word) over 4,294,967,295 below 0
L (long) below –2,147,483,648 or over 2,147,483,647 below –2,147,483,648 or over 2,147,483,647
I0
REPS2 –
500
D1 –
D2
SOTU
M8003
I1
D2 + 500 → D2
When a carry occurs, output Q0 is set as a warning indicator.
When the acknowledge pushbutton (input I1) is pressed,
the warning indicator is reset.
Acknowledge
Pushbutton
S1 –
D2
ADD(W)
Q0
S
Q0
R
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com

 Loading...
Loading...