36: Command switches to keypad
37: Command switches to terminal
38: Command switches to communication
Range: 0x00–0x27
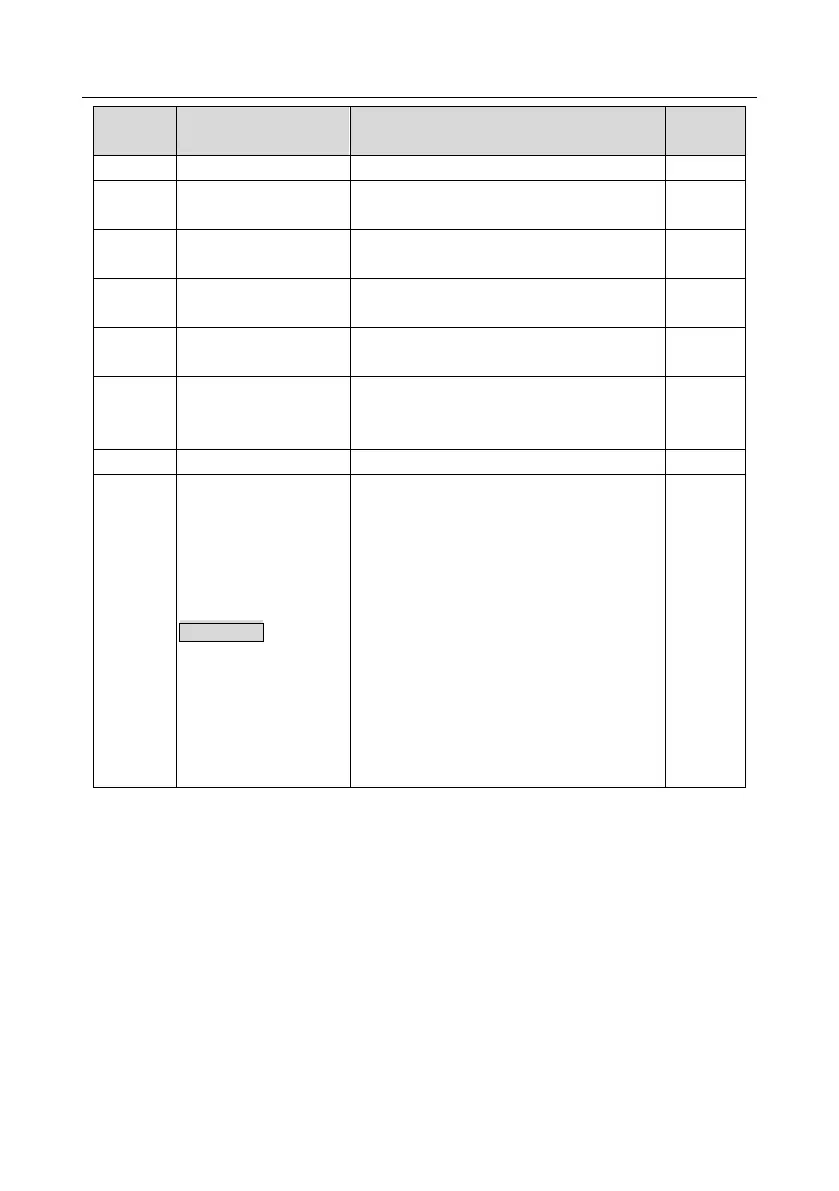
Ones: QUICK/JOG key function selection
0: No function
1: Jogging
2: Reserved
3: Switching between forward/reverse
rotation
4: Clear UP/DOWN setting
5: Coast to stop
6: Switch running command reference mode
by sequence
7: Reserved
Tens: Reserved
5.5.3 Vector control
Asynchronous motors are featured with high order, non-linear, strong coupling, and multi-variables,
which makes it very difficult to control asynchronous motors during actual application. The vector
control theory aims to solve this problem through measuring and controlling the stator current vector
of asynchronous motor, and decomposing the stator current vector into exciting current (current
component which generates internal magnet field) and torque current (current component which
generates torque) based on field orientation principle, and then controlling the amplitude value and
phase position of these two components (namely, control the stator current vector of motor) to realize
decoupling control of exciting current and torque current, thus achieving high-performance speed
regulation of asynchronous motor.
The inverter carries built-in speed sensor-less vector control algorithm, which can be used to drive the
asynchronous motor and permanent-magnet synchronous motor simultaneously. As the core
 Loading...
Loading...