MI 2893 / MI 2892 / MI 2885 Measurement methods
201
RTC
End of
Interval
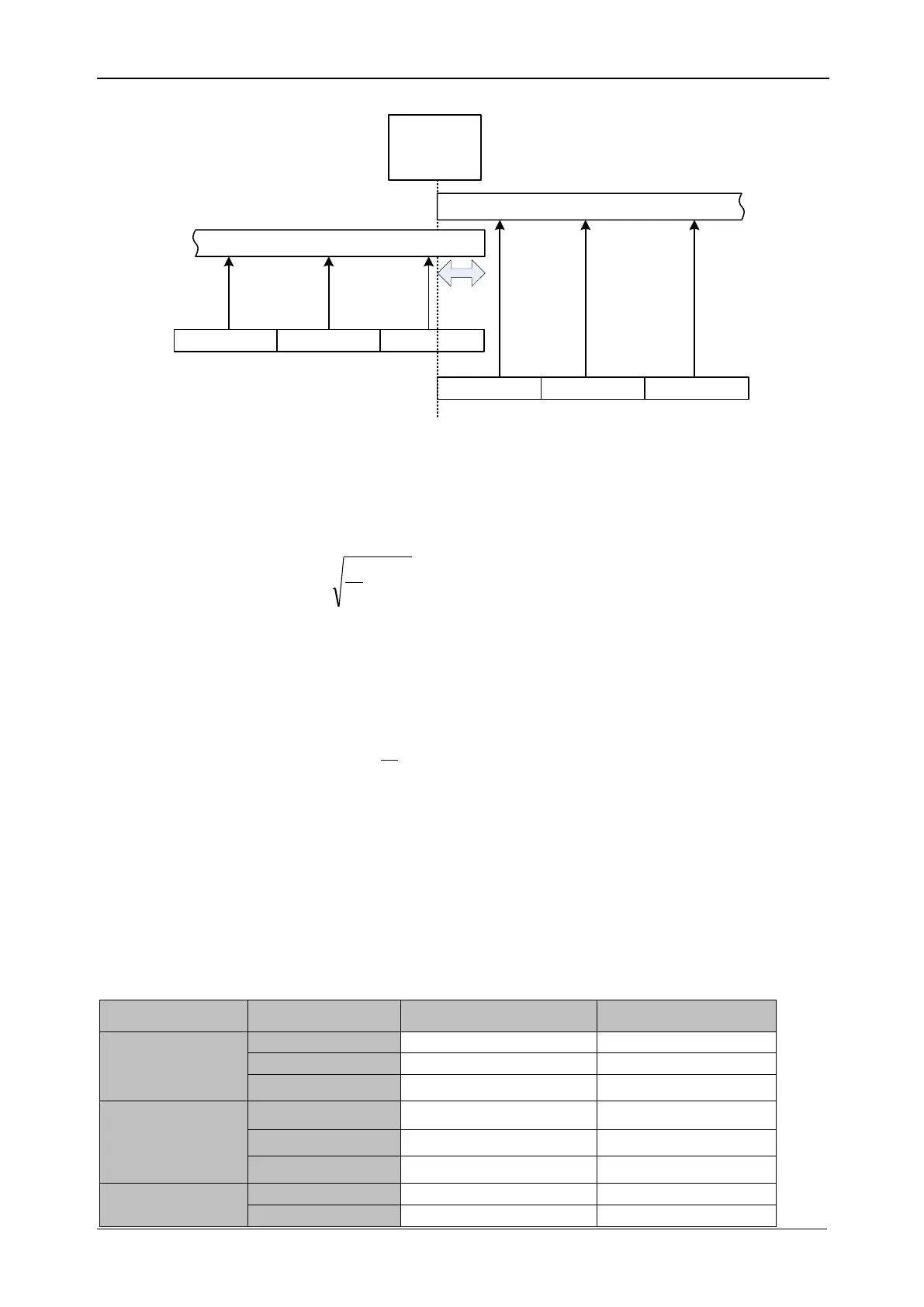
10/12 cycles 10/12 cycles 10/12 cycles
10/12 cycles 10/12 cycles 10/12 cycles
1 2 3i j k
overlap
10 min interval (x)
10 min interval (x+1)
Figure 164: Synchronization and aggregation of 10/12 cycle intervals
Depending from the quantity, for each aggregation interval instrument computes average, minimal,
maximal and/or active average value, this can be RMS (root means square) or arithmetical average.
Equations for both averages are shown below.
Where:
A
RMS
– quantity average over given aggregation interval
A – 10/12-cycle quantity value
N – number of 10/12 cycles measurements per aggregation interval.
Where:
A
avg
– quantity average over given aggregation interval
A – 10/12-cycle quantity value
N – number of 10/12 cycles measurements per aggregation interval.
In the next table averaging method for each quantity is specified:
Table 141: Data aggregation methods
 Loading...
Loading...











