7-9
7.5.2 Adjusting Alarm Limits Automatically
The monitor can automatically adjust alarm limits according to the measured vital signs,
using the auto limits function. When auto limits are selected, the monitor calculates safe
auto limits based on the latest measured values.
To get accurate auto alarm limits, you need to collect a set of measured vital signs as a
baseline. Then, in the main menu, select [Alarm Setup >>][Parameters][Auto Limits]
[Ok]. The monitor will create new alarm limits based on the measured values.
Before applying these automatically created alarm limits, confirm if they are appropriate for
your patient in the mass alarm setup menu. If not, you can adjust them manually. These
alarm limits will remain unchanged until you select auto limits again or adjust them
manually.
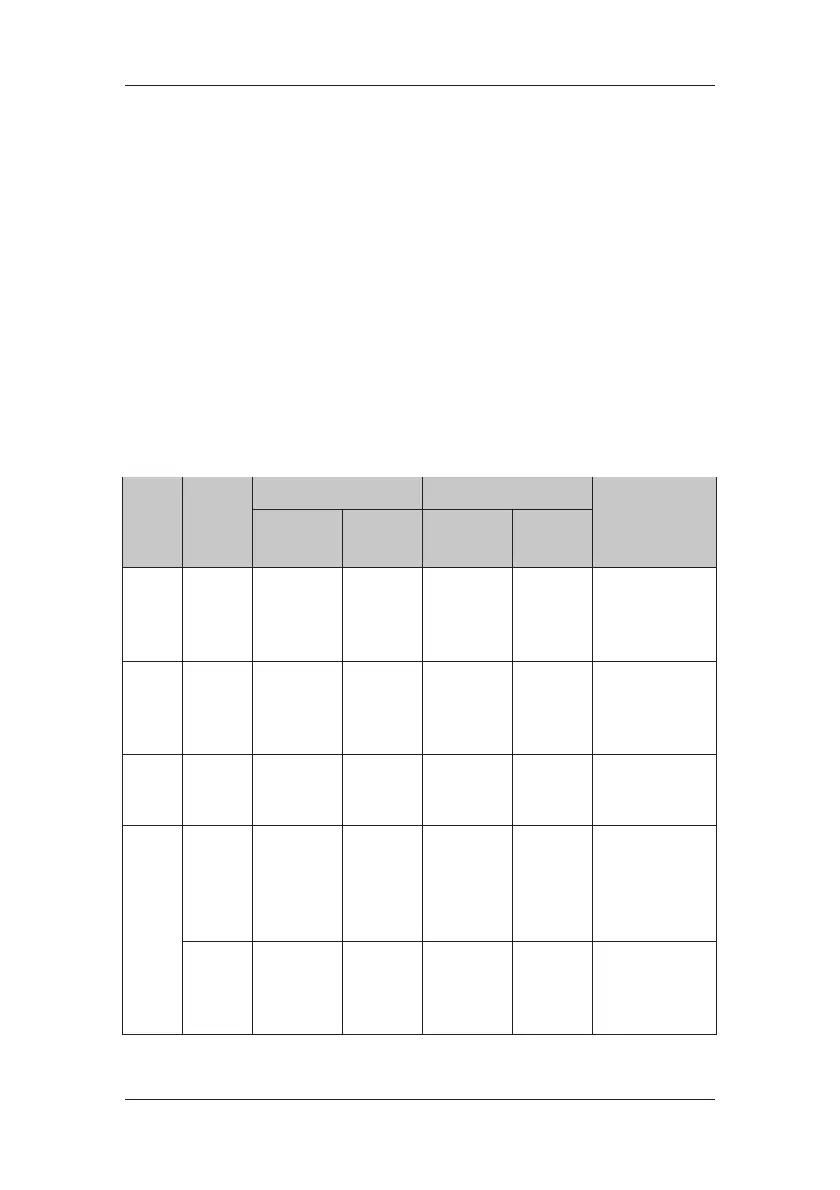
The monitor calculates the auto limits based on the following rules.
Module Parameter
Low alarm limit High alarm limit
Auto alarm limits
range
Adult/
pediatric
Neonate
Adult/
pediatric
Neonate
ECG HR/PR
(HR × 0.8) or
40bpm
(whichever is
greater)
(HR – 30) or
90bpm
(whichever
is greater)
(HR × 1.25)
or 240bpm
(whichever is
smaller)
(HR + 40) or
200bpm
(whichever
is smaller)
Adult/pediatric: 35
to 240
Neonate: 55 to 225
Resp RR
(RR × 0.5) or
6 rpm
(whichever is
greater)
(RR – 10) or
30 rpm
(whichever
is greater)
(RR × 1.5) or
30 rpm
(whichever is
smaller)
(RR + 25) or
85 rpm
(whichever
is smaller)
Adult/pediatric: 6 to
55
Neonate: 10 to 90
SpO
2
SpO
2
Same as the
default alarm
limit
Same as the
default
alarm limit
Same as the
default alarm
limit
Same as the
default
alarm limit
Same as the
measurement range
NIBP
NIBP-S
(SYS × 0.68 +
10) mmHg
(SYS – 15)
or 45mmHg
(whichever
is greater)
(SYS × 0.86 +
38) mmHg
(SYS + 15)
or
105mmHg
(whichever
is smaller)
Adult: 45 to 270
Pediatric: 45 to 185
Neonate: 40 to 115
NIBP-D
(Dia × 0.68 +
6) mmHg
(Dia – 15) or
20mmHg
(whichever
is greater)
(Dia × 0.86 +
32) mmHg
(Dia + 15) or
80mmHg
(whichever
is smaller)
Adult: 25 to 210
Pediatric: 25 to 150
Neonate: 20 to 90

 Loading...
Loading...