SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
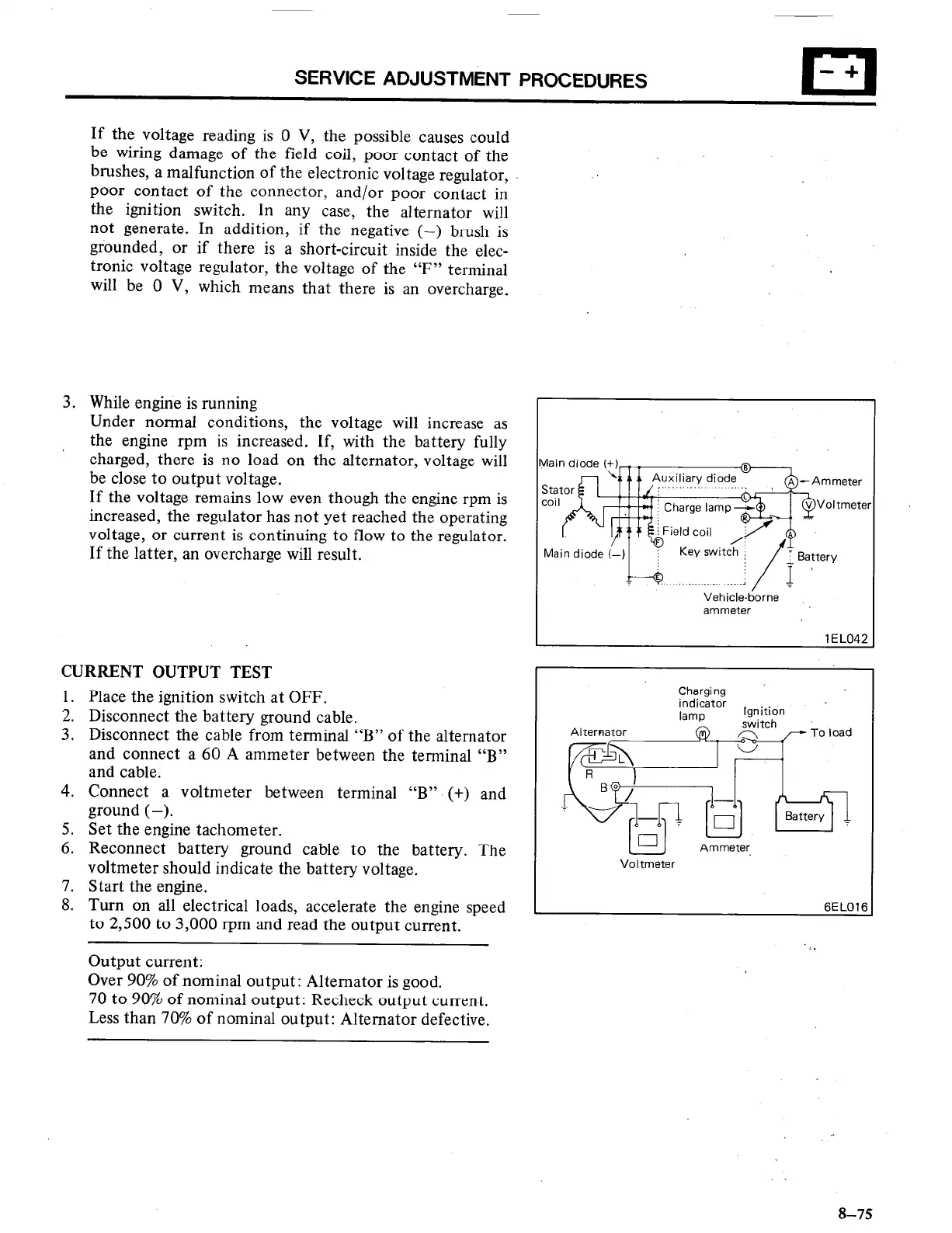
If the voltage reading is 0 V, the possible causes could
be wiring damage of the field coil, poor contact of the
brushes, a malfunction of the electronic voltage regulator,
poor contact of the connector, and/or poor contact in
the ignition switch.
In any case, the alternator will
not generate. In addition, if the negative (-) brush is
grounded, or if there is a short-circuit inside the elec-
tronic voltage regulator, the voltage of the “F” terminal
will be 0 V, which means that there is an overcharge.
3. While engine is running
Under normal conditions, the voltage will increase as
the engine rpm is increased. If, with the battery fully
charged, there is no load on the alternator, voltage will
be close to output voltage.
If the voltage remains low even though the engine rpm is
increased, the regulator has not yet reached the operating
voltage, or current is continuing to flow to the regulator.
If the latter, an overcharge will result.
CURRENT OUTPUT TEST
1. Place the ignition switch at OFF.
2. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
3. Disconnect the cable from terminal “B” of the alternator
and connect a 60 A ammeter between the terminal “B”
and cable.
4. Connect a voltmeter between terminal “B” (+) and
ground (-).
5. Set the engine tachometer.
6. Reconnect battery ground cable to the battery. The
voltmeter should indicate the battery voltage.
7. Start the engine.
8. Turn on all electrical loads, accelerate the engine speed
to 2,500 to 3,000 rpm and read the output current.
Stator
f!!Jv -
!ter
coil
ieter
@-3-t “A?
/
I
Vehicle-borne
ammeter
~
Charqinq
LEJ
Ammeter
Voltmeter
8-75
Output current:
Over 90% of nominal output: Alternator is good.
70 to 90% of nominal output: Recheck output current.
Less than 70% of nominal output: Alternator defective.

 Loading...
Loading...











