129
Connecting Programmable Terminals Section 4-10
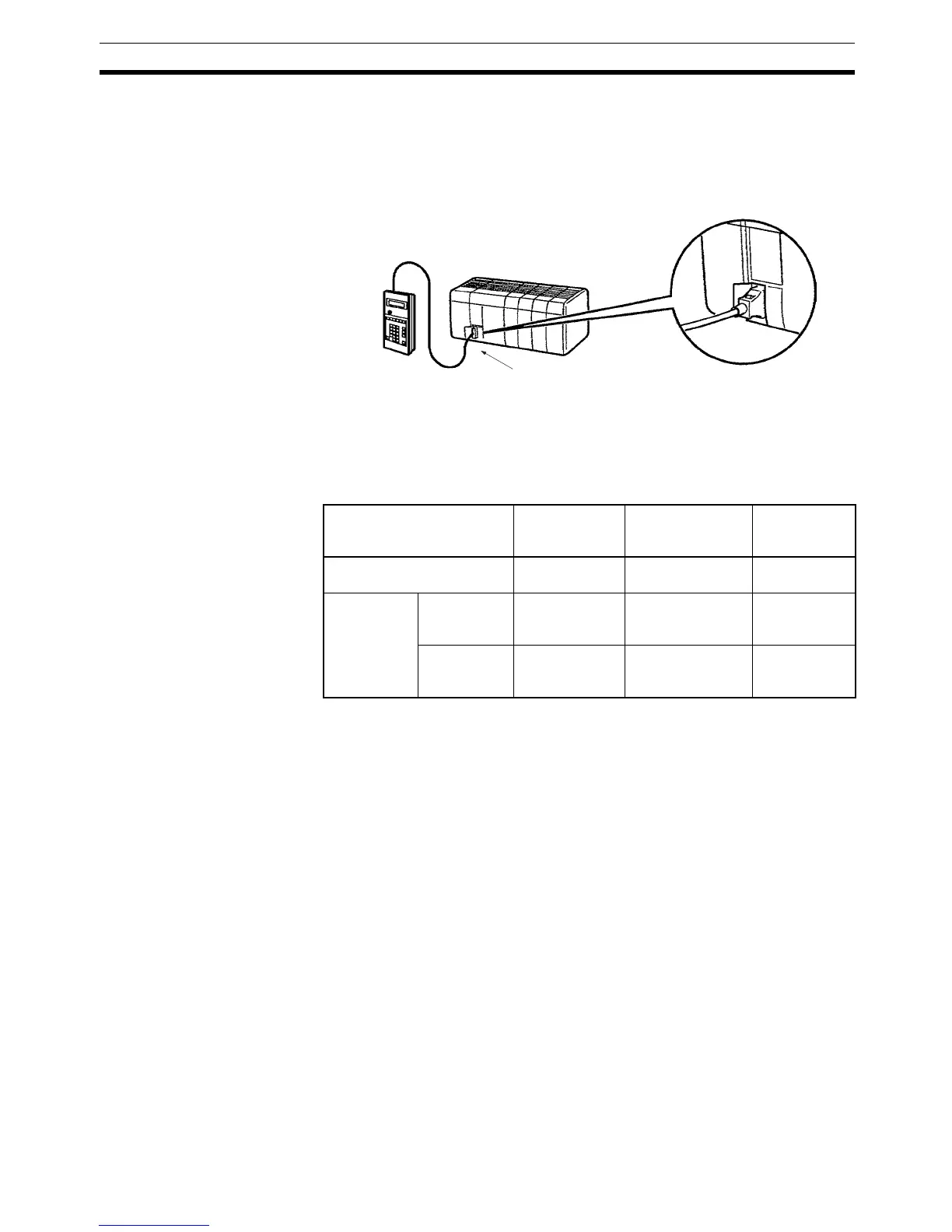
Programming Console
Connection
The CQM1H CPU Unit can be connected to a Programming Console as
shown below.
Note When connecting the CQM1H to a Programming Console, be sure to turn
OFF pin 7 on the DIP switch (factory setting). If pin 7 is ON, it will not be pos-
sible to use a Programming Console.
4-10 Connecting Programmable Terminals
The different communications configurations available for communications
with a Programming Terminal (PT) are shown in the following table.
Note 1. When communicating via a 1:1-mode NT Link, connect to the port on the
PT that supports this mode. Communications will not be possible if con-
nection is made to a port that supports only 1:N-mode communications.
2. When communicating via a 1:N-mode NT Link, connect to the port on the
PT that supports this mode. Communications will not be possible if con-
nection is made to a port that does not support this mode (e.g., the RS-
232C port on the NT30/NT30C supports only 1:1 communications).
3. The NT20S, NT600S, NT30, NT30C, NT620S, NT620C, and NT625C can-
not be used if the cycle time of the CPU Unit is 800 ms or longer (even if
only one of these PTs is used in a 1:N NT Link.)
4. The Programming Console functions of the PT (Expansion Mode) cannot
be used when connected to Serial Communications Board ports. They can
be used only by connecting to the RS-232C port on the CPU Unit.
Turn ON pin 7 on the DIP switch on the CPU Unit when using the Program-
ming Console function of the PT.
5. Set a unique unit number for each PT connected to the same PC. If the
same unit number is set for more than one PT, malfunctions will occur.
CQM1H
Peripheral port
Programming
Console
Serial communications
port
Serial commu-
nications mode
PC-to-PT ratio Programming
Console
functions
CPU Unit’s built-in RS-232C
port
NT Link
(1:1 mode)
One-to-one only Supported
(from PT)
Serial Com-
munications
Board
RS-232C port
(port 1)
NT Link
(1:1 mode,
1:N mode)
One-to-one or
one-to-many
No
RS-422A/485
(port 2)
NT Link
(1:1 mode,
1:N mode)
One-to-one or
one-to-many
No

 Loading...
Loading...











