Configuration Guide Configuring SNTP
Root Delay: indicates the round-trip time to the master clock reference source, which is a 32-bit integer.
Root Dispersion: indicates the largest difference from the master reference clock source, which is a 32-bit integer.
Reference Clock Identifier: indicates the 32-bit identifier of a reference clock source.
Reference Timestamp: indicates a 64-bit timestamp, namely, the time that is set or corrected at the last time.
Originate Timestamp: indicates a 64-bit timestamp, namely, the local time when a time synchronization request leaves from a
client.
Receive Timestamp: indicates a 64-bit timestamp, namely, the local time when a time synchronization request packet arrives at a
server.
Transmit Timestamp: indicates a 64-bit timestamp, namely, the local time when a time synchronization response packet leaves
from a server.
Authenticator (optional): indicates authentication information.
Overview
SNTP Time
Synchronization
Synchronizes time from an SNTP/NTP server to a local device.
14.3.1 SNTP Time Synchronization
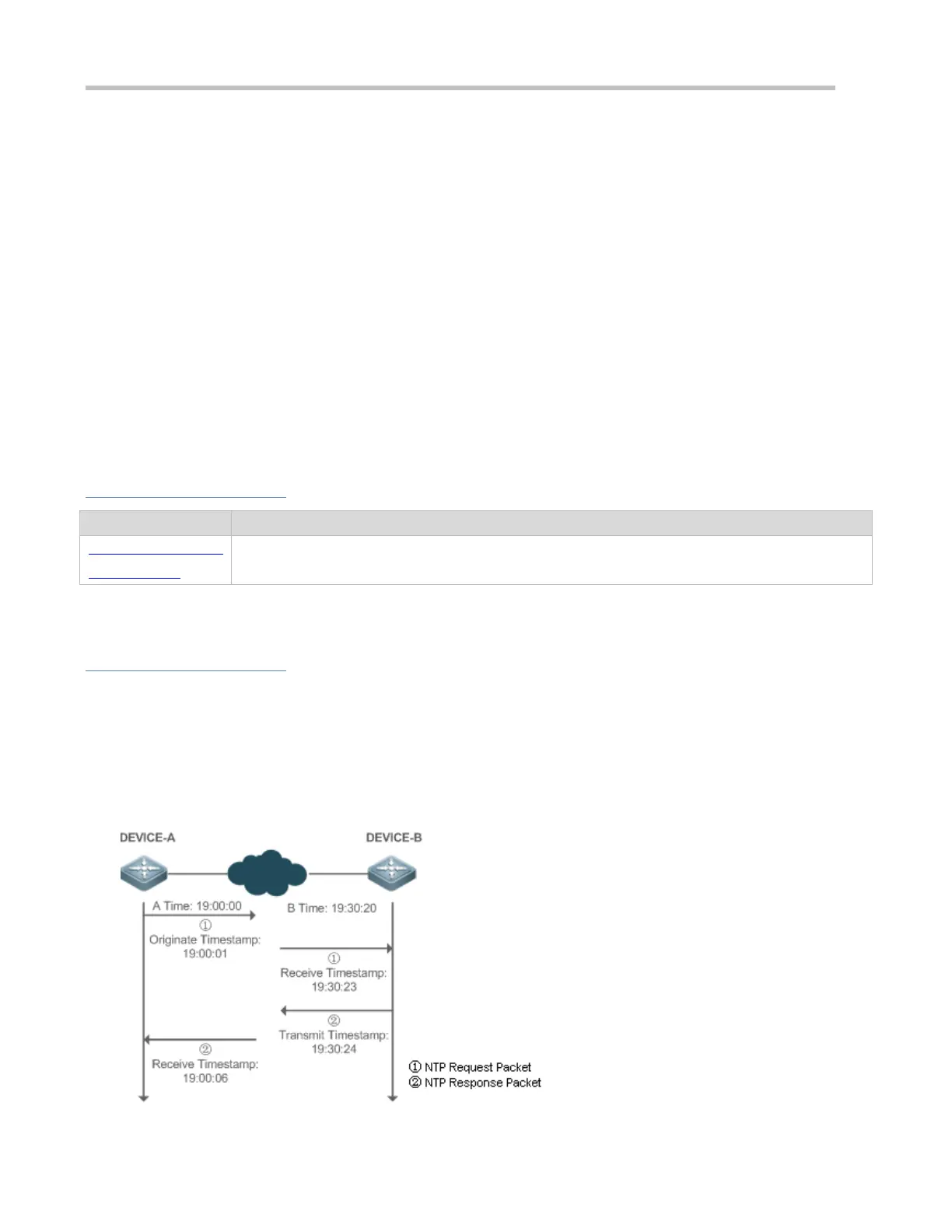
Working Principle
SNTP time synchronization is implemented by interaction of SNTP/NTP packets between a client and a server. The client sends a time
synchronization packet to the server at intervals (half an hour by default). After receiving a response packet from the server, the client
synchronizes time.
Figure 14-3 shows the format of an SNTP time synchronization packet.
Figure 14-3 Working Principle of SNTP

 Loading...
Loading...











