P
ORT
C
ONFIGURATION
3-111
CLI – Specify any interface, and then enter the threshold. The following
disables broadcast storm control for port 1, and then sets broadcast
suppression at 600 octets per second for port 2 (which applies to all ports).
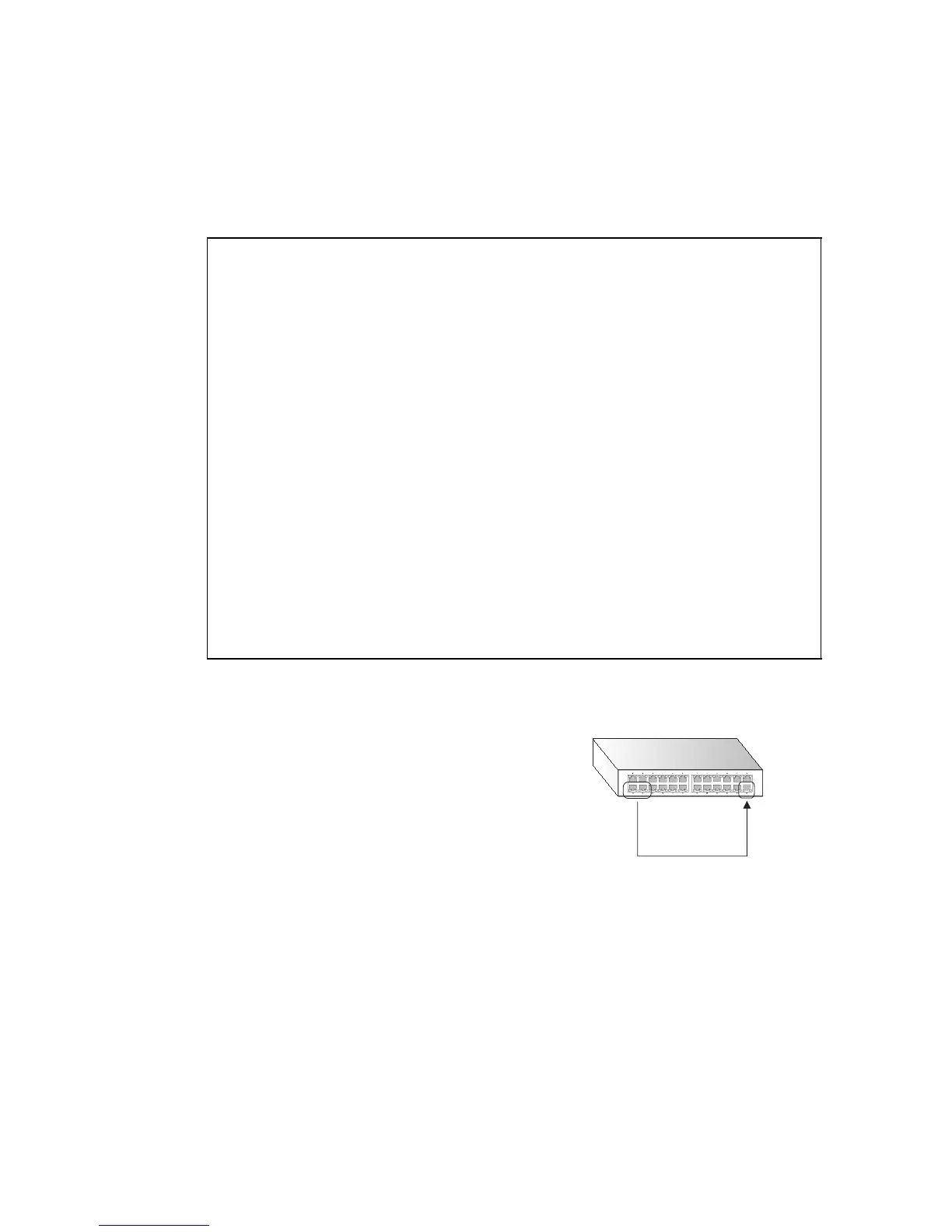
Configuring Port Mirroring
You can mirror traffic from any source
port to a target port for real-time
analysis. You can then attach a logic
analyzer or RMON probe to the target
port and study the traffic crossing the
source port in a completely unobtrusive
manner.
Command Usage
• Monitor port speed should match or exceed source port speed,
otherwise traffic may be dropped from the monitor port.
• When mirroring port traffic, the target port must be included in the
same VLAN as the source port.
Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/1 4-146
Console(config-if)#no switchport broadcast 4-152
Console(config-if)#exit
Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/2
Console(config-if)#switchport broadcast octet-rate 600 4-152
Console(config-if)#end
Console#show interfaces switchport ethernet 1/2 4-157
Information of Eth 1/2
Broadcast threshold: Enabled, 600 octets/second
Lacp status: Enabled
Ingress rate limit: disable, Level: 30
Egress rate limit: disable, Level: 30
VLAN membership mode: Hybrid
Ingress rule: Disabled
Acceptable frame type: All frames
Native VLAN: 1
Priority for untagged traffic: 0
Gvrp status: Disabled
Allowed Vlan: 1(u),
Forbidden Vlan:
Private-VLAN mode: NONE
Private-VLAN host-association: NONE
Private-VLAN mapping: NONE
Console#
Source
port(s)
Single
target
port
 Loading...
Loading...









