Acquiring Waveforms
3-34
TDS5000 Series User Manual
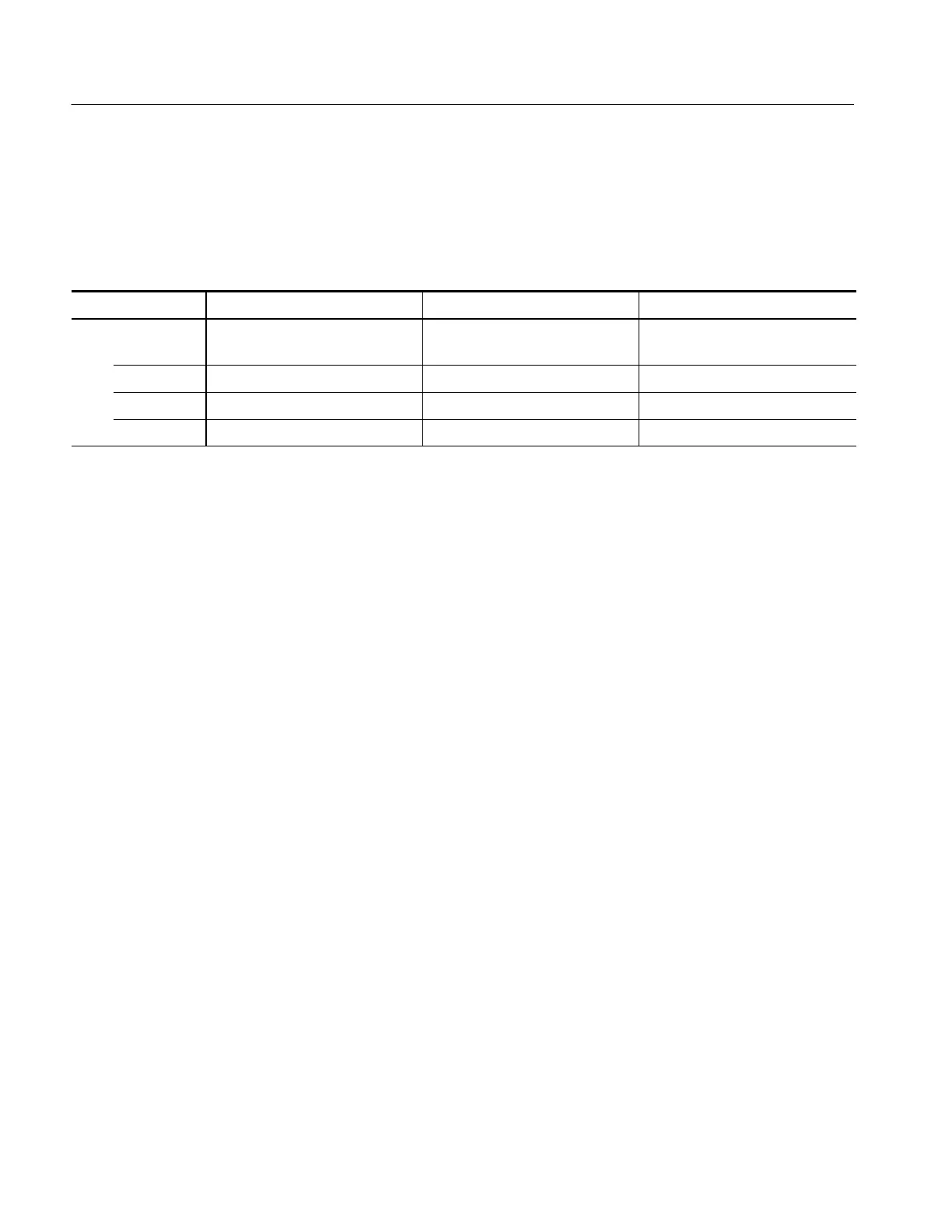
Table 3--2 shows the time base setting(s) at which the switch from real-time
sampling (RT) to equivalent-time sampling (ET) occurs for your oscilloscope.
This information applies to all TDS5000 models.
Table 3- 2: Sampling mode selection
Channels on 1 2 3or4
Time base
≥800 ps/pt RT RT RT
400 ps/pt RT RT ET
200 ps/pt RT ET ET
≤100 ps/pt ET ET ET
The type of equivalent-time sampling the oscilloscope uses is called random
equivalent-time sampling. Although it takes the samples sequentially in time, it
takes them randomly with respect to the trigger. Random sampling occurs
because the oscilloscope sample clock runs asynchronously with respect to the
input signal and the signal trigger. The oscilloscope takes samples independently
of the trigger position and displays them based on the time difference between
the sample and the trigger.
Your oscilloscope can interpolate between the samples it acquires, and does so
only when it does not have all of the actual samples it needs to fill its displayed
waveform. For instance, if you set ZOOM to progressively larger amounts of
expansion, the oscilloscope interpolates to create the intervening points in the
displayed waveform. There are two options for interpolation: linear or sin(x)/x.
(The oscilloscope can also use equivalent-time sampling to acquire more
samples; refer to Equivalent-time Sampling on page 3--33.)
H Linear interpolation computes record points between actual acquired
samples by using a straight line fit. It assumes that all of the interpolated
points fall in their appropriate point in time on that straight line. Linear
interpolation is useful for waveforms with fast rise times, such as pulse
trains.
H Sin(x)/x interpolation computes record points using a curve fit between the
actual values acquired. It assumes that all of the interpolated points fall along
that curve. This is particularly useful when acquiring more rounded
waveforms such as sine waves. Sin(x)/x interpolation is also appropriate for
general use, although it may introduce some overshoot or undershoot in
signals with fast rise times.
Interpolation

 Loading...
Loading...