Creating and Using Math Waveforms
TDS5000 Series User Manual
3- 141
The math waveform, derived from the sampled waveform, is computed based on
the following equation:
Y
n
= (X
(n+1)
− X
n
)
1
T
Where: X is the source waveform
Y is the derivative math waveform
T is the time between samples
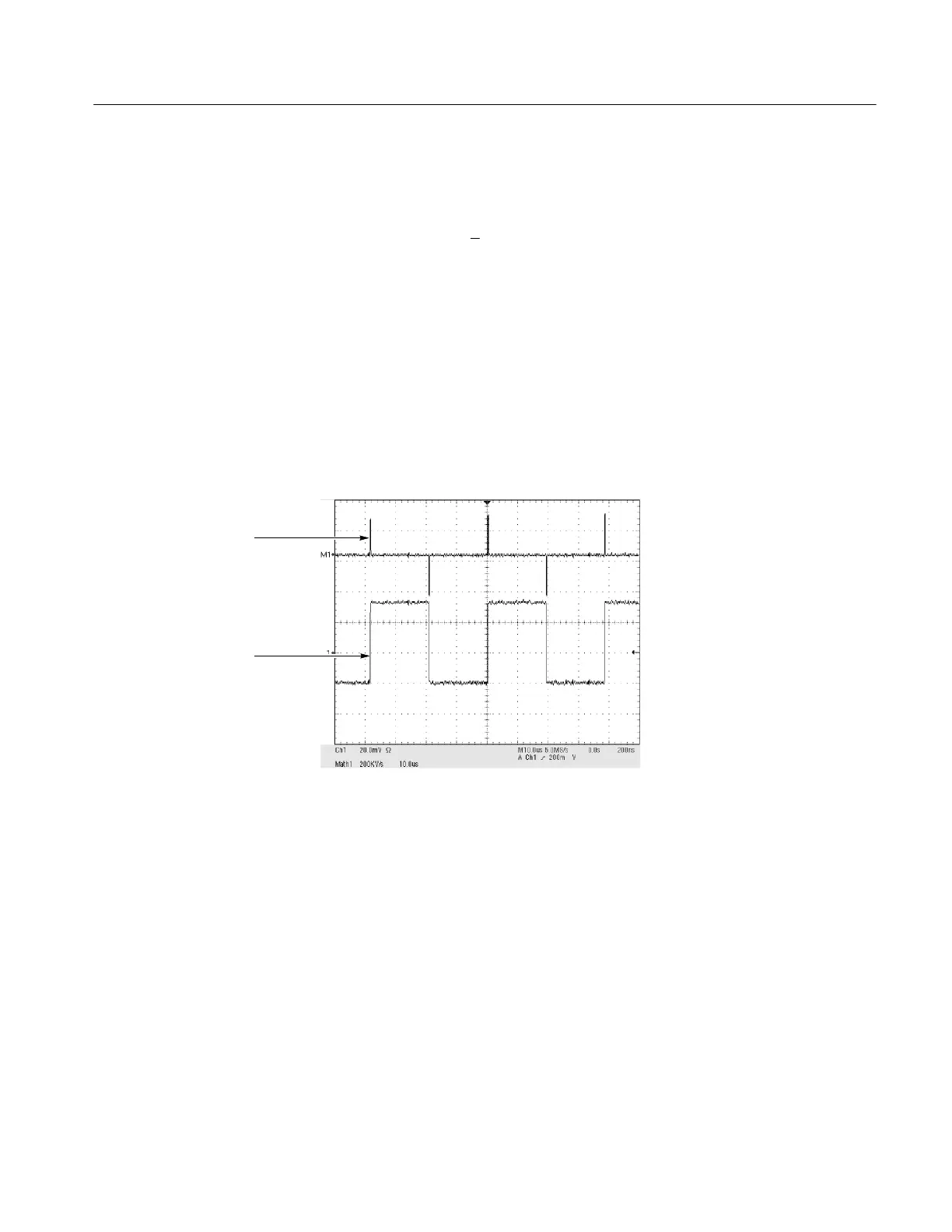
Since the resultant math waveform is a derivative waveform (See Figure 3--40),
its vertical scale is in volts/second (its horizontal scale is in seconds). The source
signal is differentiated over its entire record length; therefore, the math waveform
record length equals that of the source waveform.
Derivative math waveform
Source waveform
Figure 3- 40: Derivative math waveform
Cursor Measurements. You can also use cursors to measure derivative wave-
forms. Use the same procedure as Take Cursor Measurements on page 3--150.
When using that procedure, note that the amplitude measurements on a deriva-
tive waveform will be in volts per second rather than in volt-seconds as is
indicated for the integral waveform measured in the procedure.

 Loading...
Loading...