Creating and Using Math Waveforms
TDS5000 Series User Manual
3- 137
You create math waveforms to support the analysis of your channel and reference
waveforms. By combining and transforming source waveforms and other data
into math waveforms, you can derive the data view that your application
requires. Create math waveforms that result from:
H Mathematical operations on one or several waveforms: add, subtract,
multiply, and divide.
H Functional transformations of waveforms, such as integration, differenti-
ation, and so on.
H Spectral analysis of waveforms, such as testing impulse response.
You can create up to four math waveforms (two for the TDS5052); see Using
Math on page 3-- 138 for more examples.
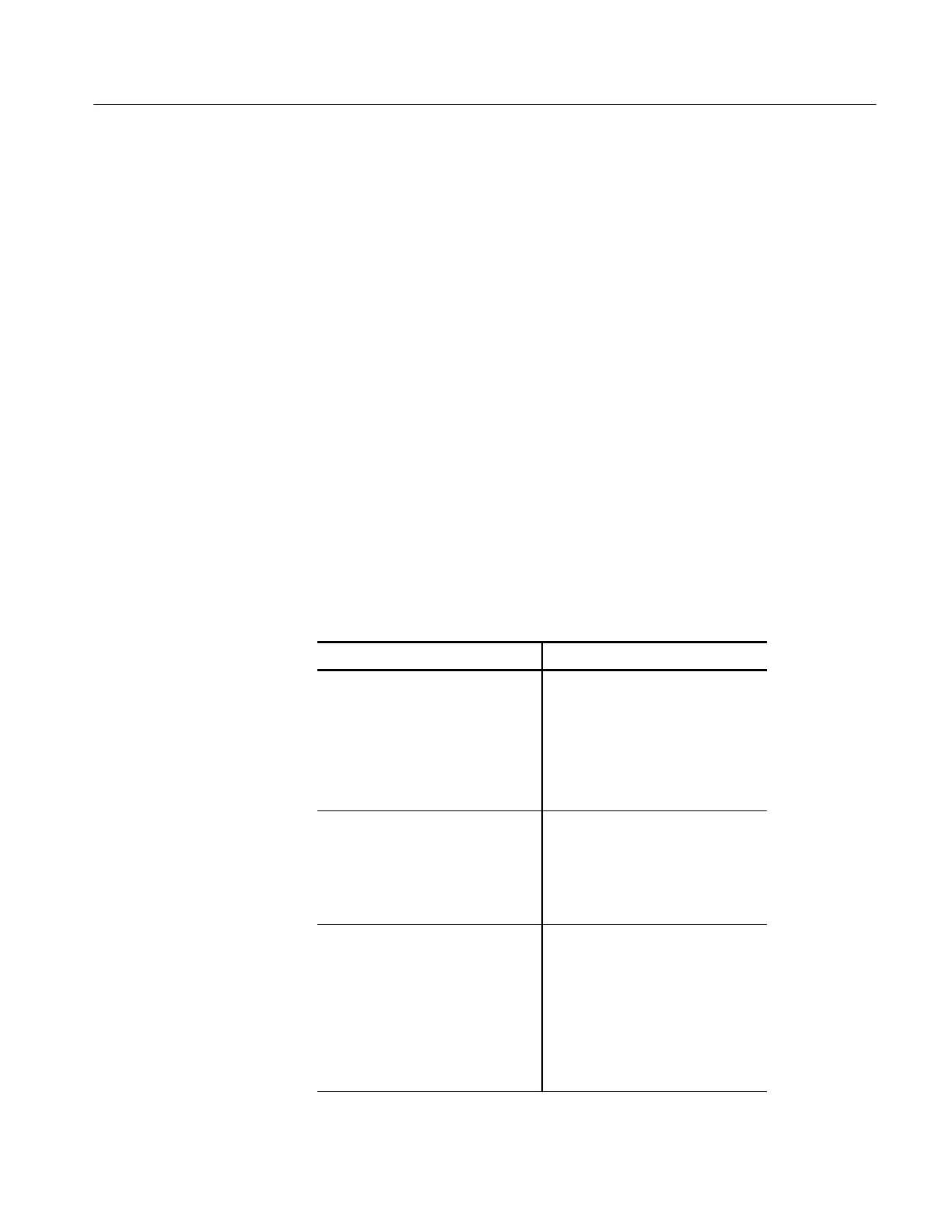
Table 3--10 shows the functions available with the standard (default) math
capabilities of this instrument versus the functionality provided when TDS5UP
Option 2A, Advanced Analysis, is installed. Note that 2A also includes
histograms, which are discussed in the previous section (Measuring Waveforms).
Table 3- 10: Functions available in Standard Math and
Advanced Math
Standard M a th Advanced Math
Math Waveform Positioning
H Vertical position and scale
H Displ ay on/off
H Labeling
Math Waveform Positioning
H Vertical position and scale
H Displ ay on/off
H Labeling
Waveform Math Operations
H Dual waveform math
Waveform Math Operations
H Equation Editor
H Averages
H Predefined expressions
FFT Math Operations
H Magnitude
FFT Math Operations
H Advanced spectral analysis
(magnitude, phase, aver-
aging)
H Locking spectral controls
H Gati ng with FFT window
types
Standard Math versus
Advanced Math

 Loading...
Loading...











