Configuration Guide 540
Configuring 802.1x Overview
1
Overview
802.1x protocol is a protocol for port-based Network Access Control. It is used to
authenticate and control access from devices connected to the ports. If the device
connected to the port is authenticated by the authentication server successfully, its
request to access the LAN will be accepted; if not, its request will be denied.
802.1x authentication uses client-server model which contains three device roles: client/
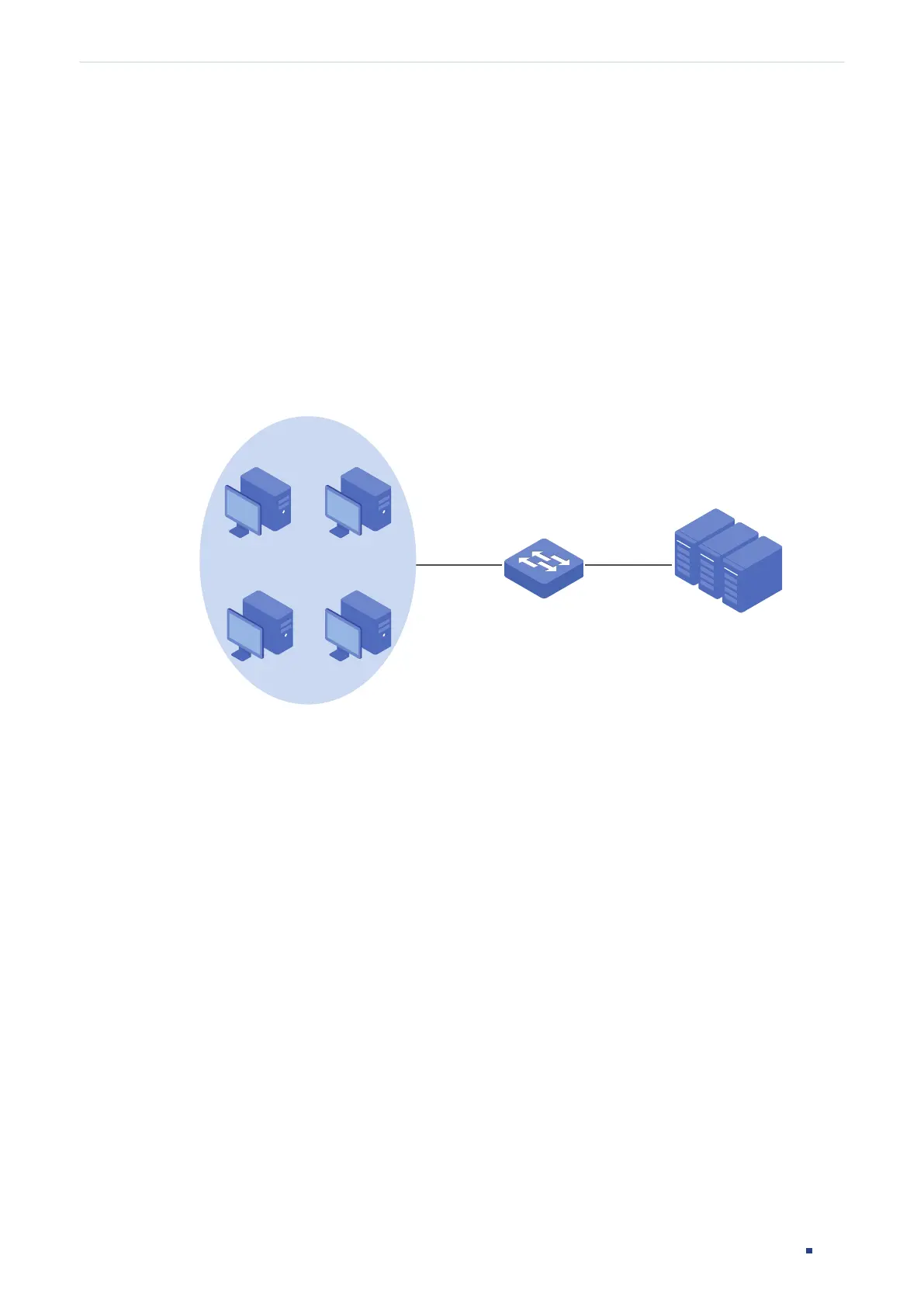
supplicant, authenticator and authentication server. This is described in the figure below:
Figure 1-1 802.1x Authentication Model
Authentication Server
Clients
Switch
Authenticator
Client
A client, usually a computer, is connected to the authenticator via a physical port. We
recommend that you install TP-Link 802.1x authentication client software on the client
hosts, enabling them to request 802.1x authentication to access the LAN.
Authenticator
An authenticator is usually a network device that supports 802.1x protocol. As the above
figure shows, the switch is an authenticator.
The authenticator acts as an intermediate proxy between the client and the authentication
server. The authenticator requests user information from the client and sends it to the
authentication server; also, the authenticator obtains responses from the authentication
server and send them to the client. The authenticator allows authenticated clients to
access the LAN through the connected ports but denies the unauthenticated clients.

 Loading...
Loading...











