Chapter 8 Configuring VLANs
Overview
8-2
Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Software Configuration Guide
78-6511-05
Overview
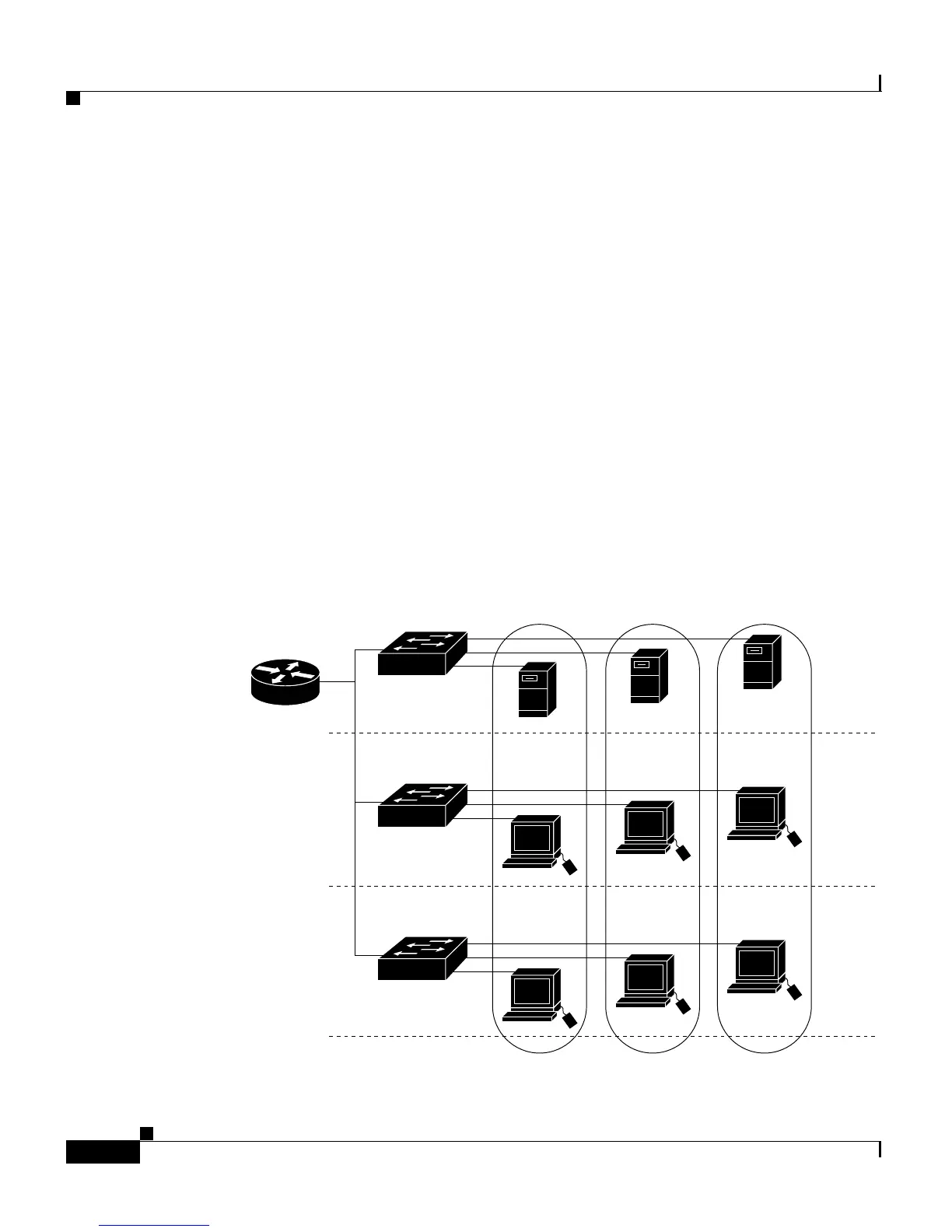
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a switched network that is logically segmented by
function, project team, or application, without regard to the physical locations of
the users. Any switch port can belong to a VLAN, and unicast, broadcast, and
multicast packets are forwarded and flooded only to stations in the VLAN. Each
VLAN is considered a logical network, and packets destined for stations that do
not belong to the VLAN must be forwarded through a router or bridge as shown
in Figure 8-1. VLANs are identified with a number of 1 to 1001.
Because a VLAN is considered a separate logical network, it contains its own
bridge Management Information Base (MIB) information and can support its own
implementation of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). For information about
managing VLAN STP instances, see the “Supported STP Instances” section on
page 6-24.
Figure 8-1 VLANs as Logically Defined Networks
Floor 1
Floor 2
Engineering
VLAN
Cisco router
Fast
Ethernet
Catalyst 2900
series XL
Catalyst 3500
series XL
Floor 3
Marketing
VLAN
Accounting
VLAN
15933
Catalyst 2900
series XL
 Loading...
Loading...











