Transmission, addressing, and routing RF packet routing
Digi XBee® 3 Zigbee® RF Module
105
AODV routing algorithm
Routing under the AODV protocol uses tables in each node that store the next hop (intermediary node
between source and destination nodes) for a destination node. If a next hop is unknown, route
discovery takes place to find a path. Since only a limited number of routes can be stored on a router,
route discovery takes place more often on a large network with communication between many
different nodes.
Node Destination address Next hop address
R3 Router 6 Coordinator
C Router 6 Router 5
R5 Router 6 Router 6
When a source node discovers a route to a destination node, it sends a broadcast route request
command. The route request command contains the source network address, the destination
network address and a path cost field (a metric for measuring route quality). As the route request
command propagates through the network (see Broadcast transmissions), each node that re-
broadcasts the message updates the path cost field and creates a temporary entry in its route
discovery table.
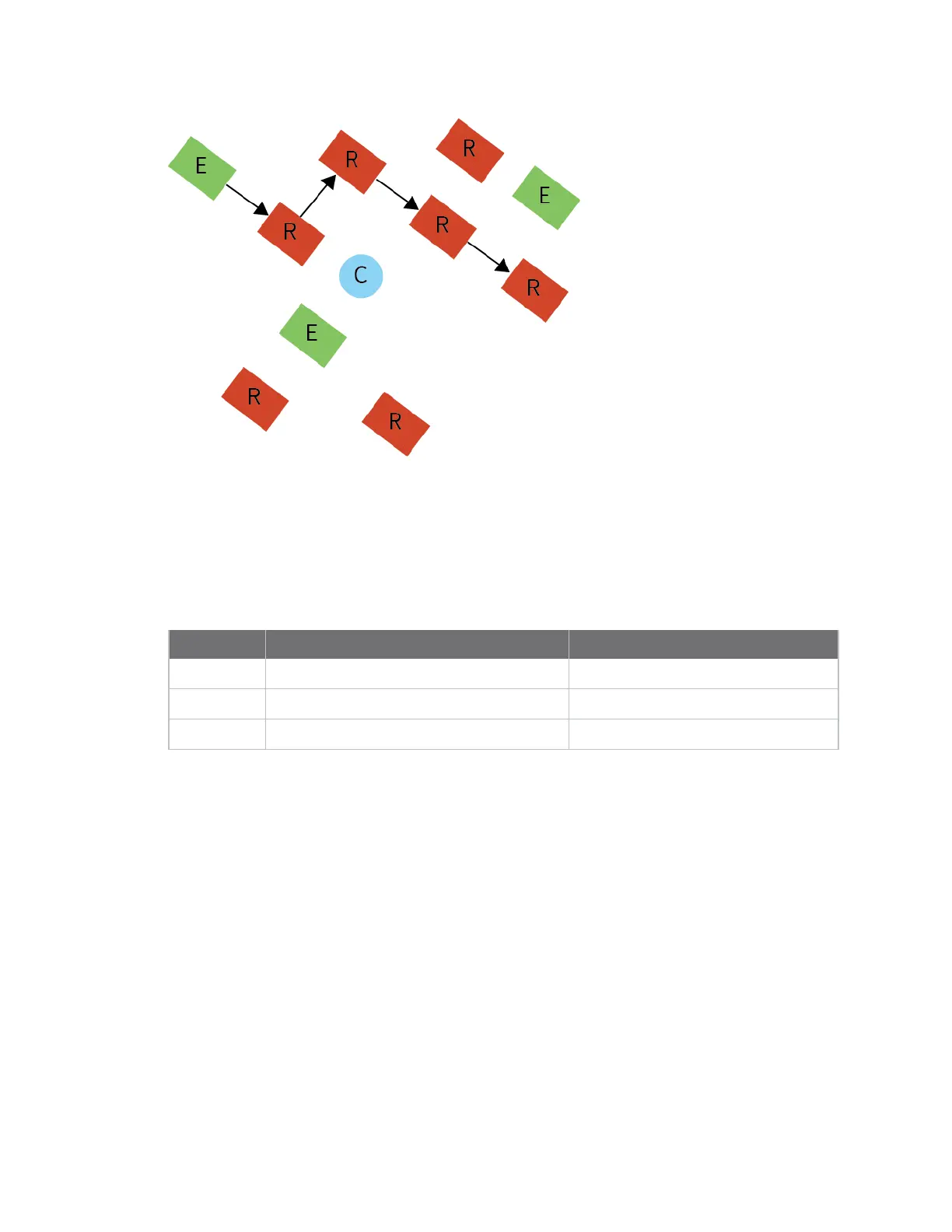
The following graphic is a sample route request (broadcast) transmission where R3 is trying to
discover a route to R6:
 Loading...
Loading...