Transmission, addressing, and routing Data transmission
Digi XBee® 3 Zigbee® RF Module
97
Broadcast transmissions
Broadcast transmissions within the Zigbee protocol are intended to be propagated throughout the
entire network such that all nodes receive the transmission. To accomplish this, the coordinator and
all routers that receive a broadcast transmission retransmits the packet three times.
Note When a router or coordinator delivers a broadcast transmission to an end device child, the
transmission is only sent once (immediately after the end device wakes and polls the parent for any
new data). For more information, see Parent operation.
Each node that transmits the broadcast also creates an entry in a local broadcast transmission table.
This entry to keeps track of each received broadcast packet to ensure the packets are not
transmitted endlessly. Each entry persists for 8 seconds, and the broadcast transmission table holds 8
entries, effectively limiting network broadcast transmissions to once per second.
For each broadcast transmission, the Zigbee stack reserves buffer space for a copy of the data packet
that retransmits the packet as needed. Large broadcast packets require more buffer space. Users
cannot change any buffer spacing; information on buffer space is for general knowledge only. The
XBee 3 Zigbee RF Module handles buffer spacing automatically.
Since each device in the network retransmits broadcast transmissions, use broadcast messages
sparingly to avoid network congestion.
Unicast transmissions
Unicast transmissions are sent from one source device to another destination device. The destination
device could be an immediate neighbor of the source, or it could be several hops away. Unicast
transmissions sent along a multiple hop path require some means of establishing a route to the
destination device. For more information, see RF packet routing.
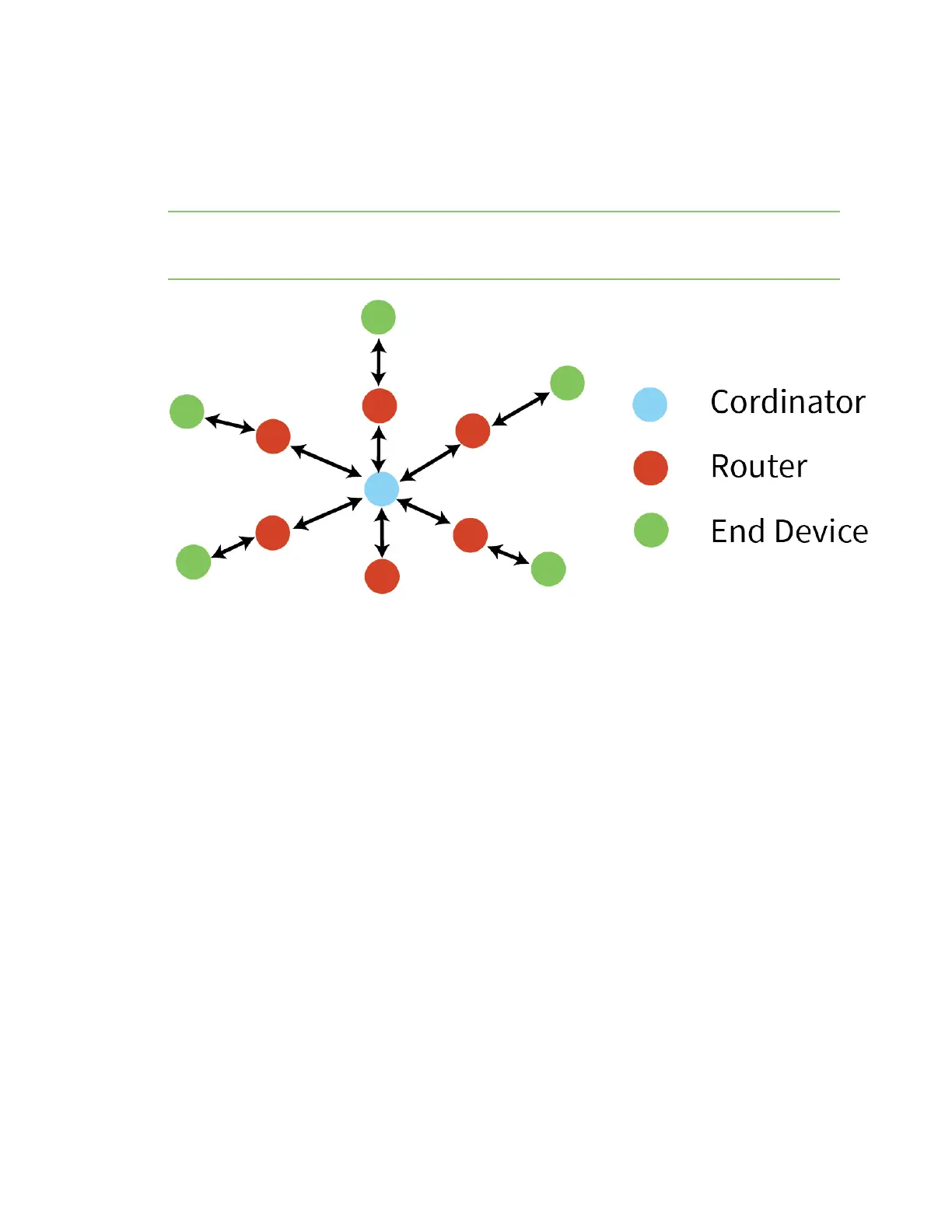
Address resolution
Each device in a Zigbee network has both a 16-bit (network) address and a 64-bit (extended) address.
The 64-bit address is unique and assigned to the device during manufacturing, and the 16-bit address
is obtained after joining a network. The 16-bit address can also change under certain conditions.
When sending a unicast transmission, the Zigbee network layer uses the 16-bit address of the
destination and each hop to route the data packet. If you do not know the 16-bit address of the
 Loading...
Loading...