Zigbee networks The Zigbee specification
Digi XBee® 3 Zigbee® RF Module
74
The Zigbee specification
Zigbee is an open global standard for low-power, low-cost, low-data-rate, wireless mesh networking
based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It represents a network layer above the 802.15.4 layers to
support advanced mesh routing capabilities. The Zigbee specification is developed by a consortium of
companies that make up the Zigbee Alliance. For more information, see zigbee.org.
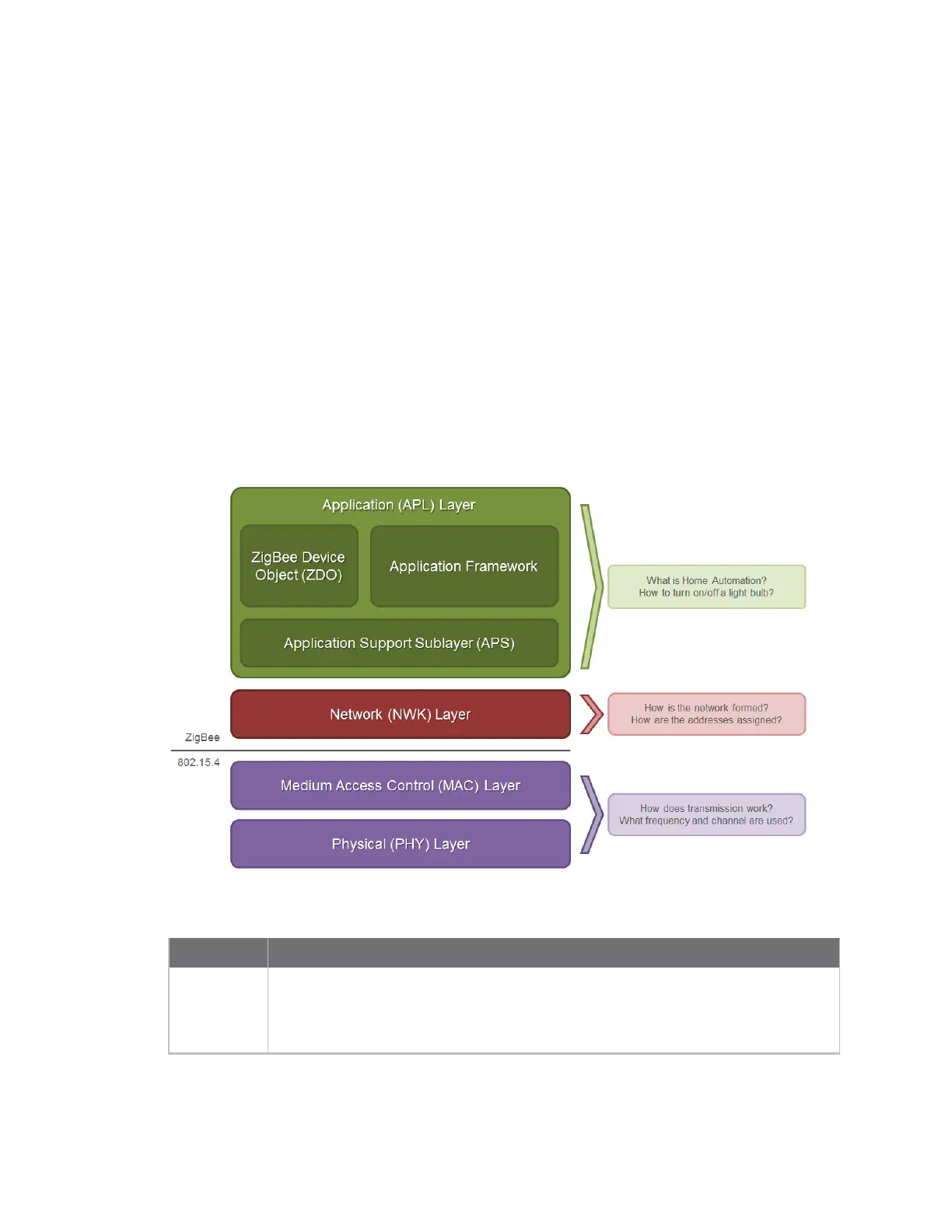
Zigbee stack layers
Most network protocols use the concept of layers to separate different components and functions
into independent modules that can be assembled in different ways.
Zigbee is built on the Physical (PHY) layer and Medium Access Control (MAC) sub-layer defined in the
IEEE 802.15.4 standard. These layers handle low-level network operations such as addressing and
message transmission/reception.
The Zigbee specification defines the Network (NWK) layer and the framework for the application (APL)
layer. The Network layer takes care of the network structure, routing, and security. The application
layer framework consists of the Application Support sub-layer (APS), the Zigbee device objects (ZDO)
and user-defined applications that give the device its specific functionality.
This table describes the Zigbee layers.
Zigbeelayer Descriptions
PHY Defines the physical operation of the Zigbee device including receive sensitivity,
channel rejection, output power, number of channels, chip modulation, and
transmission rate specifications. Most Zigbee applications operate on the 2.4 GHz
ISM band at a 250 kb/s data rate. See the IEEE 802.15.4 specification for details.
 Loading...
Loading...