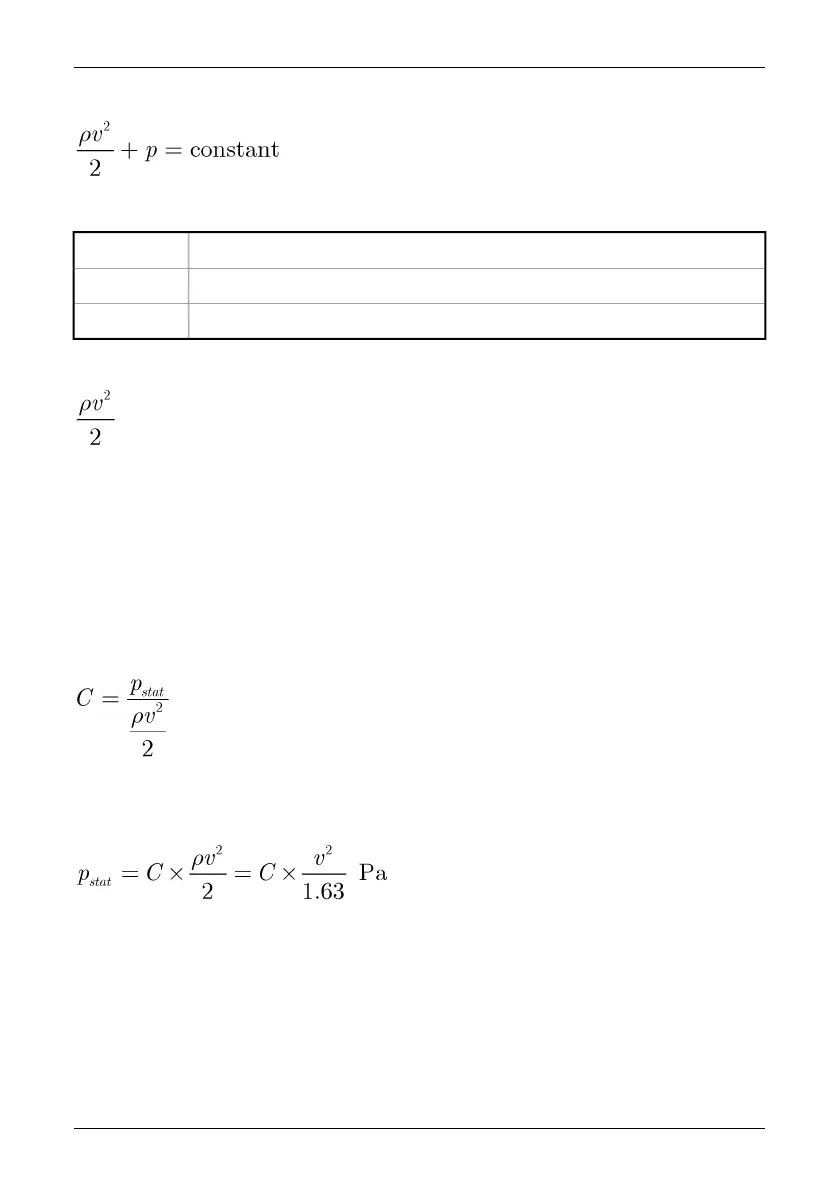
In a steady wind flow, Bernoulli’s Law applies:
where:
Air density in kg/m
3
ρ
Wind velocity in m/sv
Static pressure in Pap
and where:
denotes the dynamic pressure and p the static pressure. The total of these pressures
gives the total pressure.
Wind load against a surface makes the dynamic pressure become a static pressure
against the surface. The magnitude of this static pressure is determined by, amongst
other things, the shape of the surface and its angle to the wind direction.
The portion of the dynamic pressure that becomes a static pressure on the surface
(p
stat
) is determined by what is known as a stress concentration factor:
If ρ is 1.23 kg/m
3
(density of air at +15°C (+59°F)), this gives the following local
pressures in the wind flow:
160 Publ. No. 1558792 Rev. a460 – ENGLISH (EN) – July 1, 2010
27 – Introduction to building thermography

 Loading...
Loading...