output current since they may cause larger measurement errors or, in the worst case, they may be damaged.
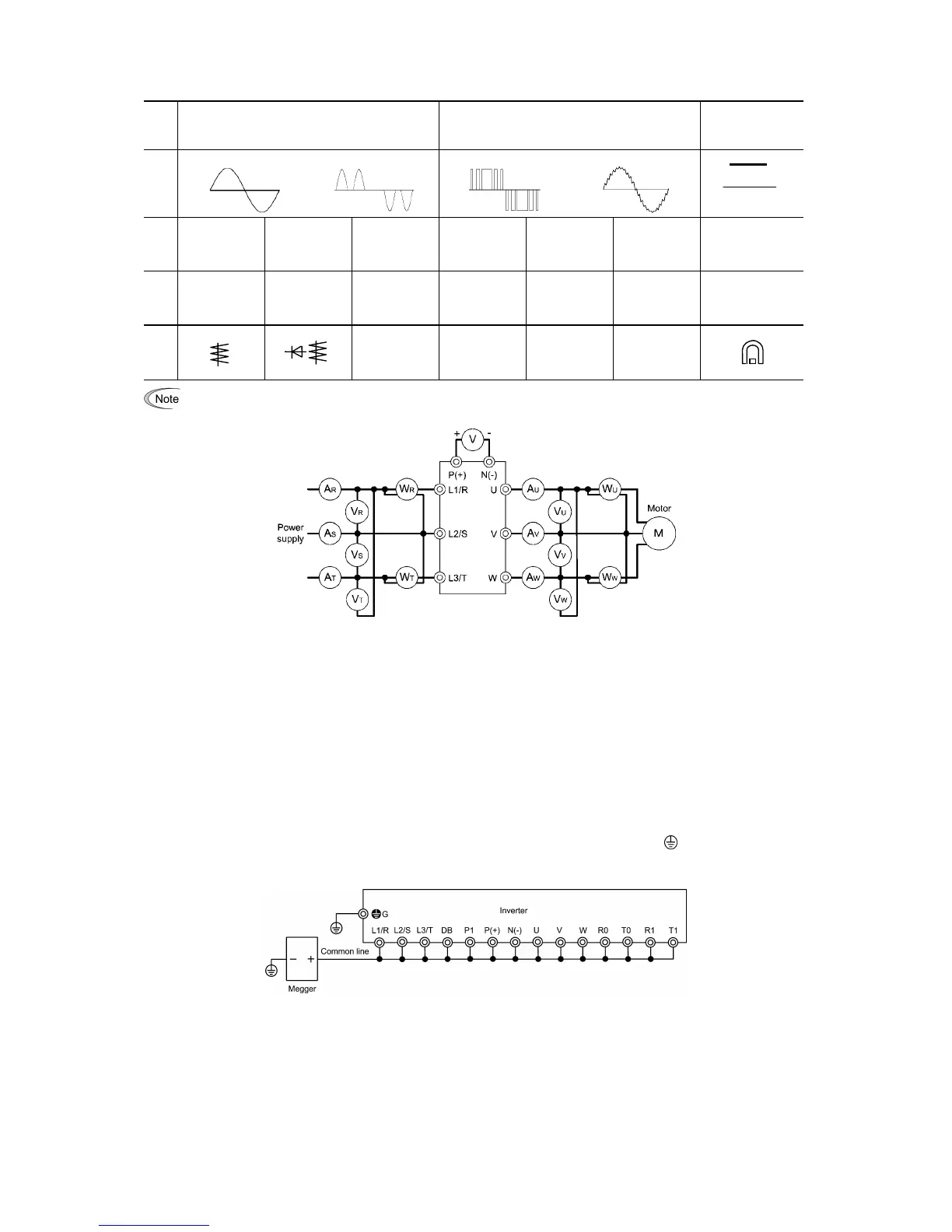
Figure 7.1 Connection of Meters
7.5 Insulation Test
Since the inverter has undergone an insulation test before shipment, avoid making a Megger test at the customer's site.
If a Megger test is unavoidable for the main circuit, observe the following instructions; otherwise, the inverter may be damaged.
A withstand voltage test may also damage the inverter if the test procedure is wrong. When the withstand voltage test is
necessary, consult your Fuji Electric representative.
(1)
Megger test of main circuit
1) Use a 500 VDC Megger and shut off the main power supply without fail before measurement.
2) If the test voltage leaks to the control circuit due to the wiring, disconnect all the wiring from the control circuit.
3) Connect the main circuit terminals with a common line as shown in Figure 7.2.
4) The Megger test must be limited to across the common line of the main circuit and the ground (
).
5) Value of 5 MΩ or more displayed on the Megger indicates a correct state. (The value is measured on an inverter alone.)
Figure 7.2 Main Circuit Terminal Connection for Megger Test
(2) Insulation test of control circuit
Do not make a Megger test or withstand voltage test for the control circuit. Use a high resistance range tester for the control
circuit.
1) Disconnect all the external wiring from the control circuit terminals.
2) Perform a continuity test to the ground. One MΩ or a larger measurement indicates a correct state.
(3) Insulation test of external main circuit and sequence control circuit
Disconnect all the wiring connected to the inverter so that the test voltage is not applied to the inverter.

 Loading...
Loading...











