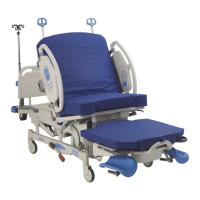
Electrical System
Chapter 3: Theory of Operation
Affinity® Four Birthing Bed Service Manual (195826 REV 2) 3 - 3
3
CONTROL BOARD
The bed is operated by a logic control P.C. board. This unit controls the electrical functions of the bed:
hilow, head section, foot section, night light, and optional air system.
AC Input Power
The control board is powered via connector P2, pins 1 and 3, while the bed is plugged into wall power.
The typical voltage between these two pins is 25 V AC, 50/60 Hz. This power is provided by an isolation
step down transformer. The voltage here at no load and 120 V, 60 Hz is typically 25.4 V AC. Positive
Temperature Coefficient (PTC) fuses, RT3 and RT4, are used for transformer overcurrent protection.
These PTC fuses could trip anywhere between 10 to 20 Arms. These PTC fuses are sized to protect the
transformer and any downstream overload or shorts without nuisance tripping during the bed's normal
operation.
DC Input Power
Two 12 V, 7.0 Ah batteries connected in series are provided at connector P5, pins 1 and 2, as backup
power for bed articulation and nurse call function. Externally, there is a 10 A fuse between the batteries.
PTC fuses RT1 and RT8 provide additional overcurrent protection. The typical current draw on the
battery during sleep mode is approximately 0.35 mAdc.
AC to DC Power Conversion
The full wave bridge diode, BR1, and bulk capacitors C5 and C6 make up the linear power supply that
converts AC power to DC power. The two 1K-ohm resistors are used to discharge the bulk capacitors
when AC power is removed. This DC power is named Vmot. The voltage range is approximately 20 to 40
V DC depending on the line voltage and load current.
Power Control
The main control relay, K2, supplies DC power to the motor and main logic regulators from either Vmot
or Vbat_p (protected battery). This relay coil is powered directly by the battery. Only in the energized
state can the relay supply battery power to the motors. Basic operation of the main control relay is:
when AC power is available relay K2 is de-energized and supplies Vmot to the board. When AC power is
not available and relay K2 is de-energized, the only power being drawn from the battery is U40, the
siderail logic regulator. The current draw on the battery during sleep mode is approximately 0.35 mAdc.
In this sleep mode, siderail LEDs are not illuminated but the rest of the siderail circuits are energized.
When the caregiver or patient presses the correct siderail control, or the trend-like position handle, a
wakeup signal is sent. If AC power is not available, the wakeup signal sets the flip-flop, U19, and
energizes relay K2, which powers up the control board. The relay will remain active until the wakeup
signal goes low and the sleep timer, U1 and U12, expires. Approximately 3.7 minutes after releasing the
siderail control. The current draw on the battery during the awake mode is approximately 0.25 Adc. The
AC Detect circuit monitor the transformer secondary, “VAC+”, and will show no AC at 19.8 vrms. AC is
active at 20vrms and greater.
 Loading...
Loading...