Electrical System
Chapter 3: Theory of Operation
Affinity® Four Birthing Bed Service Manual (195826 REV 2) 3 - 5
3
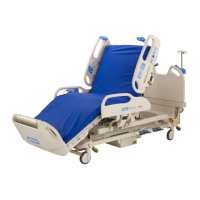
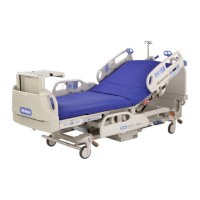
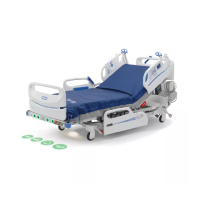
Articulation Lockout Control
Connector P3 links the lockout control to the control board. Pins 1 and 3 of connector P3 carry all the
motor current and these are the pins that are controlled by the lockout control. So the lockout control
disconnects all power to the motor supervisory relay. When activated this control also activates the
siderail lockout LEDs.
Motor Drivers
The lockout control provides motor power to the supervisory relay, K4. The supervisory relay supplies
power to the head, hilow, and foot motor relays. The supervisory relay is activated whenever a motor
function is requested to operate as a safety for individual motor relay failures. Each motor has two relays,
one for up and one for down. The contacts for the two relays are set up in an H-bridge fashion with the
motor coil grounded when the relays are de-energized. This aids dynamic motor braking. A set of four
motor coil recirculation diodes are provided to protect the relay contacts as they are switching. In
general, the individual motor relays turn on approximately 40 milliseconds before the supervisory relay.
The motor and supervisory relays turn off at about the same time.
The hilow motor uses a smart FET to turn on and off the hilow motor. This was necessary to keep the
relay contacts from sticking due to the high load current of this motor. The smart FET, U39, turns on last
and off first, keeping the switching loads out of the relays.
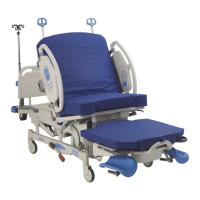
Hilow And Foot Position Limits
The hilow and foot position limits are necessary to keep the foot and hilow mechanisms from crashing
into each other during articulation. The foot and hilow motors have internal potentiometers with wiper
outputs that correspond to the actuator stroke. These potentiometer outputs are fed into some opamp
buffers which then feed into comparators to generate actuator stroke limits. The buffers are necessary
to isolate the noisy potentiometers from the noise sensitive high speed comparators. The on-board trim
potentiometers and the resistor strings provide voltage reference adjustments for the actuator stroke
limits. Upper and lower limit LEDs are provided for ease of adjustment.
Potentiometer R8 controls LBD2 (limit bed down 2). This limit, LBD2, stops the hilow down motion when
the foot section is at it lower limit. LBD2 is measured from the floor to the flattened seat section and is
23.00-23.50 inches (584.2-596.9 mm). Upper and lower limit LEDs are provided for ease of adjustment
Complex Programmable Logic Device (CPLD), U9, Functions:
1. Acts as master for SPI communications between itself and both siderail caregiver boards. It
generates the clock and shift/load signals to collect and shift the 32 bits of input control data from
each rail. This 32 bit stream is identical from each rail and is “or”-ed together in the CPLD. The stream
is fed into a 32 bit serial to parallel shift register. Each shift register output is latched into a flip-flop
using the shift/load signal. These flip-flop outputs represent a control on the siderail.
2. Receives inputs from Pendant controls and Trend-like position handle switches. These signals are
direct and mix with the limit logic in order to run the articulation motors.
 Loading...
Loading...