12.4 Formulae
201
RMS current I (A rms)
Single-phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single-phase 3-wire
1P3W
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W2M
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W3M
Three-phase 4-wire
3P4W
I1
I4
I1
I2
I4
I1
I2
I4
I1
I2
I3
I4
I1
I2
I3
I4
• Calculate RMS current about once every 10 cycles at 50 Hz and every 12 cycles at 60 Hz with a single
wave (256 points).
• The RMS current for CH4 can be calculated regardless of the connection method.
c: measured channel M: number of samples s: number of sampling points
Ic
1
M
-----
Ics()
2
S0=
M1–
∑
=
ave
1
2
---
I1 I2+()=
Iave
2
---
I1 I2+()=
Iave
3
---
I1 I2 I3++()=
ave
3
---
I1 I2 I3++()=
Active power P (W)
Single-phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single-phase 3-wire
1P3W
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W2M
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W3M
Three-phase 4-wire
3P4W
P1 P1
P2
P1
P2
P1
P2
P3
P1
P2
P3
• Calculate active power about once every 10 cycles at 50 Hz or every 12 cycles at 60 Hz with a single
wave (256 points).
• For three-phase 3-wire 3M and three-phase 4-wire connections, use phase-to-neutral voltage as the volt-
age waveform Ucs.
Three-phase 3-wire 3M: U1s = (U1s - U3s)/3, U2s = (U2s - U1s)/3, and U3s = (U3s - U2s)/3
• Polarity symbols for active power P indicate the power direction when power is being consumed (+P) and
when power is being regenerated (-P).
c: measured channel M: number of samples s: number of sampling points
Pc
1
M
-----
Ucs Ics×()
S0=
∑
=
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
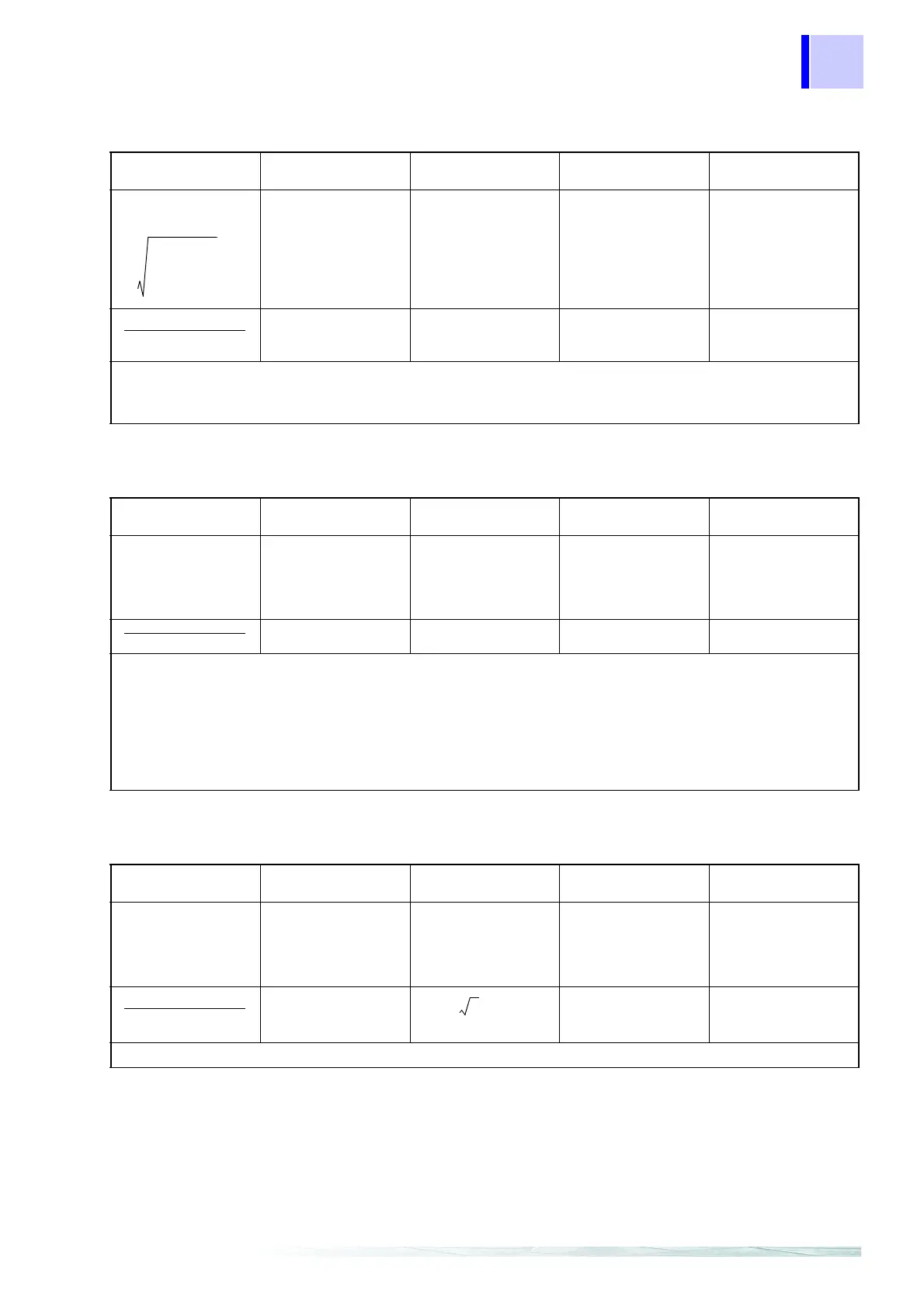
Apparent power S (VA)
Single-phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single-phase 3-wire
1P3W
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W2M
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W3M
Three-phase 4-wire
3P4W
S1
(When P>, make P =
S.)
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S3
S1
S2
S3
• For three-phase 3-wire 3M and three-phase 4-wire connections, use phase-to-neutral voltage for Uc.
c: measured channel M: number of samples s: number of sampling points
×
1
2
Ssum
3
2
-------
S1 S2+()=
1
2
3
1
2
3
 Loading...
Loading...