Appendix
220
Harmonics phase angle and harmonic phase difference
The harmonic voltage phase angle and harmonic current phase angle
are the standard for the PLL source phase (for input based on PLL
when U1, U2, or U3 is selected on this device) fundamental wave
component.
The differences in phase of each harmonic order component and the
phase of the fundamental wave component is expressed as an angle
(
°) and - indicates a LAG, whereas + indicates a LEAD.
The harmonic voltage-current phase difference expresses the differ-
ence between the phase of each harmonic voltage component and the
phase of each harmonic current component of each channel as an
angle (
°).
The sum is the total power factor of each harmonic order (calculated
from the total harmonic power and the total harmonic reactive power)
expressed as an angle (
°). When the harmonic voltage-current phase
difference is between -90
° and +90°, the harmonic order is flowing in
the direction of the load. When it is between +90
° and +180° or -90°
and -180°, the harmonic order is flowing away from the load.
K Factor
Shows the power loss caused by the harmonic current in transformers.
Also referred to as the “multiplication factor.” The K factor (KF) is for-
mulated as shown below:
k: Order of harmonics
Ik: Ratio of the harmonic current to the funda-
mental wave current [%]
Higher-order harmonic currents have a greater influence on the K fac-
tor than lower-order harmonic currents.
Purpose of mea-
surement
To measure the K factor in a transformer when subjected to maximum
load. If the measured K factor is larger than the multiplication factor of
the transformer used, the transformer must be replaced with one with
a larger K factor, or the load on the transformer must be reduced. The
replacement transformer should have a K factor one rank higher than
the measured K factor for the transformer being replaced.
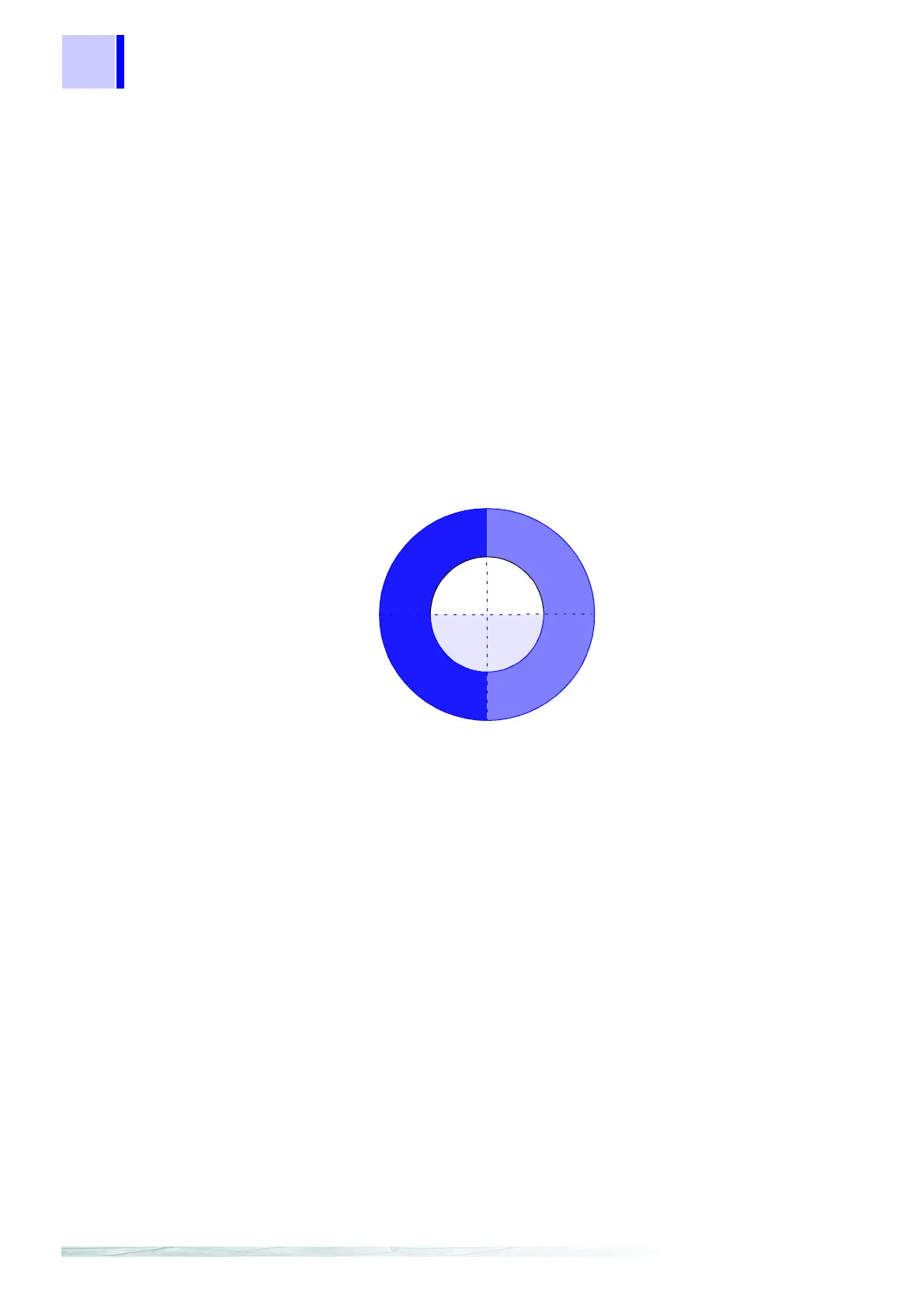
0°
90°
-90°
±180°
Harmonic phase angle
Voltage and
current phase
difference
e
Out-
flow
Inflow
LEAD
LAG
Voltage and
current phase
angles
KF
k
2
I
k
×
2
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
k2=
50
∑
I
k
2
k2=
50
∑
-----------------------------------------=
 Loading...
Loading...