25
The IP voice traffic received on a WAN interface is forwarded through the CPU on the MPU
to SIC-2BSV, where the traffic is decompressed and sent to the TE device.
• When a BSV interface operates in user mode, traffic is processed as follows:
The digital voice traffic received from the B channels on the BSV interface is decompressed
and forwarded through the CPU on the MPU to a local FXS or FXO analog voice interface.
The voice signals received on the local FXS or FXO analog voice interface are processed
by VoIP and forwarded through the CPU on the MPU to the SIC-2BSV. The SIC-2BSV
decompresses the traffic and sends the traffic out of the BSV interface to the ISDN switch.
• Working in conjunction with the FXS or FXO analog voice interface modules, SIC-2BSV
provides flexibility in voice call routing.
• The ISDN BRI D channel signaling is processed separately on the CPU.
• A BSV interface can be connected to an ISDN phone to supply power to the phone.
• The SIC-2BSV is dedicated to voice applications.
Interface specifications
Table 43 Interface specifications
Connector RJ-45
Number of connectors 2
Interface standard ITU-T I.430, Q.921, Q.931
Interface rate 192 Kbps
Cable ISDN S interface cable
Supported service Voice access over ISDN S interface cable
Interface LEDs
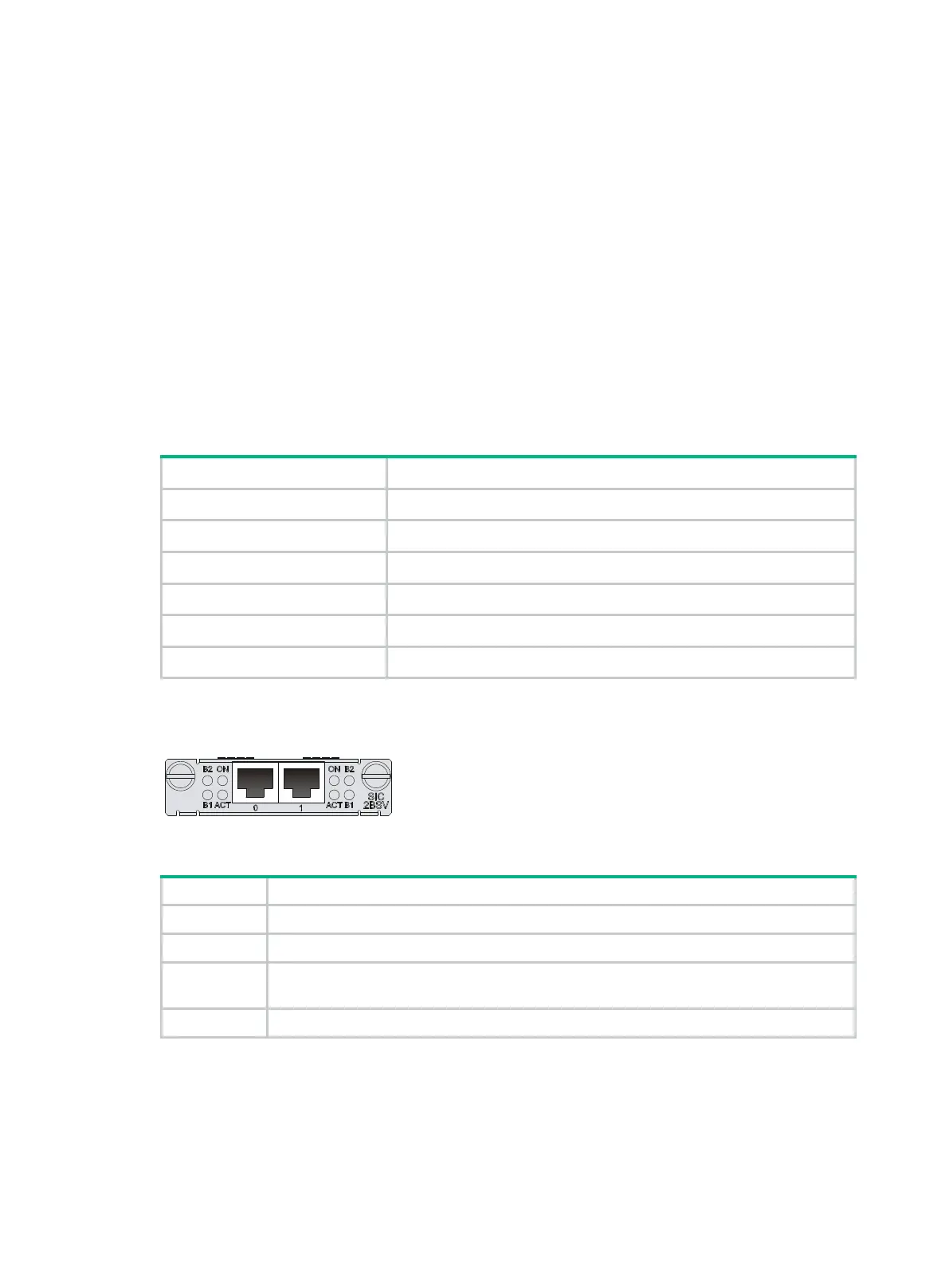
Figure 31 SIC-2BSV panel
Table 44 LED description
B1 Flashing indicates data is being transmitted or received on the B1 channel.
B2 Flashing green indicates data is being transmitted or received on the B2 channel.
ACT
• Flashing yellow indicates the link is being activated.
• Steady green indicates the link is active.
On Steady green indicates the module is powered on.
Interface cables and connection methods
For more information about BSV interface cables and connection methods, see "BSV/BSE
interface."

 Loading...
Loading...




