9-13
INTERRUPT CONTROL UNIT
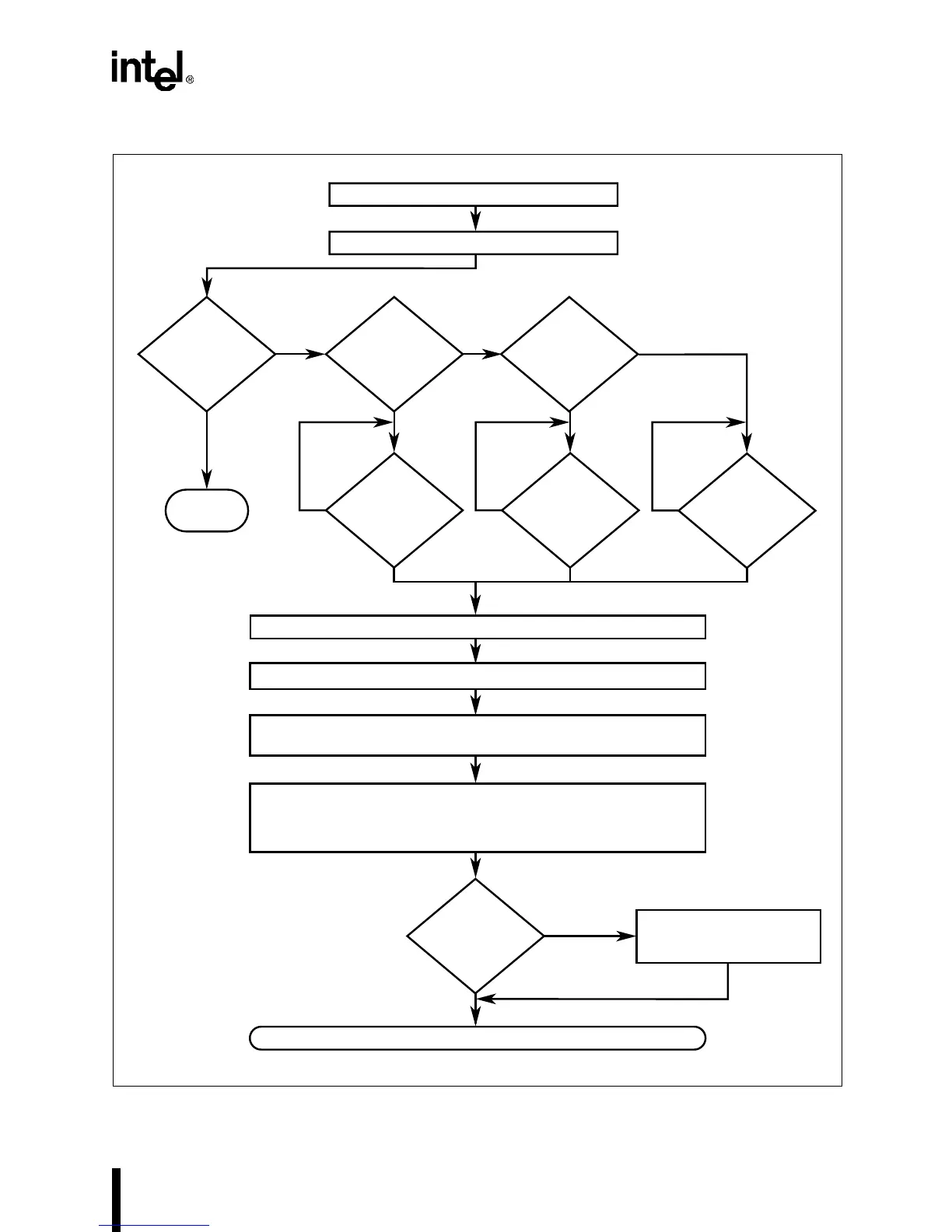
Figure 9-5. Interrupt Process – Master Request from Slave Source
A2429-02
Master receives IR2 interrupt request.
Master sets its IR2 pending bit.
Master sends request to CPU. CPU initiates interrupt acknowledge cycle.
Master clears IR2 pending bit and sets IR2 in-service bit.
Slave clears its pending bit, sets its in-service bit, and puts its interrupt
vector number on the bus.
The CPU uses its operating mode and the interrupt vector number to find
the interrupt service routine's address. The CPU processes the interrupt.
Interrupt routine sends an EOI command to the slave, clearing its IR2
in-service bit
An interrupt return instruction is issued, ending the interrupt process.
Interrupt routine sends an
EOI command to the master,
clearing its IR2 in-service bit.
Does
slave have
other
in-service bits
set?
Is
request
enabled?
Is
special
mask mode
enabled?
Is
the
IR2 in-service
bit
set?
End
Yes No No
YesYesNo
Yes No No
YesYesNo
Is
request
higher level
than any set
in-service
bits?
Is
request
equal or higher
than any set
in-service
bits?
(operating in
fully nested
mode)
Yes
No
Is master
operating in
special-fully
nested
mode?
 Loading...
Loading...











