14-3
CHIP-SELECT UNIT
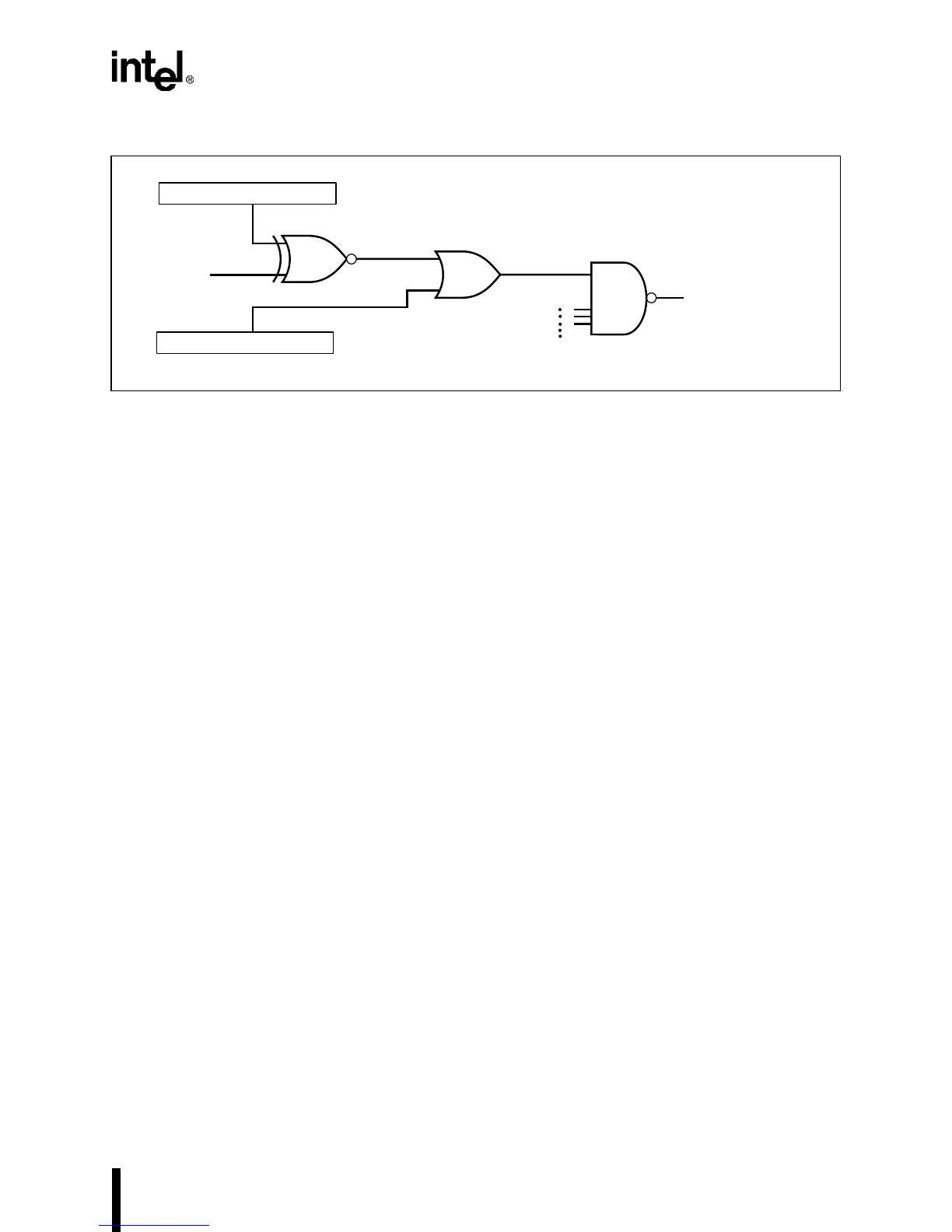
Figure 14-1. Channel Address Comparison Logic
The lower address bits are excluded from address comparisons (only 15 bits are compared). For
memory addresses which have 26-bit addresses, the minimum channel address block size is 2
Kbytes; for I/O addresses with 16-bit addresses, the minimum channel address block size is 2
bytes.
NOTE
The starting address of any channel address block must be a multiple of the
block size. For example, a 256 Kbyte block can only start at an address that is
a multiple of 256 Kbytes (0H, 4000H, 8000H, etc.).
Because you can set ones in the channel mask to exclude certain address bits from comparisons,
you can increase the size of a channel’s address block (by powers of 2 in Kbytes for memory ad-
dresses and by powers of 2 in bytes for I/O addresses). Figure 14-2 illustrates how memory ad-
dress block sizes are determined from the channel’s mask; the concept is the same for I/O address
block sizes (replace Kbyte with byte). As shown in Figure 14-2, the bit location of the right-most
zero in the channel mask determines the channel’s active address block size.
A2533-01
15-bit Channel Address
15-bit Channel Mask
Address
bit
x
bit
x
bit
x
Chip-select
Channel Output
 Loading...
Loading...











