10-29
TIMER/COUNTER UNIT
You can interleave reads and writes of the same counter; for example, if the counter is pro-
grammed for the two-byte read/write selection, the following sequence is valid.
1. Read least-significant byte.
2. Write new least-significant byte.
3. Read most-significant byte.
4. Write new most-significant byte.
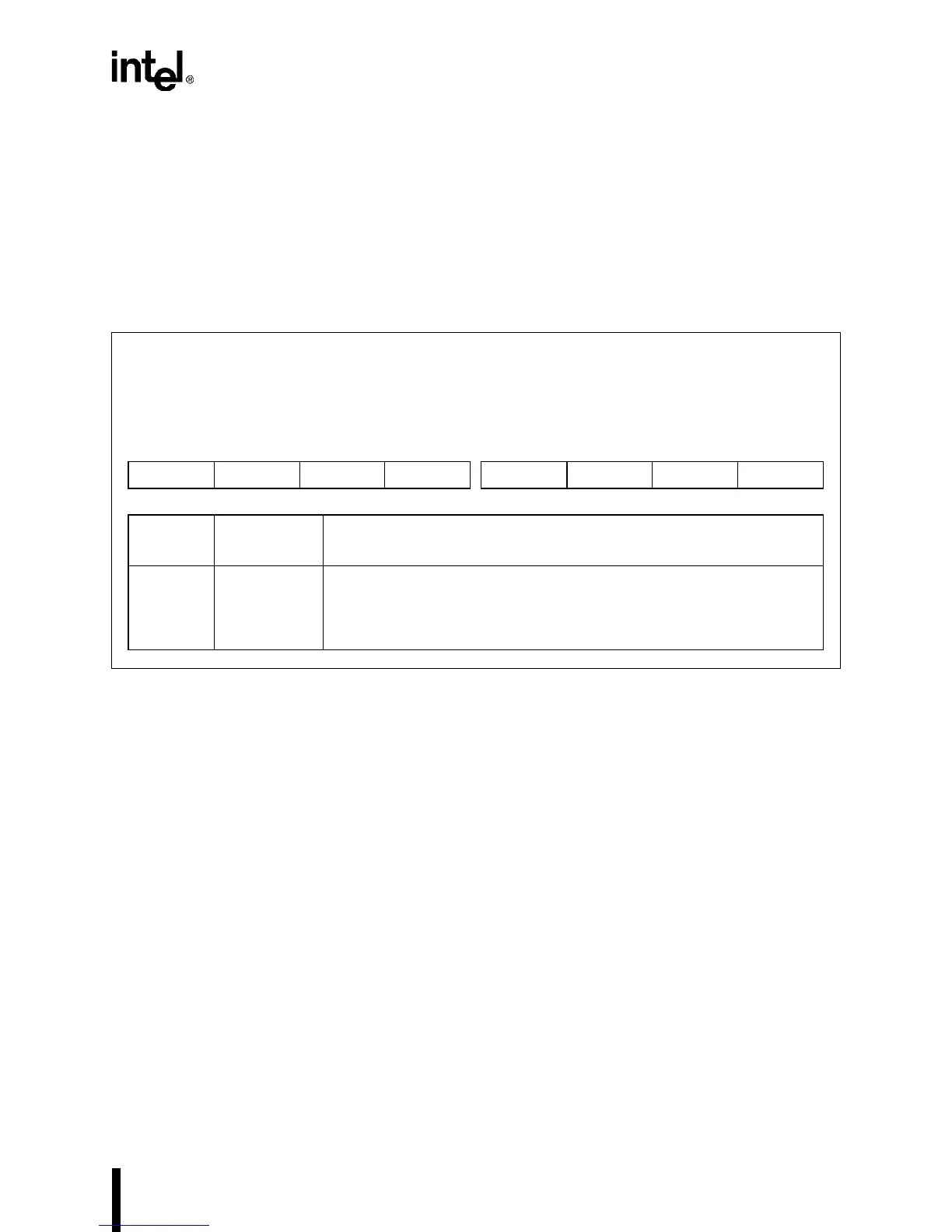
Figure 10-28. Timer
n
Register (TMR
n
– Read Format)
Timer
n
(Read Format)
TMR
n
(
n
= 0–2)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
F040H, F041H
F042H
0040H, 0041H
0042H
XXH
7 0
CV7 CV6 CV5 CV4 CV3 CV2 CV1 CV0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7–0 CV7:0 Count Value:
These bits contain the counter’s count value. When reading the
counter’s count value, follow the read selection specified in the counter’s
control word.
 Loading...
Loading...











