12-11
DMA CONTROLLER
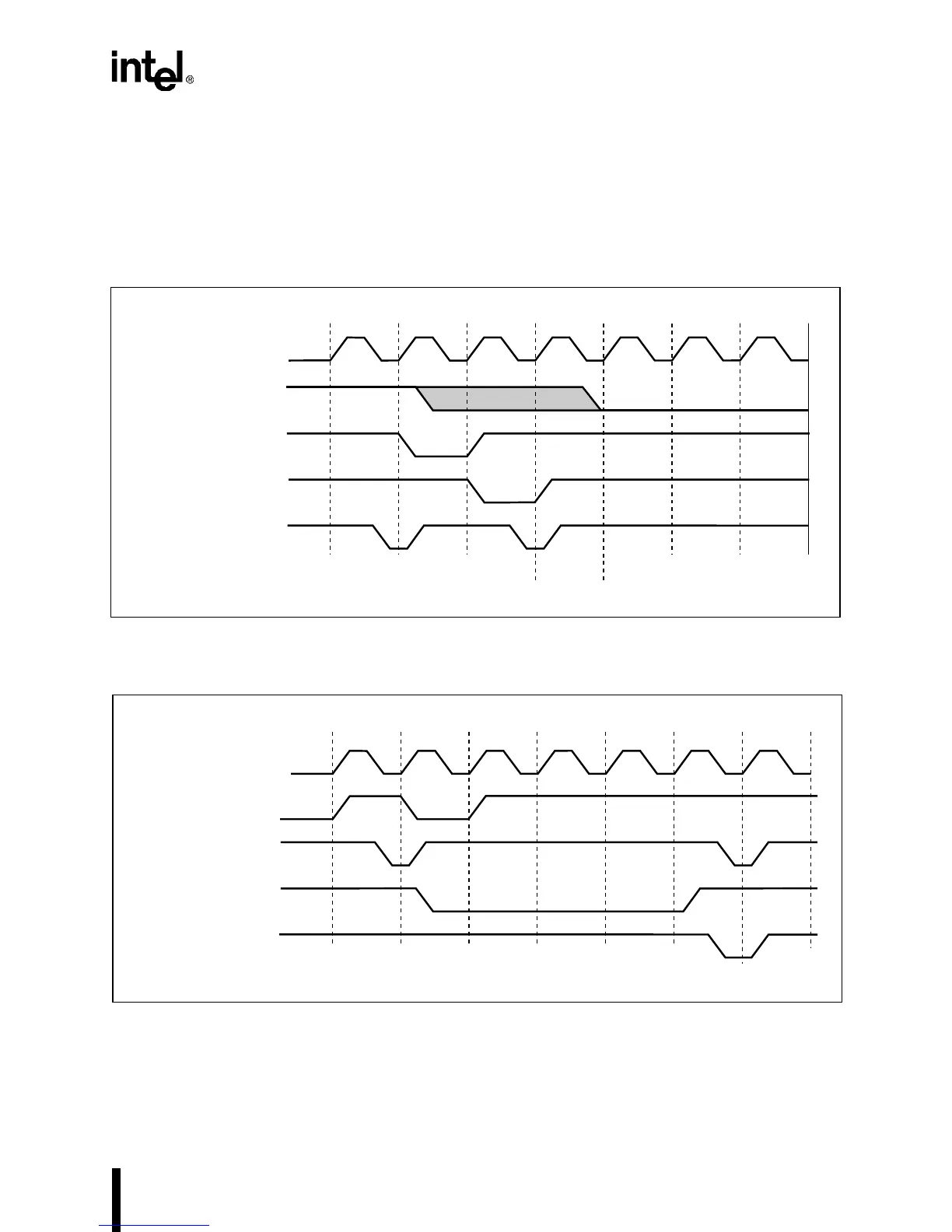
Terminating a buffer transfer by deasserting DREQn can also be done either synchronously or
asynchronously. The effect is identical to that of synchronous or asynchronous sampling of
EOP#. When DREQn is used to terminate a DMA transfer in asynchronous mode, DREQn must
be sampled inactive one CLKOUT before READY#. In synchronous mode it must be sampled
inactive at the same time as READY#. When DREQn is sampled active in either of the above
cases another DMA cycle is executed (depending on operating mode).
Figure 12-6. Buffer Transfer Ended by an Expired Byte Count
Figure 12-7. Buffer Transfer Ended by the EOP# Input
A2483-02
CLKOUT
DRQ
n
ADS#
EOP#
(As an output)
READY#
T2 T2 T
x
T
x
T1 Ti T
x
DMA Cycle
x
Cycle
A2482-02
CLKOUT
ADS#
READY#
EOP# (Async)
EOP# (Sync)
T2 T2T2 T2T1
Ti
T2
DMA Cycle

 Loading...
Loading...











