1220
Text String Processing Instructions Section 3-33
3-33 Text String Processing Instructions
This section describes instructions used to manipulate text strings.
3-33-1 Text String Processing Overview
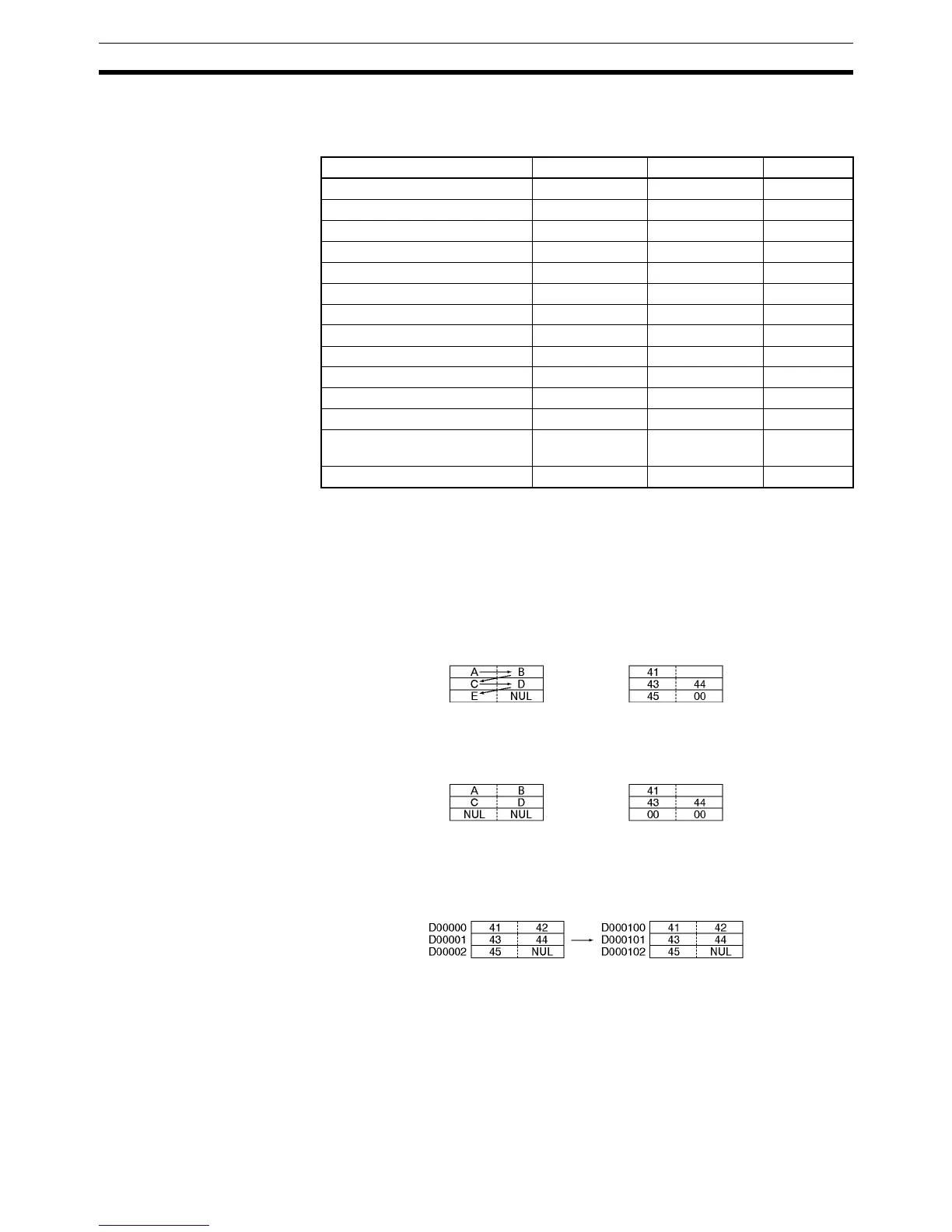
Data from the beginning until a NUL code (00 hex) is handled as text string
data expressed in ASCII (except for 1-byte, special characters). It is stored
from leftmost to rightmost bytes, and from rightmost to leftmost words.
When there is an odd number of characters, 00 hex (NUL code) is stored in
the available space in the rightmost byte of the final word.
When there is an even number of characters, 0000 hex (two NUL codes) is
stored in the leftmost and rightmost bytes of the word following the final word.
As shown in the following diagram, a text string can be specified by simply
designating the first word of that string. The text string data up until the next
NUL code (00 hex) will then be handled as a single block of ASCII data.
Text string processing instructions can be used to execute at a PLC the vari-
ous kinds of text string processing (product data, and so on) that used to be
executed at the host computer.
Instruction Mnemonic Function code Page
MOV STRING MOV$ 664 1221
CONCATENATE STRING +$ 656 1223
GET STRING LEFT LEFT$ 652 1226
GET STRING RIGHT RGHT$ 653 1228
GET STRING MIDDLE MID$ 654 1230
FIND IN STRING FIND$ 660 1233
STRING LENGTH LEN$ 650 1235
REPLACE IN STRING RPLC$ 661 1237
DELETE STRING DEL$ 658 1240
EXCHANGE STRING XCHG$ 665 1242
CLEAR STRING CLR$ 666 1245
INSERT INTO STRING INS$ 657 1246
String Comparison Instructions =$, <>$, <$, <=$,
>$, >=$
670 to 675 1250
WRITE TEXT FILE TWRIT 704 1255
=
Example: Text string ABCDE
42
42
=
Example: Text string ABCD
Example: MOV$ D00000 D00100

 Loading...
Loading...











