835
Subroutines Section 3-19
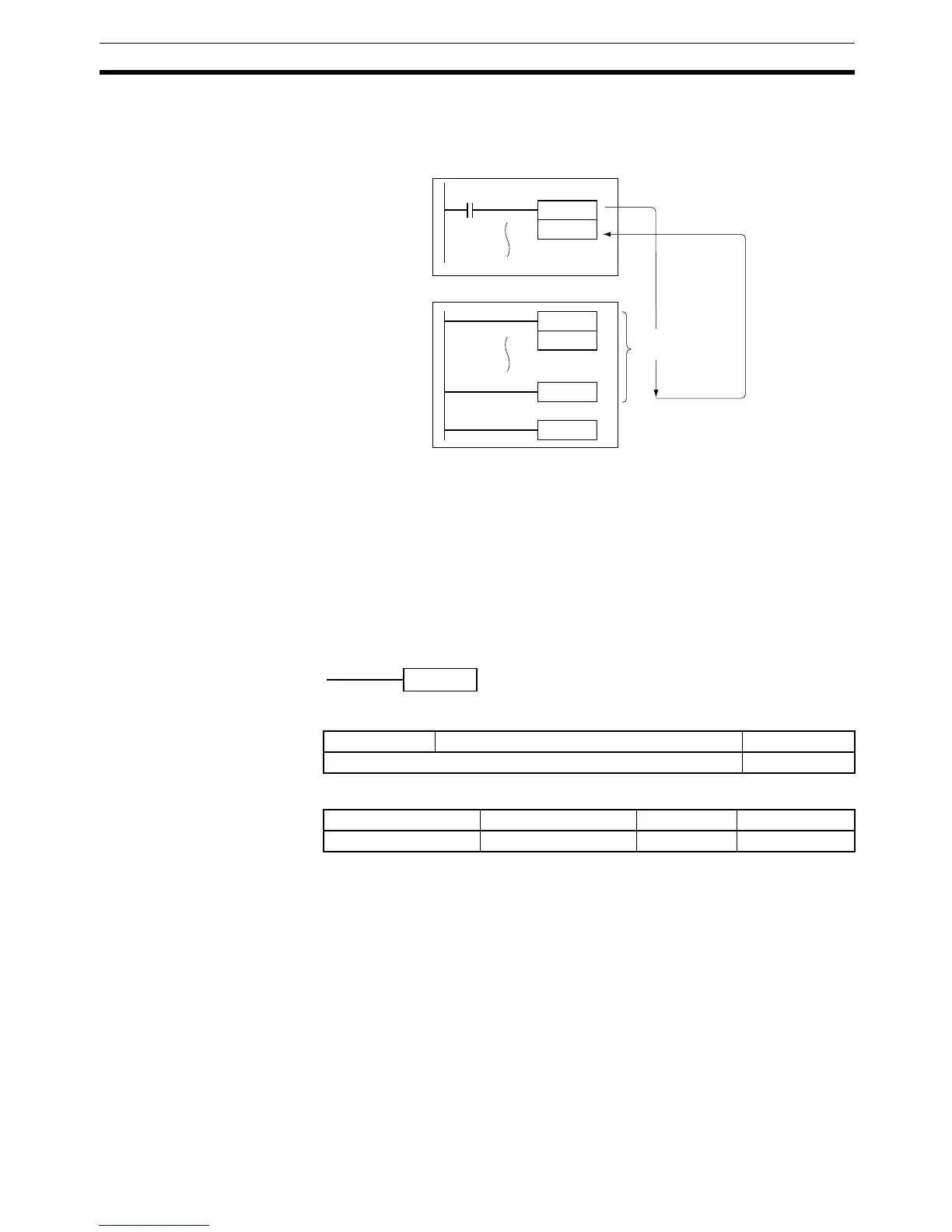
Example When CIO 000000 is ON in the following example, global subroutine 10 is
executed and program execution returns to the next instruction after the
GSBS(750) instruction that called the subroutine.
3-19-7 GLOBAL SUBROUTINE RETURN: GRET(752)
Purpose Indicates the end of a subroutine program. Used in combination with
GSBN(751) to define a subroutine region.
This instruction is supported by CS1-H, CJ1-H, CJ1M, and CS1D CPU Units
only.
GRET(752) is used in combination with GSBS(750) and GSBN(751), the
GLOBAL SUBROUTINE CALL and GLOBAL SUBROUTINE ENTRY instruc-
tions.
Ladder Symbol
Variations
Applicable Program Areas
Description GRET(752) indicates the end of a global subroutine and GSBN(751) indicates
the beginning of a global subroutine. See
3-19-6 GLOBAL SUBROUTINE
ENTRY: GSBN(751)
for more details on the operation of global subroutines.
When program execution reaches GRET(752) it is automatically returned to
the next instruction after the GSBS(750) instruction that called the global sub-
routine.
Precautions When the subroutine is not being executed, the instructions are treated as
NOP(000).
Example See
3-19-6 GLOBAL SUBROUTINE ENTRY: GSBN(751) for examples of the
operation of GRET(752).
GSBS
#10
000000
GSBN
#10
GRET
END
Global subroutine
region
Cyclic or interrupt task
Interrupt task 0
GRET(752)
Variations Executed Each Cycle for ON Condition GRET(752)
Immediate Refreshing Specification Not supported
Block program areas Step program areas Subroutines Interrupt tasks
Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed OK

 Loading...
Loading...











