503
Conversion Instructions Section 3-12
256-to-8 bit Conversion
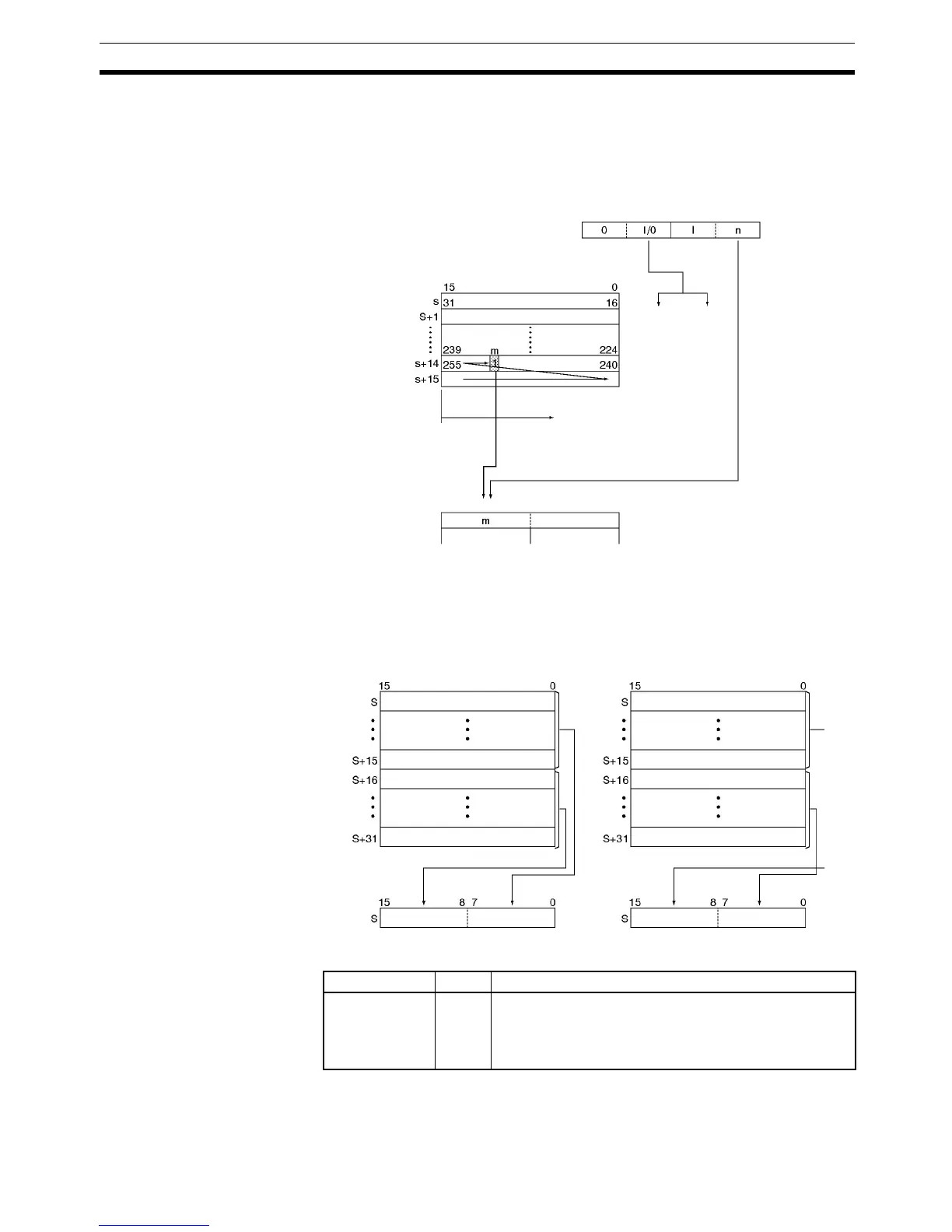
When the fourth (leftmost) digit of C is 1, DMPX(077) finds the locations of the
leftmost (highest bit address) or rightmost (lowest bit address) ON bits in one
or two 16-word ranges of source words. The locations of these bits are written
to R beginning with the specified byte. (Set the third digit of C to 0 to find the
leftmost ON bits or 1 to find the rightmost ON bits.)
When two bytes are being converted, DMPX(077) will write the values to the
bytes in R from right to left and will wrap around to the rightmost byte if the
leftmost byte (byte 1) has been specified as the starting byte.
The following diagram shows some example values for C and the 256-to-8 bit
conversions that they produce.
Flags
Precautions If the conversion data contains 0000 hex, but other data is to be encoded,
separate the conversion by using more than one DMPX(077) instructions.
DMPX(077) D0000 D0100 #0300
R
C
Leftmost
bit
Rightmost
bit
=0 (Convert one 16-word range.)
Finds leftmost bit
(Highest bit address)
256-to-8 bit decoding
(The location of the leftmost bit in the
16-word range (m) is written to R.)
n=1 (Start with byte 1.)
C: #1010 C: #1011
Digit 1 Digit 0 Digit 1 Digit 0
Name Label Operation
Error Flag ER ON if any of the source words contains 0000 hex (i.e., no
bit to encode).
ON if C is not within the specified ranges.
OFF in all other cases.
 Loading...
Loading...











