590
Floating-point Math Instructions Section 3-15
Real number = (–1)
s
2
e–127
(1.f)
s: Sign
e: Exponent
f: Mantissa
The floating-point data format conforms to the IEEE754 standards. Data is
expressed in 32 bits, as follows:
Number of Digits The number of effective digits for floating-point data is seven digits for deci-
mal.
Floating-point Data The following data can be expressed by floating-point data:
•–
∞
• –3.402823 x 10
38
≤ value ≤ –1.402398 x 10
–45
•0
• 1.402398 x 10
–45
≤ value ≤ 3.402823 x 10
38
•+∞
• Not a number (NaN)
Special Numbers The formats for NaN,
±∞, and 0 are as follows:
NaN*: e = 255, f
≠ 0
+
∞: e = 255, f = 0, s= 0
–
∞: e = 255, f = 0, s= 1
0: e = 0
*NaN (not a number) is not a valid floating-point number. Executing floating-
point calculation instructions will not result in NaN.
Writing Floating-point
Data
When floating-point is specified for the data format in the I/O memory edit dis-
play in the CX-Programmer, standard decimal numbers input in the display
are automatically converted to the floating-point format shown above
(IEEE754-format) and written to I/O Memory. Data written in the IEEE754-for-
mat is automatically converted to standard decimal format when monitored on
the display.
Data No. of bits Contents
s: sign 1 0: positive; 1: negative
e: exponent 8 The exponent (e) value ranges from 0 to 255.
The actual exponent is the value remaining after
127 is subtracted from e, resulting in a range of
–127 to 128. “e=0” and “e=255” express special
numbers.
f: mantissa 23 The mantissa portion of binary floating-point
data fits the formal 2.0 > 1.f ≥1.0.
se f
31 30 23 22 0
Sign Exponent Mantissa
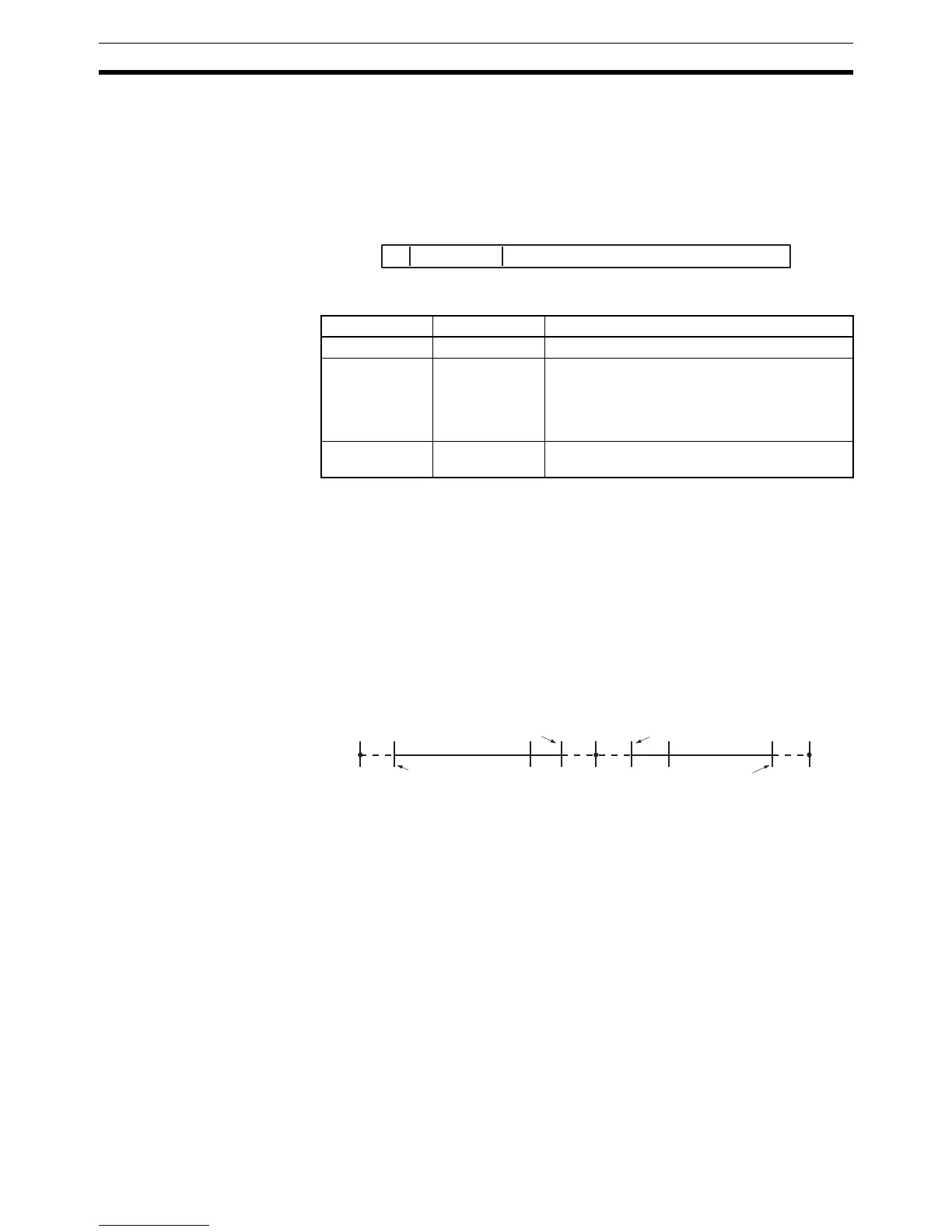
−1.402398 x 10
–45
1.402398 x 10
–45
– ∞
+
–3.402823 x 10
38
3.402823 x 10
38
–1
0
1
∞
 Loading...
Loading...











