Configuration Guide 802.1x Configuration
The following chapters introduce the propriety features of Ruijie’s network products:
To make it easy for broadband operators and to accommodate use in special environments, our 802.1x has been
expanded on the basis of the account (such expansion is completely based on the standard, and has totally compatible
with IEEE 802.1x).
Configuring the IP authorization mode
The 802.1x implemented by Ruijie Network can force the authenticated users to use fixed IP. By configuring the IP
authorization mode, the administrator can limit the way the user gets IP address. There are four IP authorization modes:
DISABLE, DHCP SERVER, RADIUS SERVER and SUPPLICANT. They are detailed below respectively:
DISABLE mode (default): The device has no limitation for the user IP, and the user only needs to pass the authentication
to be able to access the network.
DHCP SERVER mode: The user IP is obtained via specified DHCP SERVER, and only the IP allocated by the specified
DHCP SERVER is considered legal. For the DHCP mode, it is possible to use DHCP relay option82 to implement a more
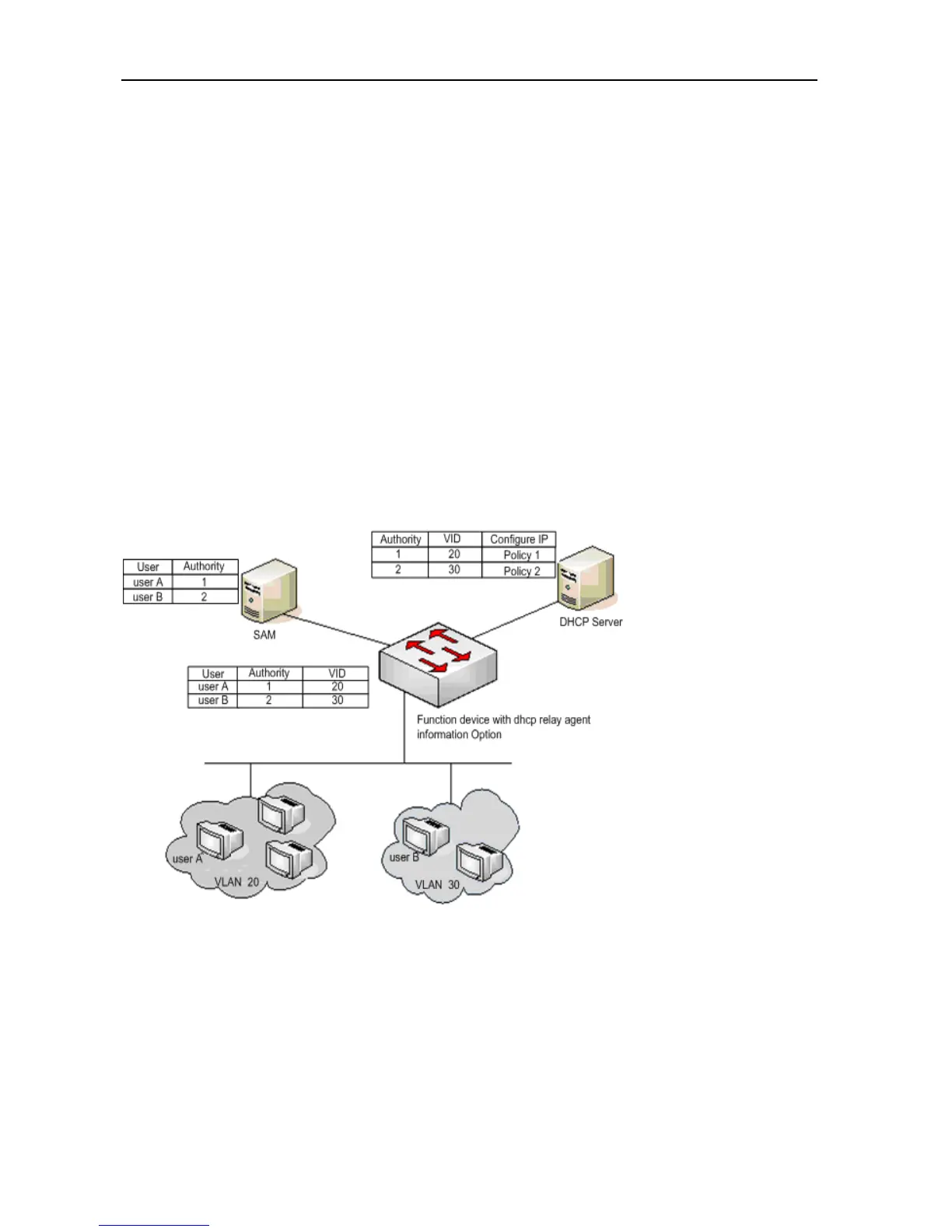
flexible IP allocation policy with the 802.1X. Here is a typical diagram for the plan:
Figure 0-2
The user initiates IP requests via the DHCP Client. The network device with dhcp relay option82 converges the user
authority on the SAM server to construct the option82 field and encapsulate it in the DHCP request message. That
option82 field consists of “vid + permission”. The DHCP Server chooses different allocation policies by using the option82
field.
In this mode, it is required to configure the DHCP Relay and the related option82. If the DHCP relay function is enabled
and the option82 policy is selected, see the DHCP Relay Configuration Guide and Command References for the
configurations.

 Loading...
Loading...









