Programming and Operating Manual (Milling)
108 6FC5398-4DP10-0BA1, 01/2014
Conditional program jumps
Functionality
Jump conditions
are formulated after the
. If the jump condition (
) is satisfied, the jump takes
place.
The jump destination can be a block with a
or with a
. This block must be located within the program.
Conditional jump instructions require a separate block. Several conditional jump instructions can be located in the same
block.
By using conditional program jumps, you can also considerably shorten the program, if necessary.
IF condition GOTOF label ;Jump forward
IF condition GOTOB label ;Jump backwards
GOTOF ;Jump direction forward (in the direction of the last block of the program)
GOTOB ;Jump direction backwards (in the direction of the first block of the program)
Label ;Selected string for the label (jump label) or block number
IF ;Introduction of the jump condition
Condition ;Arithmetic parameter, arithmetic expression for formulating the condition
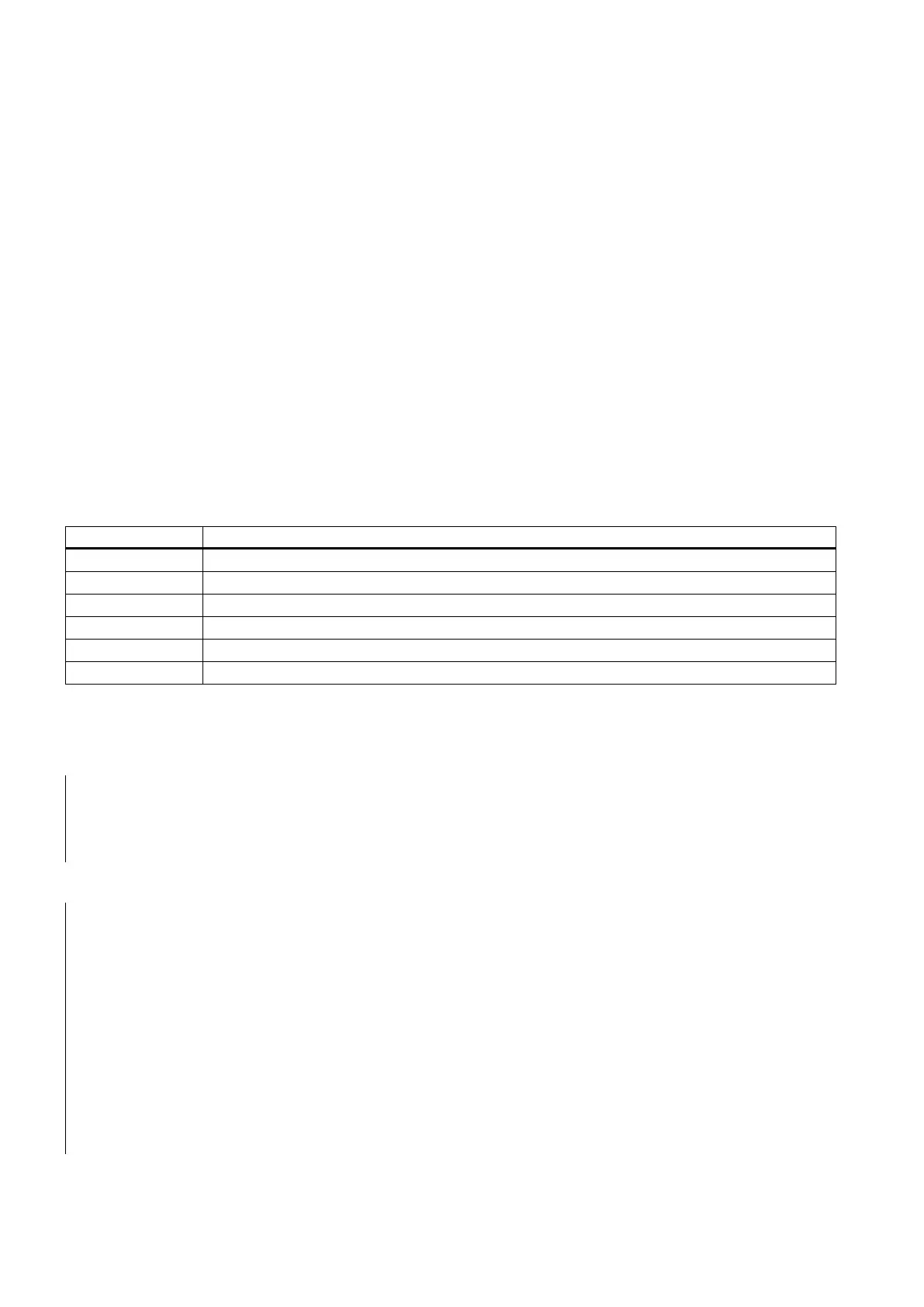
= = Equal to
< > Not equal to
> greater than
< less than
> = greater than or equal to
< = less than or equal to
The comparison operations support formulating of a jump condition. Arithmetic expressions can also be compared.
The result of comparison operations is "satisfied" or "not satisfied." "Not satisfied" sets the value to zero.
Programming example for comparison operators
; R6 greater than or equal to SIN (R7) squared
;If R1 is not null then go to the block having LABEL1
N100 IF R1>1 GOTOF LABEL2 ;If R1 is greater than 1 then go to the block having
N1000 IF R45==R7+1 GOTOB LABEL3 ;If R45 is equal to R7 plus 1 then go to the block
 Loading...
Loading...
















