Voltage Protection 27, 59
Voltage protection has the task to protect electrical equipment against undervoltage and overvoltage. Both
operational states are abnormal as overvoltage may cause for example insulation problems or undervoltage
may cause stability problems.
There are two elements each available for overvoltage protection and undervoltage protection.
Applications
•
Abnormally high voltages often occur e.g. in low loaded, long distance transmission lines, in islanded
systems when generator voltage regulation fails, or after full load rejection of a generator from the
system.
•
The undervoltage protection function detects voltage collapses on transmission lines and electrical
machines and prevents inadmissible operating states and a possible loss of stability.
Measurement Principle
Connection/Measured Values
The voltages supplied to the device may correspond to the three phase-to-ground voltages V
A-N
, V
B-N
, V
C-N
or
the two phase-to-phase voltages (V
A-B
, V
B-C
) and the displacement voltage (ground voltage V
N
) or - in the case
of a single-phase connection - any phase-to-ground voltage. The connection type has been specified during
the configuration in parameter 213 VT Connect. 3ph (see Section ).
The following table indicates which voltages can be evaluated by the function. The settings for this are made
in the P.System Data 1 (see Section ). Furthermore, it is indicated to which value the threshold must be
set. All voltages are fundamental frequency values.
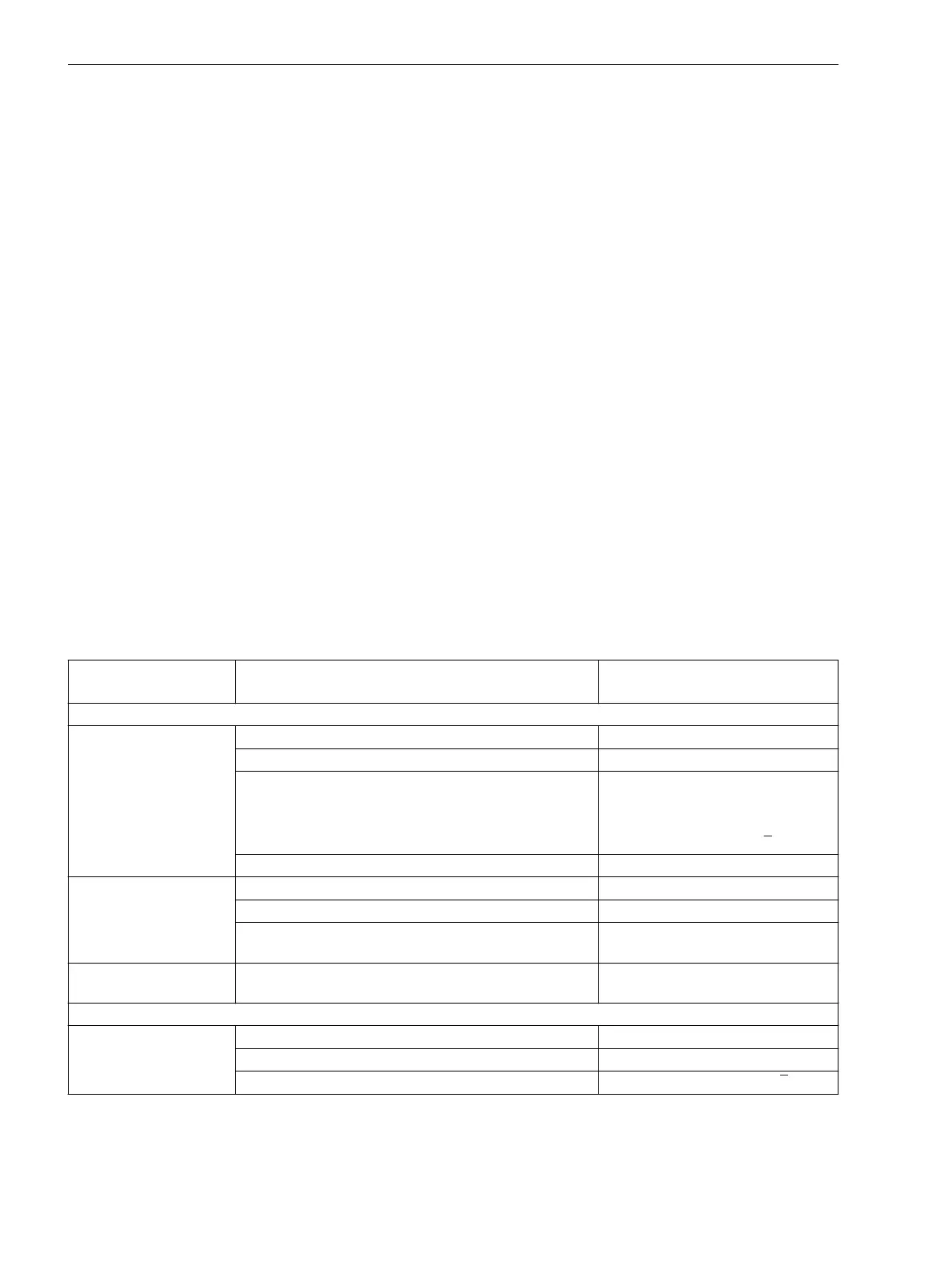
Table 2-8
Voltage protection, selectable voltages
Connection, threephase
(parameter213)
Selectable voltage
parameter 614/ 615
Threshold to be set as
Overvoltage
Van, Vbn, Vcn
Vphph (largest phase-to-phase voltage) Phase-to-phase voltage
Vph-n ((largest phase-to-ground voltage) Phase-to-ground voltage
V1(positive sequence voltage) Positive sequence voltage calculated
from
phase-to-groundvoltage or
phase-tophase voltage / √3
V2 (negative sequence voltage) Negative sequence voltage
Vab, Vbc, VGnd
Vab, Vbc
Vab, Vbc, VSyn
Vab, Vbc, Vx
Vphph (largest phase-to-phase voltage) Leiter-Leiter-Spannung
V1(positive sequence voltage) Positive sequence voltage
V2 (negative sequence voltage) Negative sequence voltage
Vph-g, VSyn
None (direct evaluation of the voltage connected to
voltage input 1)
Direct voltage value
Undervoltage
Van, Vbn, Vcn
Vphph (smallest phase-to-phase voltage) Phase-to-phase voltage
Vph-n (smallest phase-to-ground voltage) Phase-to-ground voltage
V1 (positive sequence voltage) Positive sequence voltage· √3
2.6
2.6.1
Functions
2.6 Voltage Protection 27, 59
122 SIPROTEC 4, 7SJ80, Manual
E50417-G1140-C343-A8, Edition 12.2017

 Loading...
Loading...











